Matthew Raffel
MetaCluster: Enabling Deep Compression of Kolmogorov-Arnold Network
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) replace scalar weights with per-edge vectors of basis coefficients, thereby boosting expressivity and accuracy but at the same time resulting in a multiplicative increase in parameters and memory. We propose MetaCluster, a framework that makes KANs highly compressible without sacrificing accuracy. Specifically, a lightweight meta-learner, trained jointly with the KAN, is used to map low-dimensional embedding to coefficient vectors, shaping them to lie on a low-dimensional manifold that is amenable to clustering. We then run K-means in coefficient space and replace per-edge vectors with shared centroids. Afterwards, the meta-learner can be discarded, and a brief fine-tuning of the centroid codebook recovers any residual accuracy loss. The resulting model stores only a small codebook and per-edge indices, exploiting the vector nature of KAN parameters to amortize storage across multiple coefficients. On MNIST, CIFAR-10, and CIFAR-100, across standard KANs and ConvKANs using multiple basis functions, MetaCluster achieves a reduction of up to 80$\times$ in parameter storage, with no loss in accuracy. Code will be released upon publication.
BeaverTalk: Oregon State University's IWSLT 2025 Simultaneous Speech Translation System
May 29, 2025Abstract:This paper discusses the construction, fine-tuning, and deployment of BeaverTalk, a cascaded system for speech-to-text translation as part of the IWSLT 2025 simultaneous translation task. The system architecture employs a VAD segmenter for breaking a speech stream into segments, Whisper Large V2 for automatic speech recognition (ASR), and Gemma 3 12B for simultaneous translation. Regarding the simultaneous translation LLM, it is fine-tuned via low-rank adaptors (LoRAs) for a conversational prompting strategy that leverages a single prior-sentence memory bank from the source language as context. The cascaded system participated in the English$\rightarrow$German and English$\rightarrow$Chinese language directions for both the low and high latency regimes. In particular, on the English$\rightarrow$German task, the system achieves a BLEU of 24.64 and 27.83 at a StreamLAAL of 1837.86 and 3343.73, respectively. Then, on the English$\rightarrow$Chinese task, the system achieves a BLEU of 34.07 and 37.23 at a StreamLAAL of 2216.99 and 3521.35, respectively.
FlashKAT: Understanding and Addressing Performance Bottlenecks in the Kolmogorov-Arnold Transformer
May 20, 2025Abstract:The Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) has been gaining popularity as an alternative to the multi-layer perceptron (MLP) with its increased expressiveness and interpretability. However, the KAN can be orders of magnitude slower due to its increased computational cost and training instability, limiting its applicability to larger-scale tasks. Recently, the Kolmogorov-Arnold Transformer (KAT) has been proposed, which can achieve FLOPs similar to the traditional Transformer with MLPs by leveraging Group-Rational KAN (GR-KAN). Unfortunately, despite the comparable FLOPs, our characterizations reveal that the KAT is still 123x slower in training speeds, indicating that there are other performance bottlenecks beyond FLOPs. In this paper, we conduct a series of experiments to understand the root cause of the slowdown in KAT. We uncover that the slowdown can be isolated to memory stalls and, more specifically, in the backward pass of GR-KAN caused by inefficient gradient accumulation. To address this memory bottleneck, we propose FlashKAT, which builds on our restructured kernel that minimizes gradient accumulation with atomic adds and accesses to slow memory. Evaluations demonstrate that FlashKAT can achieve a training speedup of 86.5x compared with the state-of-the-art KAT, while reducing rounding errors in the coefficient gradients. Our code is available at https://github.com/OSU-STARLAB/FlashKAT.
Towards Universal Semantics With Large Language Models
May 17, 2025Abstract:The Natural Semantic Metalanguage (NSM) is a linguistic theory based on a universal set of semantic primes: simple, primitive word-meanings that have been shown to exist in most, if not all, languages of the world. According to this framework, any word, regardless of complexity, can be paraphrased using these primes, revealing a clear and universally translatable meaning. These paraphrases, known as explications, can offer valuable applications for many natural language processing (NLP) tasks, but producing them has traditionally been a slow, manual process. In this work, we present the first study of using large language models (LLMs) to generate NSM explications. We introduce automatic evaluation methods, a tailored dataset for training and evaluation, and fine-tuned models for this task. Our 1B and 8B models outperform GPT-4o in producing accurate, cross-translatable explications, marking a significant step toward universal semantic representation with LLMs and opening up new possibilities for applications in semantic analysis, translation, and beyond.
Simultaneous Masking, Not Prompting Optimization: A Paradigm Shift in Fine-tuning LLMs for Simultaneous Translation
May 16, 2024


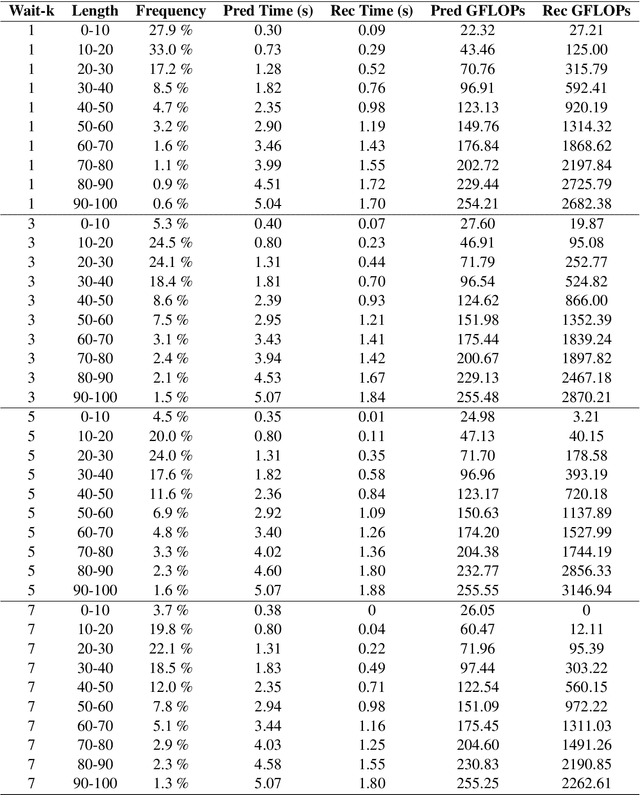
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance in various language processing tasks, motivating their adoption in simultaneous translation. Current fine-tuning methods to adapt LLMs for simultaneous translation focus on prompting optimization strategies using either data augmentation or prompt structure modifications. However, these methods suffer from several issues, such as an unnecessarily expanded training set, computational inefficiency from dumping the KV cache, increased prompt sizes, or restriction to a single decision policy. To eliminate these issues, we propose a new paradigm in fine-tuning LLMs for simultaneous translation, called SimulMask. It utilizes a novel attention mask technique that models simultaneous translation during fine-tuning by masking attention connections under a desired decision policy. Applying the proposed SimulMask on a Falcon LLM for the IWSLT 2017 dataset, we have observed a significant translation quality improvement compared to state-of-the-art prompting optimization strategies on three language pairs when averaged across four different latency regimes while reducing the computational cost.
Simul-LLM: A Framework for Exploring High-Quality Simultaneous Translation with Large Language Models
Dec 12, 2023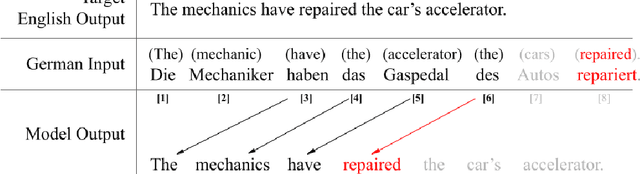

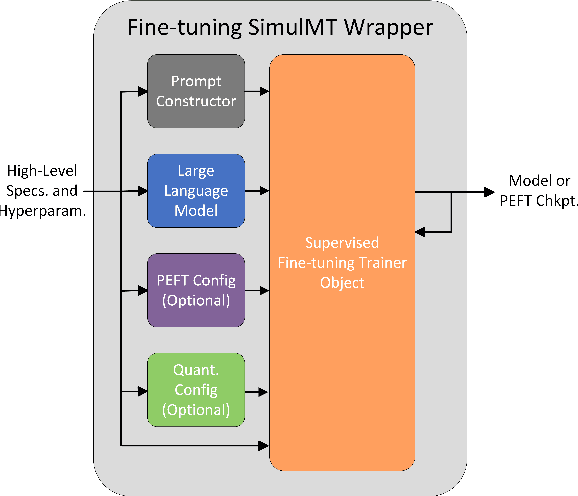

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) with billions of parameters and pretrained on massive amounts of data are now capable of near or better than state-of-the-art performance in a variety of downstream natural language processing tasks. Neural machine translation (NMT) is one such task that LLMs have been applied to with great success. However, little research has focused on applying LLMs to the more difficult subset of NMT called simultaneous translation (SimulMT), where translation begins before the entire source context is available to the model. In this paper, we address key challenges facing LLMs fine-tuned for SimulMT, validate classical SimulMT concepts and practices in the context of LLMs, explore adapting LLMs that are fine-tuned for NMT to the task of SimulMT, and introduce Simul-LLM, the first open-source fine-tuning and evaluation pipeline development framework for LLMs focused on SimulMT.
Implicit Memory Transformer for Computationally Efficient Simultaneous Speech Translation
Jul 03, 2023Abstract:Simultaneous speech translation is an essential communication task difficult for humans whereby a translation is generated concurrently with oncoming speech inputs. For such a streaming task, transformers using block processing to break an input sequence into segments have achieved state-of-the-art performance at a reduced cost. Current methods to allow information to propagate across segments, including left context and memory banks, have faltered as they are both insufficient representations and unnecessarily expensive to compute. In this paper, we propose an Implicit Memory Transformer that implicitly retains memory through a new left context method, removing the need to explicitly represent memory with memory banks. We generate the left context from the attention output of the previous segment and include it in the keys and values of the current segment's attention calculation. Experiments on the MuST-C dataset show that the Implicit Memory Transformer provides a substantial speedup on the encoder forward pass with nearly identical translation quality when compared with the state-of-the-art approach that employs both left context and memory banks.
Shiftable Context: Addressing Training-Inference Context Mismatch in Simultaneous Speech Translation
Jul 03, 2023Abstract:Transformer models using segment-based processing have been an effective architecture for simultaneous speech translation. However, such models create a context mismatch between training and inference environments, hindering potential translation accuracy. We solve this issue by proposing Shiftable Context, a simple yet effective scheme to ensure that consistent segment and context sizes are maintained throughout training and inference, even with the presence of partially filled segments due to the streaming nature of simultaneous translation. Shiftable Context is also broadly applicable to segment-based transformers for streaming tasks. Our experiments on the English-German, English-French, and English-Spanish language pairs from the MUST-C dataset demonstrate that when applied to the Augmented Memory Transformer, a state-of-the-art model for simultaneous speech translation, the proposed scheme achieves an average increase of 2.09, 1.83, and 1.95 BLEU scores across each wait-k value for the three language pairs, respectively, with a minimal impact on computation-aware Average Lagging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge