Matteo Martinelli
Digital Twins & ZeroConf AI: Structuring Automated Intelligent Pipelines for Industrial Applications
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The increasing complexity of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), particularly in the industrial domain, has amplified the challenges associated with the effective integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques. Fragmentation across IoT and IIoT technologies, manifested through diverse communication protocols, data formats and device capabilities, creates a substantial gap between low-level physical layers and high-level intelligent functionalities. Recently, Digital Twin (DT) technology has emerged as a promising solution, offering structured, interoperable and semantically rich digital representations of physical assets. Current approaches are often siloed and tightly coupled, limiting scalability and reuse of AI functionalities. This work proposes a modular and interoperable solution that enables seamless AI pipeline integration into CPS by minimizing configuration and decoupling the roles of DTs and AI components. We introduce the concept of Zero Configuration (ZeroConf) AI pipelines, where DTs orchestrate data management and intelligent augmentation. The approach is demonstrated in a MicroFactory scenario, showing support for concurrent ML models and dynamic data processing, effectively accelerating the deployment of intelligent services in complex industrial settings.
* Author-accepted manuscript of a paper published in the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (IEEE SMC), October 2025, doi: 10.1109/SMC58881.2025.11343418
Individual and Collective Autonomous Development
Oct 03, 2021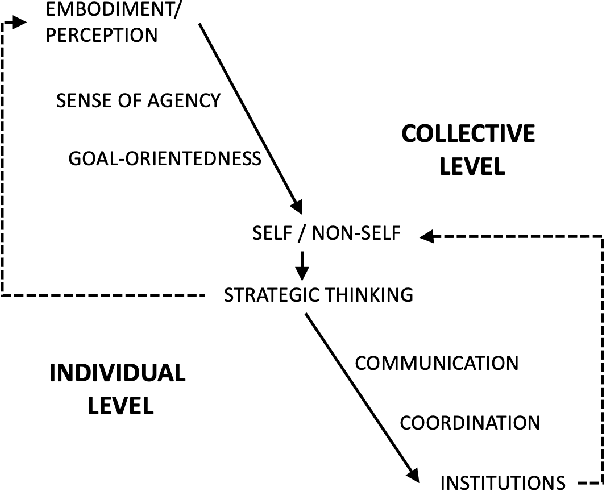
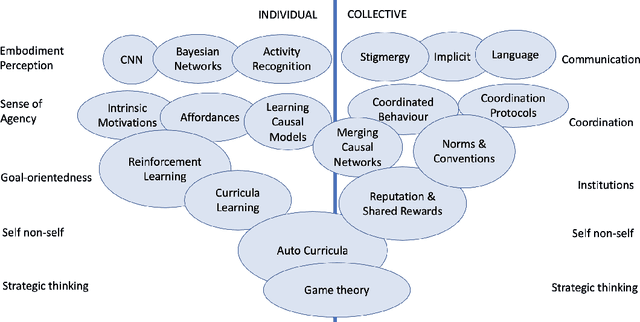
Abstract:The increasing complexity and unpredictability of many ICT scenarios let us envision that future systems will have to dynamically learn how to act and adapt to face evolving situations with little or no a priori knowledge, both at the level of individual components and at the collective level. In other words, such systems should become able to autonomously develop models of themselves and of their environment. Autonomous development includes: learning models of own capabilities; learning how to act purposefully towards the achievement of specific goals; and learning how to act collectively, i.e., accounting for the presence of others. In this paper, we introduce the vision of autonomous development in ICT systems, by framing its key concepts and by illustrating suitable application domains. Then, we overview the many research areas that are contributing or can potentially contribute to the realization of the vision, and identify some key research challenges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge