Marco Picone
Digital Twins & ZeroConf AI: Structuring Automated Intelligent Pipelines for Industrial Applications
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The increasing complexity of Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), particularly in the industrial domain, has amplified the challenges associated with the effective integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) techniques. Fragmentation across IoT and IIoT technologies, manifested through diverse communication protocols, data formats and device capabilities, creates a substantial gap between low-level physical layers and high-level intelligent functionalities. Recently, Digital Twin (DT) technology has emerged as a promising solution, offering structured, interoperable and semantically rich digital representations of physical assets. Current approaches are often siloed and tightly coupled, limiting scalability and reuse of AI functionalities. This work proposes a modular and interoperable solution that enables seamless AI pipeline integration into CPS by minimizing configuration and decoupling the roles of DTs and AI components. We introduce the concept of Zero Configuration (ZeroConf) AI pipelines, where DTs orchestrate data management and intelligent augmentation. The approach is demonstrated in a MicroFactory scenario, showing support for concurrent ML models and dynamic data processing, effectively accelerating the deployment of intelligent services in complex industrial settings.
* Author-accepted manuscript of a paper published in the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (IEEE SMC), October 2025, doi: 10.1109/SMC58881.2025.11343418
Blockchain Federated Learning for Sustainable Retail: Reducing Waste through Collaborative Demand Forecasting
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Effective demand forecasting is crucial for reducing food waste. However, data privacy concerns often hinder collaboration among retailers, limiting the potential for improved predictive accuracy. In this study, we explore the application of Federated Learning (FL) in Sustainable Supply Chain Management (SSCM), with a focus on the grocery retail sector dealing with perishable goods. We develop a baseline predictive model for demand forecasting and waste assessment in an isolated retailer scenario. Subsequently, we introduce a Blockchain-based FL model, trained collaboratively across multiple retailers without direct data sharing. Our preliminary results show that FL models have performance almost equivalent to the ideal setting in which parties share data with each other, and are notably superior to models built by individual parties without sharing data, cutting waste and boosting efficiency.
* Author-accepted manuscript of a paper published in the IEEE International Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), 2025, pp. 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCC65549.2025.11326299
The Gaussian-Head OFL Family: One-Shot Federated Learning from Client Global Statistics
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Classical Federated Learning relies on a multi-round iterative process of model exchange and aggregation between server and clients, with high communication costs and privacy risks from repeated model transmissions. In contrast, one-shot federated learning (OFL) alleviates these limitations by reducing communication to a single round, thereby lowering overhead and enhancing practical deployability. Nevertheless, most existing one-shot approaches remain either impractical or constrained, for example, they often depend on the availability of a public dataset, assume homogeneous client models, or require uploading additional data or model information. To overcome these issues, we introduce the Gaussian-Head OFL (GH-OFL) family, a suite of one-shot federated methods that assume class-conditional Gaussianity of pretrained embeddings. Clients transmit only sufficient statistics (per-class counts and first/second-order moments) and the server builds heads via three components: (i) Closed-form Gaussian heads (NB/LDA/QDA) computed directly from the received statistics; (ii) FisherMix, a linear head with cosine margin trained on synthetic samples drawn in an estimated Fisher subspace; and (iii) Proto-Hyper, a lightweight low-rank residual head that refines Gaussian logits via knowledge distillation on those synthetic samples. In our experiments, GH-OFL methods deliver state-of-the-art robustness and accuracy under strong non-IID skew while remaining strictly data-free.
FedBGS: A Blockchain Approach to Segment Gossip Learning in Decentralized Systems
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning (PPFL) is a Decentralized machine learning paradigm that enables multiple participants to collaboratively train a global model without sharing their data with the integration of cryptographic and privacy-based techniques to enhance the security of the global system. This privacy-oriented approach makes PPFL a highly suitable solution for training shared models in sectors where data privacy is a critical concern. In traditional FL, local models are trained on edge devices, and only model updates are shared with a central server, which aggregates them to improve the global model. However, despite the presence of the aforementioned privacy techniques, in the classical Federated structure, the issue of the server as a single-point-of-failure remains, leading to limitations both in terms of security and scalability. This paper introduces FedBGS, a fully Decentralized Blockchain-based framework that leverages Segmented Gossip Learning through Federated Analytics. The proposed system aims to optimize blockchain usage while providing comprehensive protection against all types of attacks, ensuring both privacy, security and non-IID data handling in Federated environments.
* Author-accepted manuscript of a paper published in the 2025 IEEE 45th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems Workshops (ICDCSW), pp. 760-770, doi: 10.1109/ICDCSW63273.2025.00136
The Water Health Open Knowledge Graph
May 18, 2023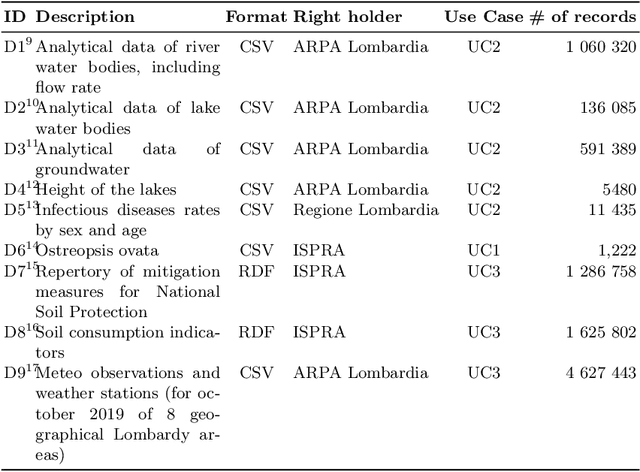
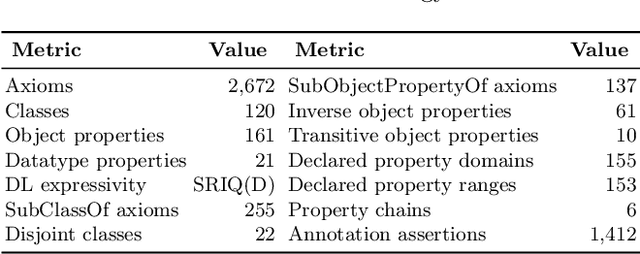
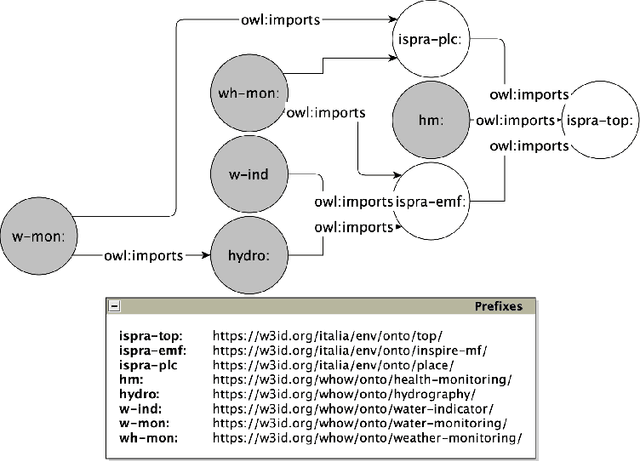
Abstract:Recently, an increasing interest in the management of water and health resources has been recorded. This interest is fed by the global sustainability challenges posed to the humanity that have water scarcity and quality at their core. Thus, the availability of effective, meaningful and open data is crucial to address those issues in the broader context of the Sustainable Development Goals of clean water and sanitation as targeted by the United Nations. In this paper, we present the Water Health Open Knowledge Graph (WHOW-KG) along with its design methodology and analysis on impact. WHOW-KG is a semantic knowledge graph that models data on water consumption, pollution, infectious disease rates and drug distribution. The WHOW-KG is developed in the context of the EU-funded WHOW (Water Health Open Knowledge) project and aims at supporting a wide range of applications: from knowledge discovery to decision-making, making it a valuable resource for researchers, policymakers, and practitioners in the water and health domains. The WHOW-KG consists of a network of five ontologies and related linked open data, modelled according to those ontologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge