Mathieu Roget
Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, LIS, Marseille, France
On Quantum Perceptron Learning via Quantum Search
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:With the growing interest in quantum machine learning, the perceptron -- a fundamental building block in traditional machine learning -- has emerged as a valuable model for exploring quantum advantages. Two quantum perceptron algorithms based on Grover's search, were developed in arXiv:1602.04799 to accelerate training and improve statistical efficiency in perceptron learning. This paper points out and corrects a mistake in the proof of Theorem 2 in arXiv:1602.04799. Specifically, we show that the probability of sampling from a normal distribution for a $D$-dimensional hyperplane that perfectly classifies the data scales as $\Omega(\gamma^{D})$ instead of $\Theta({\gamma})$, where $\gamma$ is the margin. We then revisit two well-established linear programming algorithms -- the ellipsoid method and the cutting plane random walk algorithm -- in the context of perceptron learning, and show how quantum search algorithms can be leveraged to enhance the overall complexity. Specifically, both algorithms gain a sub-linear speed-up $O(\sqrt{N})$ in the number of data points $N$ as a result of Grover's algorithm and an additional $O(D^{1.5})$ speed-up is possible for cutting plane random walk algorithm employing quantum walk search.
Quantum Perceptron Revisited: Computational-Statistical Tradeoffs
Jun 04, 2021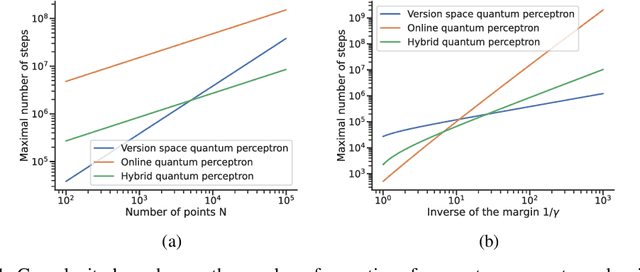
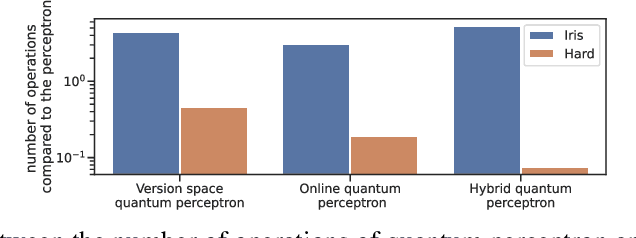
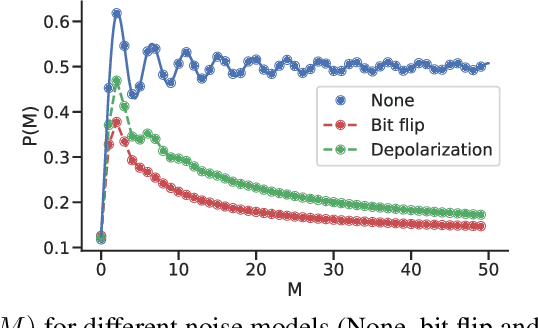
Abstract:Quantum machine learning algorithms could provide significant speed-ups over their classical counterparts; however, whether they could also achieve good generalization remains unclear. Recently, two quantum perceptron models which give a quadratic improvement over the classical perceptron algorithm using Grover's search have been proposed by Wiebe et al. arXiv:1602.04799 . While the first model reduces the complexity with respect to the size of the training set, the second one improves the bound on the number of mistakes made by the perceptron. In this paper, we introduce a hybrid quantum-classical perceptron algorithm with lower complexity and better generalization ability than the classical perceptron. We show a quadratic improvement over the classical perceptron in both the number of samples and the margin of the data. We derive a bound on the expected error of the hypothesis returned by our algorithm, which compares favorably to the one obtained with the classical online perceptron. We use numerical experiments to illustrate the trade-off between computational complexity and statistical accuracy in quantum perceptron learning and discuss some of the key practical issues surrounding the implementation of quantum perceptron models into near-term quantum devices, whose practical implementation represents a serious challenge due to inherent noise. However, the potential benefits make correcting this worthwhile.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge