Massimiliano di Luca
A Kalman Filter model for synchronization in musical ensembles
Nov 08, 2024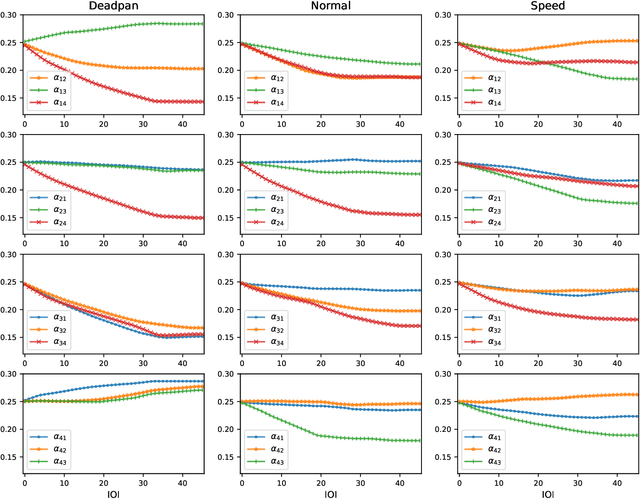
Abstract:The synchronization of motor responses to rhythmic auditory cues is a fundamental biological phenomenon observed across various species. While the importance of temporal alignment varies across different contexts, achieving precise temporal synchronization is a prominent goal in musical performances. Musicians often incorporate expressive timing variations, which require precise control over timing and synchronization, particularly in ensemble performance. This is crucial because both deliberate expressive nuances and accidental timing deviations can affect the overall timing of a performance. This discussion prompts the question of how musicians adjust their temporal dynamics to achieve synchronization within an ensemble. This paper introduces a novel feedback correction model based on the Kalman Filter, aimed at improving the understanding of interpersonal timing in ensemble music performances. The proposed model performs similarly to other linear correction models in the literature, with the advantage of low computational cost and good performance even in scenarios where the underlying tempo varies.
Perception of Mechanical Properties via Wrist Haptics: Effects of Feedback Congruence
Apr 12, 2022



Abstract:Despite non-co-location, haptic stimulation at the wrist can potentially provide feedback regarding interactions at the fingertips without encumbering the user's hand. Here we investigate how two types of skin deformation at the wrist (normal and shear) relate to the perception of the mechanical properties of virtual objects. We hypothesized that a congruent mapping between force at the fingertips and deformation at the wrist would be better, i.e. mapping finger normal force to skin indentation at the wrist, and shear force to skin shear at the wrist, would result in better perception than other mappings that either mixed or merged the two direction into a single type of feedback. We performed an experiment where haptic devices at the wrist rendered either normal or shear feedback during manipulation of virtual objects with varying stiffness, mass, or friction properties. Perception of mechanical properties was more accurate with congruent skin stimulation than noncongruent. In addition, discrimination performance and subjective reports were positively influenced by congruence. This study demonstrates that users can perceive mechanical properties via haptic feedback provided at the wrist with a consistent mapping between haptic feedback and interaction forces at the fingertips, regardless of congruence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge