Masanori Ishigaki
Probabilistic Visual Navigation with Bidirectional Image Prediction
Mar 20, 2020


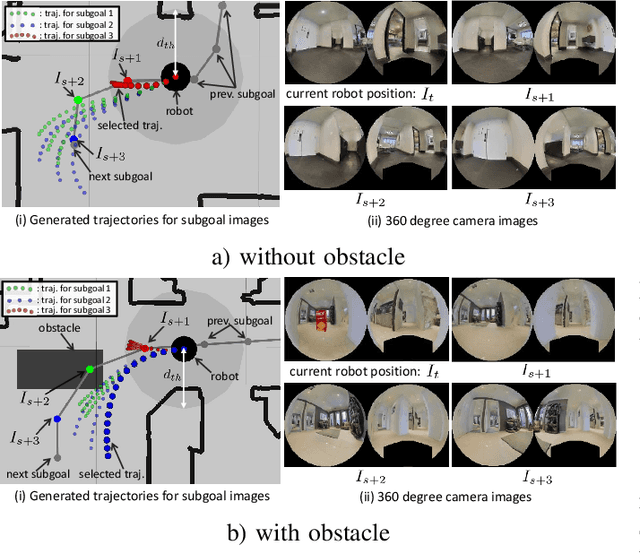
Abstract:Humans can robustly follow a visual trajectory defined by a sequence of images (i.e. a video) regardless of substantial changes in the environment or the presence of obstacles. We aim at endowing similar visual navigation capabilities to mobile robots solely equipped with a RGB fisheye camera. We propose a novel probabilistic visual navigation system that learns to follow a sequence of images with bidirectional visual predictions conditioned on possible navigation velocities. By predicting bidirectionally (from start towards goal and vice versa) our method extends its predictive horizon enabling the robot to go around unseen large obstacles that are not visible in the video trajectory. Learning how to react to obstacles and potential risks in the visual field is achieved by imitating human teleoperators. Since the human teleoperation commands are diverse, we propose a probabilistic representation of trajectories that we can sample to find the safest path. Integrated into our navigation system, we present a novel localization approach that infers the current location of the robot based on the virtual predicted trajectories required to reach different images in the visual trajectory. We evaluate our navigation system quantitatively and qualitatively in multiple simulated and real environments and compare to state-of-the-art baselines.Our approach outperforms the most recent visual navigation methods with a large margin with regard to goal arrival rate, subgoal coverage rate, and success weighted by path length (SPL). Our method also generalizes to new robot embodiments never used during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge