Martin Gillis
Improving Detection of Rare Nodes in Hierarchical Multi-Label Learning
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:In hierarchical multi-label classification, a persistent challenge is enabling model predictions to reach deeper levels of the hierarchy for more detailed or fine-grained classifications. This difficulty partly arises from the natural rarity of certain classes (or hierarchical nodes) and the hierarchical constraint that ensures child nodes are almost always less frequent than their parents. To address this, we propose a weighted loss objective for neural networks that combines node-wise imbalance weighting with focal weighting components, the latter leveraging modern quantification of ensemble uncertainties. By emphasizing rare nodes rather than rare observations (data points), and focusing on uncertain nodes for each model output distribution during training, we observe improvements in recall by up to a factor of five on benchmark datasets, along with statistically significant gains in $F_{1}$ score. We also show our approach aids convolutional networks on challenging tasks, as in situations with suboptimal encoders or limited data.
Hierarchical Multi-Label Classification with Missing Information for Benthic Habitat Imagery
Sep 10, 2024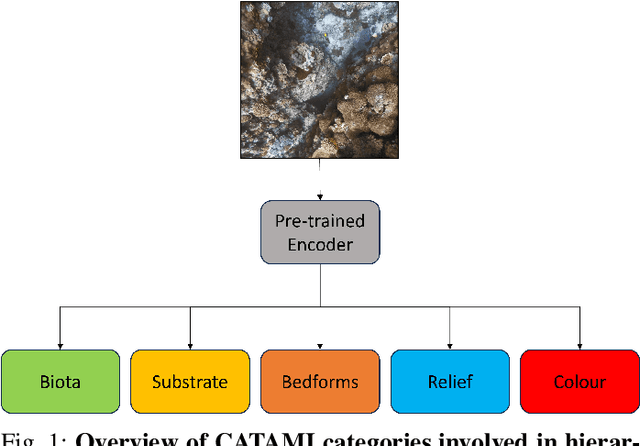
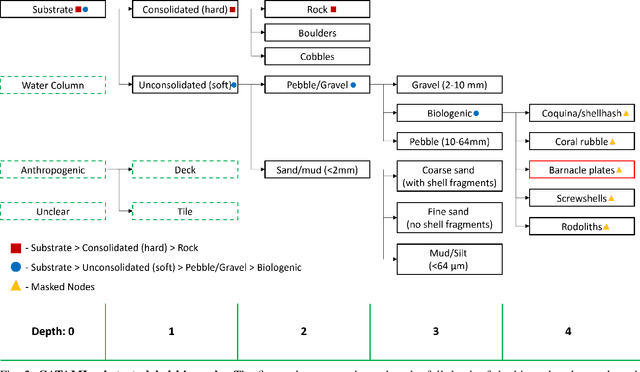
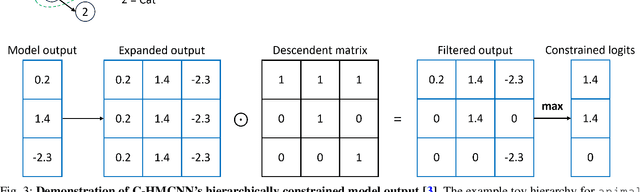
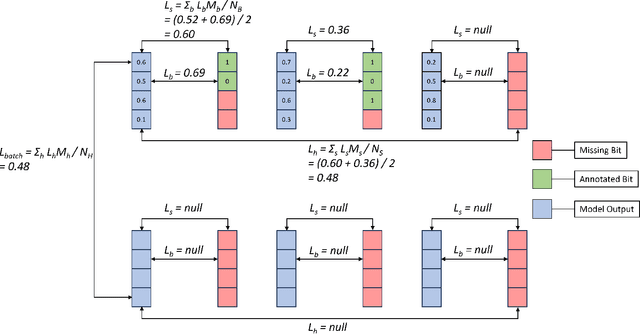
Abstract:In this work, we apply state-of-the-art self-supervised learning techniques on a large dataset of seafloor imagery, \textit{BenthicNet}, and study their performance for a complex hierarchical multi-label (HML) classification downstream task. In particular, we demonstrate the capacity to conduct HML training in scenarios where there exist multiple levels of missing annotation information, an important scenario for handling heterogeneous real-world data collected by multiple research groups with differing data collection protocols. We find that, when using smaller one-hot image label datasets typical of local or regional scale benthic science projects, models pre-trained with self-supervision on a larger collection of in-domain benthic data outperform models pre-trained on ImageNet. In the HML setting, we find the model can attain a deeper and more precise classification if it is pre-trained with self-supervision on in-domain data. We hope this work can establish a benchmark for future models in the field of automated underwater image annotation tasks and can guide work in other domains with hierarchical annotations of mixed resolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge