Markus Endler
Wireless Connectivity of a Ground-and-Air Sensor Network
Nov 19, 2022Abstract:This paper shows that, when considering outdoor scenarios and wireless communications using the IEEE 802.11 protocol with dipole antennas, the ground reflection is a significant propagation mechanism. This way, the Two-Ray model for this environment allows predicting, with some accuracy, the received signal power. This study is relevant for the application in the communication between overflying Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and ground sensors. In the proposed Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) scenario, the UAVs must receive information from the environment, which is collected by sensors positioned on the ground, and need to maintain connectivity between them and the base station, in order to maintain the quality of service, while moving through the environment.
GrADyS-GS -- A ground station for managing field experiments with Autonomous Vehicles and Wireless Sensor Networks
Apr 01, 2022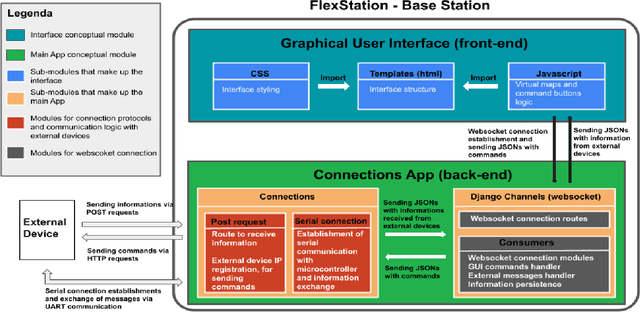
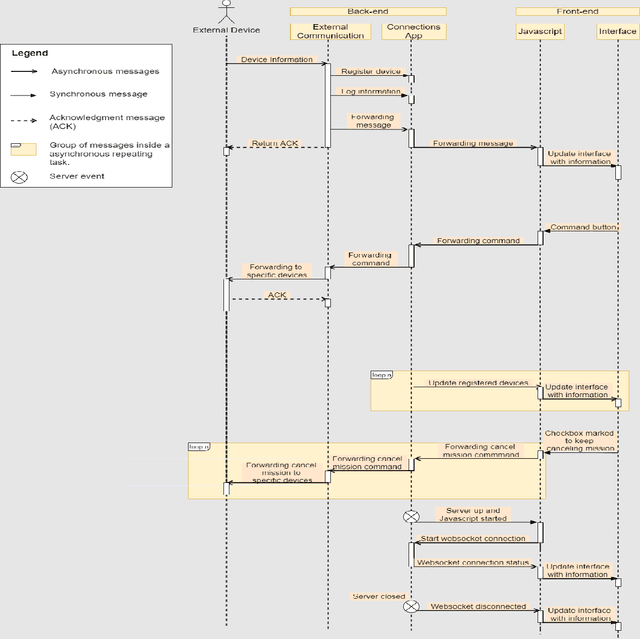
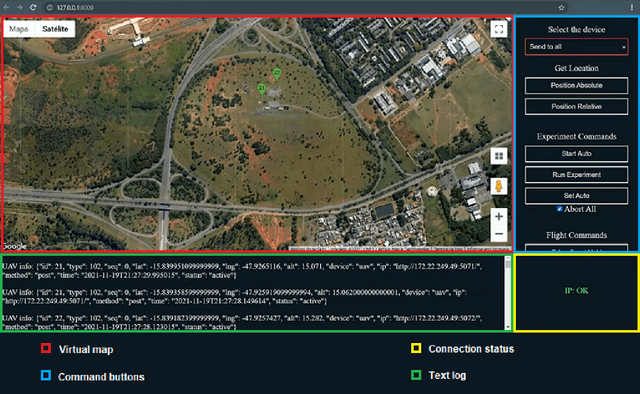
Abstract:In many kinds of research, collecting data is tailored to individual research. It is usual to use dedicated and not reusable software to collect data. GrADyS Ground Station framework (GrADyS-GS) aims to collect data in a reusable manner with dynamic background tools. This technical report describes GrADyS-GS, a ground station software designed to connect with various technologies to control, monitor, and store results of Mobile Internet of Things field experiments with Autonomous Vehicles (UAV) and Sensor Networks (WSN). In the GrADyS project GrADyS-GS is used with ESP32-based IoT devices on the ground and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (quad-copters) in the air. The GrADyS-GS tool was created to support the design, development and testing of simulated movement coordination algorithms for the AVs, testing of customized Bluetooth Mesh variations, and overall communication, coordination, and context-awareness field experiments planed in the GraDyS project. Nevertheless, GrADyS-GS is also a general purpose tool, as it relies on a dynamic and easy-to-use Python and JavaScript framework that allows easy customization and (re)utilization in another projects and field experiments with other kinds of IoT devices, other WSN types and protocols, and other kinds of mobile connected flying or ground vehicles. So far, GrADyS-GS has been used to start UAV flights and collects its data in s centralized manner inside GrADyS project.
GrADyS-SIM -- A OMNET++/INET simulation framework for Internet of Flying things
Feb 16, 2022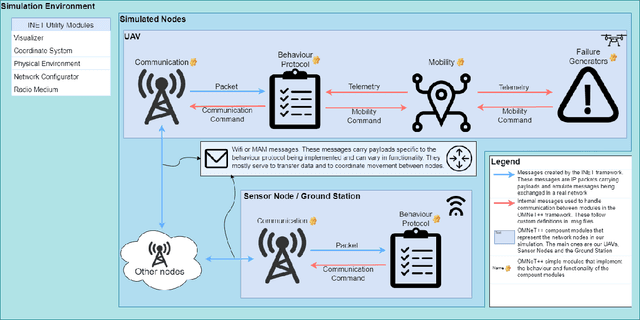
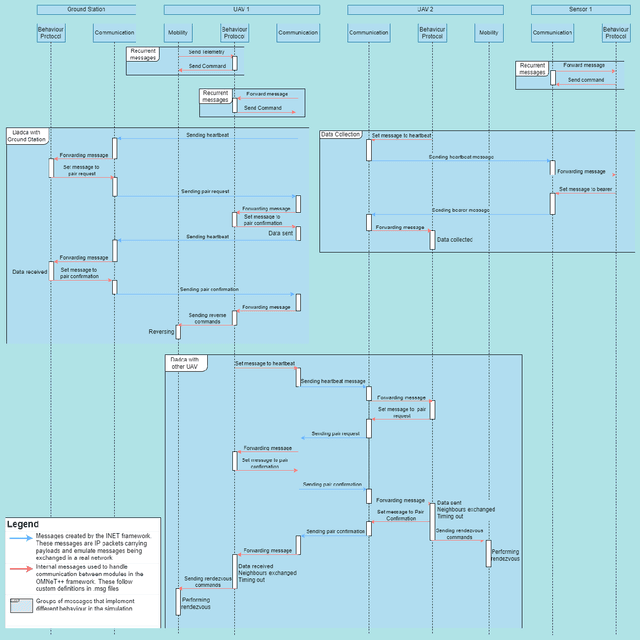
Abstract:This technical report describes GrADyS-SIM, a framework for simulating cooperating swarms of UAVs in joint mission in hypothetical landscape and communicating through RF radios. The framework was created to aid and verify the communication, coordination and context-awareness protocols being developed in the GrADyS project. GrADyS-SIM uses the OMNeT++ simulation library and its INET model suite and and allows for addition of modified or customized versions of some simulated components, network configurations and vehicle coordination, so that new coordination protocols can be developed and tested through the framework. The framework simulates UAV movement dictated by file containing some MAVLink instructions and affected on the fly by different network situations. The UAV swarm coordination protocol emerges from individual interactions between UAVs and has the objective of optimizing the collection of sensor data over an area. It also allows for the simulation of some types of failures to test the protocol adaptability. Every node in the simulation is highly configurable making testing different network opographies, coordination protocols, node hardware configurations and more a quick task.
Bridging the Gap between Semantics and Multimedia Processing
Dec 02, 2019
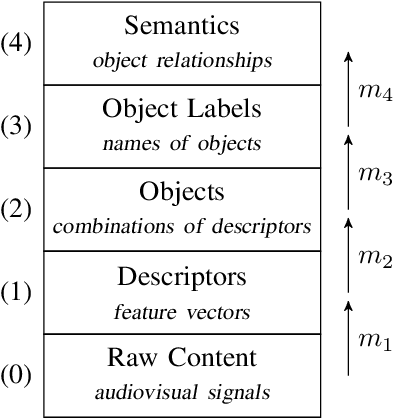
Abstract:In this paper, we give an overview of the semantic gap problem in multimedia and discuss how machine learning and symbolic AI can be combined to narrow this gap. We describe the gap in terms of a classical architecture for multimedia processing and discuss a structured approach to bridge it. This approach combines machine learning (for mapping signals to objects) and symbolic AI (for linking objects to meanings). Our main goal is to raise awareness and discuss the challenges involved in this structured approach to multimedia understanding, especially in the view of the latest developments in machine learning and symbolic AI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge