Mark J. Coates
Motion Inbetweening via Deep $Δ$-Interpolator
Jan 27, 2022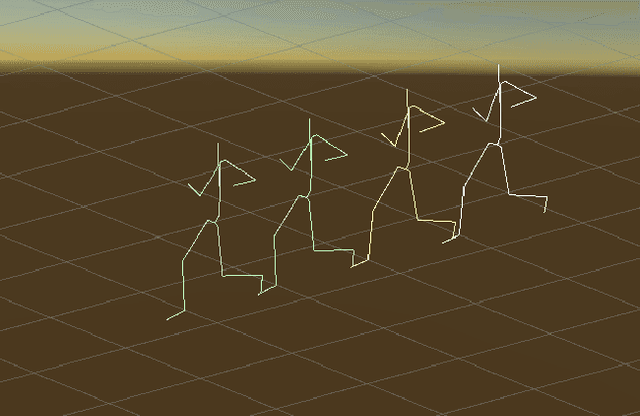
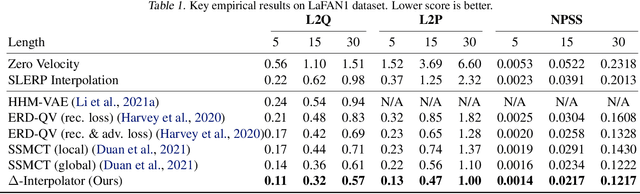
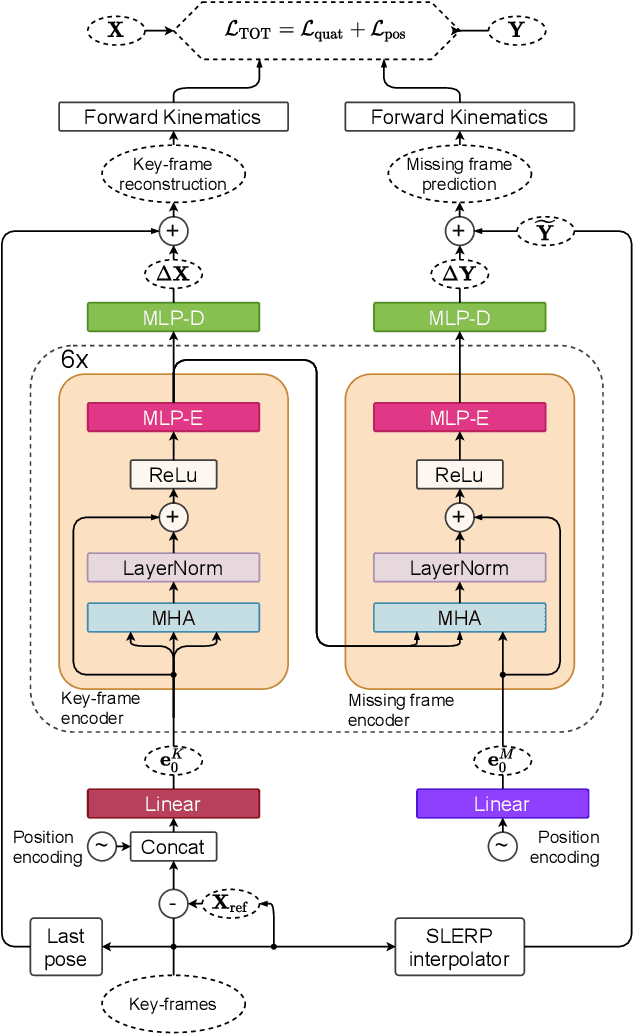
Abstract:We show that the task of synthesizing missing middle frames, commonly known as motion in-betweening in the animation industry, can be solved more accurately and effectively if a deep learning interpolator operates in the delta mode, using the spherical linear interpolator as a baseline. We demonstrate our empirical findings on the publicly available LaFAN1 dataset. We further generalize this result by showing that the $\Delta$-regime is viable with respect to the reference of the last known frame (also known as the zero-velocity model). This supports the more general conclusion that deep in-betweening in the reference frame local to input frames is more accurate and robust than in-betweening in the global (world) reference frame advocated in previous work. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/boreshkinai/delta-interpolator.
FC-GAGA: Fully Connected Gated Graph Architecture for Spatio-Temporal Traffic Forecasting
Jul 30, 2020



Abstract:Forecasting of multivariate time-series is an important problem that has applications in many domains, including traffic management, cellular network configuration, and quantitative finance. In recent years, researchers have demonstrated the value of applying deep learning architectures for these problems. A special case of the problem arises when there is a graph available that captures the relationships between the time-series. In this paper we propose a novel learning architecture that achieves performance competitive with or better than the best existing algorithms, without requiring knowledge of the graph. The key elements of our proposed architecture are (i) jointly performing backcasting and forecasting with a deep fully-connected architecture; (ii) stacking multiple prediction modules that target successive residuals; and (iii) learning a separate causal relationship graph for each layer of the stack. We can view each layer as predicting a component of the time-series; the differing nature of the causal graphs at different layers can be interpreted as indicating that the multivariate predictive relationships differ for different components. Experimental results for two public traffic network datasets illustrate the value of our approach, and ablation studies confirm the importance of each element of the architecture.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge