Mark G. Wallace
Minimal Conditions for Beneficial Neighbourhood Search and Local Descent
Nov 08, 2024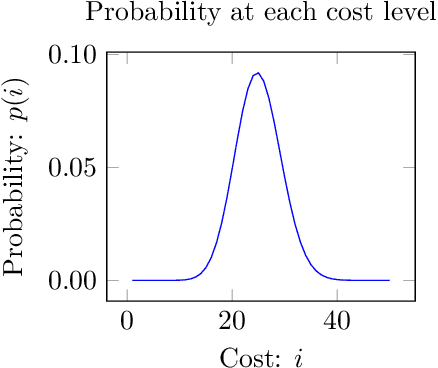
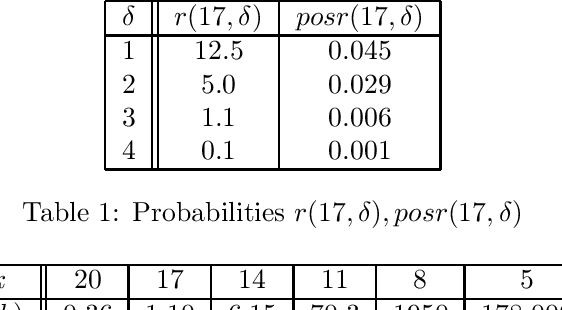
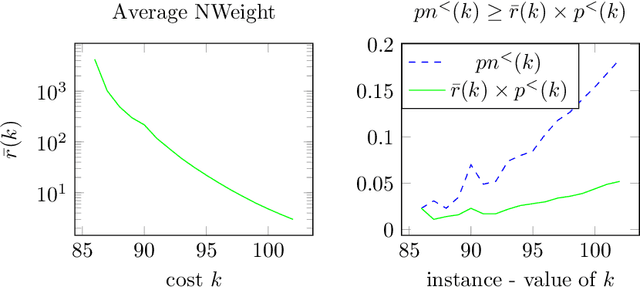
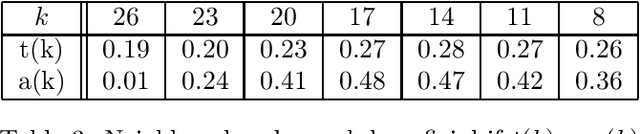
Abstract:This paper investigates what properties a neighbourhood requires to support beneficial local search. We show that neighbourhood locality, and a reduction in cost probability towards the optimum, support a proof that search among neighbours is more likely to find an improving solution in a single search step than blind search. This is the first paper to introduce such a proof. The concepts underlying these properties are illustrated on a satisfiability problem class, and on travelling salesman problems. Secondly, for a given cost target t, we investigate a combination of blind search and local descent termed local blind descent, and present various conditions under which the expected number of steps to reach a cost better than t using local blind descent, is proven to be smaller than with blind search. Experiments indicate that local blind descent, given target cost t, should switch to local descent at a starting cost that reduces as t approaches the optimum.
Solving the Resource Constrained Project Scheduling Problem with Generalized Precedences by Lazy Clause Generation
Sep 02, 2010
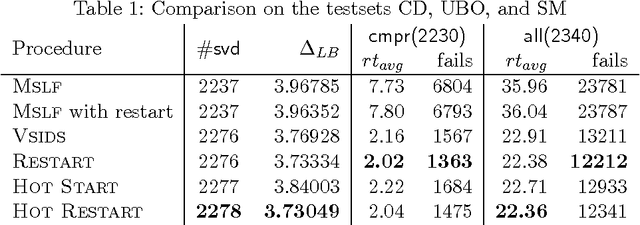

Abstract:The technical report presents a generic exact solution approach for minimizing the project duration of the resource-constrained project scheduling problem with generalized precedences (Rcpsp/max). The approach uses lazy clause generation, i.e., a hybrid of finite domain and Boolean satisfiability solving, in order to apply nogood learning and conflict-driven search on the solution generation. Our experiments show the benefit of lazy clause generation for finding an optimal solutions and proving its optimality in comparison to other state-of-the-art exact and non-exact methods. The method is highly robust: it matched or bettered the best known results on all of the 2340 instances we examined except 3, according to the currently available data on the PSPLib. Of the 631 open instances in this set it closed 573 and improved the bounds of 51 of the remaining 58 instances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge