Mario Jarmasz
Roget's Thesaurus: a Lexical Resource to Treasure
Apr 01, 2012Abstract:This paper presents the steps involved in creating an electronic lexical knowledge base from the 1987 Penguin edition of Roget's Thesaurus. Semantic relations are labelled with the help of WordNet. The two resources are compared in a qualitative and quantitative manner. Differences in the organization of the lexical material are discussed, as well as the possibility of merging both resources.
* 6 pages
Not As Easy As It Seems: Automating the Construction of Lexical Chains Using Roget's Thesaurus
Apr 01, 2012Abstract:Morris and Hirst present a method of linking significant words that are about the same topic. The resulting lexical chains are a means of identifying cohesive regions in a text, with applications in many natural language processing tasks, including text summarization. The first lexical chains were constructed manually using Roget's International Thesaurus. Morris and Hirst wrote that automation would be straightforward given an electronic thesaurus. All applications so far have used WordNet to produce lexical chains, perhaps because adequate electronic versions of Roget's were not available until recently. We discuss the building of lexical chains using an electronic version of Roget's Thesaurus. We implement a variant of the original algorithm, and explain the necessary design decisions. We include a comparison with other implementations.
* 5 pages
Keyphrase Extraction : Enhancing Lists
Apr 01, 2012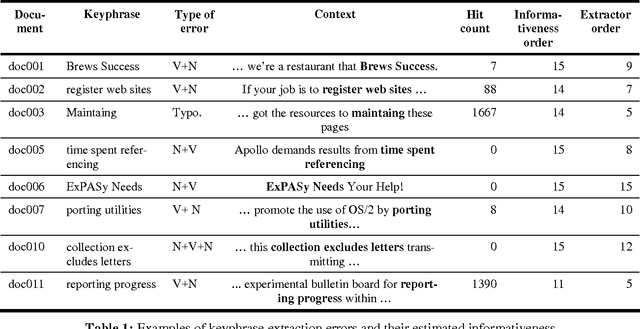
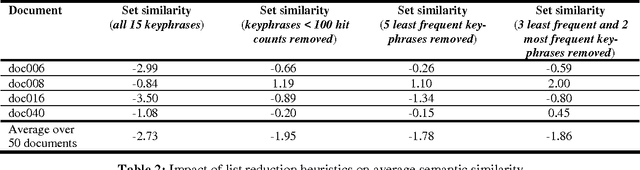


Abstract:This paper proposes some modest improvements to Extractor, a state-of-the-art keyphrase extraction system, by using a terabyte-sized corpus to estimate the informativeness and semantic similarity of keyphrases. We present two techniques to improve the organization and remove outliers of lists of keyphrases. The first is a simple ordering according to their occurrences in the corpus; the second is clustering according to semantic similarity. Evaluation issues are discussed. We present a novel technique of comparing extracted keyphrases to a gold standard which relies on semantic similarity rather than string matching or an evaluation involving human judges.
Roget's Thesaurus and Semantic Similarity
Apr 01, 2012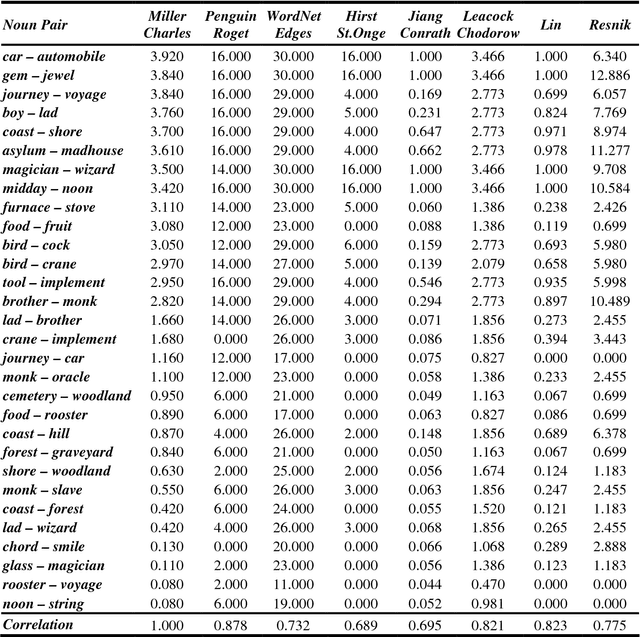



Abstract:We have implemented a system that measures semantic similarity using a computerized 1987 Roget's Thesaurus, and evaluated it by performing a few typical tests. We compare the results of these tests with those produced by WordNet-based similarity measures. One of the benchmarks is Miller and Charles' list of 30 noun pairs to which human judges had assigned similarity measures. We correlate these measures with those computed by several NLP systems. The 30 pairs can be traced back to Rubenstein and Goodenough's 65 pairs, which we have also studied. Our Roget's-based system gets correlations of .878 for the smaller and .818 for the larger list of noun pairs; this is quite close to the .885 that Resnik obtained when he employed humans to replicate the Miller and Charles experiment. We further evaluate our measure by using Roget's and WordNet to answer 80 TOEFL, 50 ESL and 300 Reader's Digest questions: the correct synonym must be selected amongst a group of four words. Our system gets 78.75%, 82.00% and 74.33% of the questions respectively.
* 8 pages
Roget's Thesaurus as a Lexical Resource for Natural Language Processing
Mar 31, 2012



Abstract:WordNet proved that it is possible to construct a large-scale electronic lexical database on the principles of lexical semantics. It has been accepted and used extensively by computational linguists ever since it was released. Inspired by WordNet's success, we propose as an alternative a similar resource, based on the 1987 Penguin edition of Roget's Thesaurus of English Words and Phrases. Peter Mark Roget published his first Thesaurus over 150 years ago. Countless writers, orators and students of the English language have used it. Computational linguists have employed Roget's for almost 50 years in Natural Language Processing, however hesitated in accepting Roget's Thesaurus because a proper machine tractable version was not available. This dissertation presents an implementation of a machine-tractable version of the 1987 Penguin edition of Roget's Thesaurus - the first implementation of its kind to use an entire current edition. It explains the steps necessary for taking a machine-readable file and transforming it into a tractable system. This involves converting the lexical material into a format that can be more easily exploited, identifying data structures and designing classes to computerize the Thesaurus. Roget's organization is studied in detail and contrasted with WordNet's. We show two applications of the computerized Thesaurus: computing semantic similarity between words and phrases, and building lexical chains in a text. The experiments are performed using well-known benchmarks and the results are compared to those of other systems that use Roget's, WordNet and statistical techniques. Roget's has turned out to be an excellent resource for measuring semantic similarity; lexical chains are easily built but more difficult to evaluate. We also explain ways in which Roget's Thesaurus and WordNet can be combined.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge