Marinus J. Lagerwerf
A computationally efficient reconstruction algorithm for circular cone-beam computed tomography using shallow neural networks
Oct 01, 2020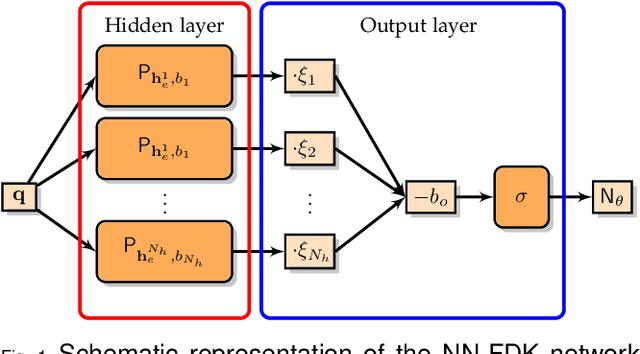
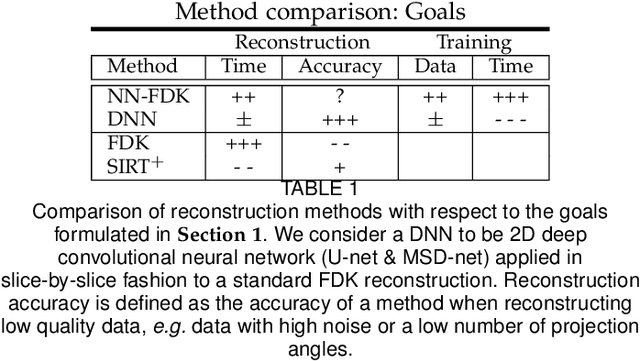
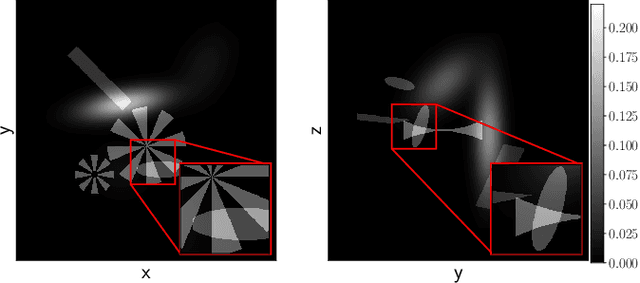
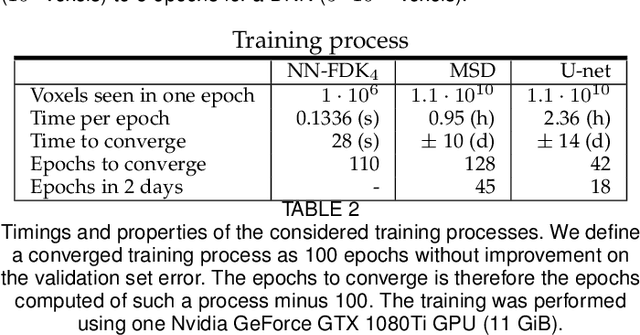
Abstract:Circular cone-beam (CCB) Computed Tomography (CT) has become an integral part of industrial quality control, materials science and medical imaging. The need to acquire and process each scan in a short time naturally leads to trade-offs between speed and reconstruction quality, creating a need for fast reconstruction algorithms capable of creating accurate reconstructions from limited data. In this paper we introduce the Neural Network Feldkamp-Davis-Kress (NN-FDK) algorithm. This algorithm adds a machine learning component to the FDK algorithm to improve its reconstruction accuracy while maintaining its computational efficiency. Moreover, the NN-FDK algorithm is designed such that it has low training data requirements and is fast to train. This ensures that the proposed algorithm can be used to improve image quality in high throughput CT scanning settings, where FDK is currently used to keep pace with the acquisition speed using readily available computational resources. We compare the NN-FDK algorithm to two standard CT reconstruction algorithms and to two popular deep neural networks trained to remove reconstruction artifacts from the 2D slices of an FDK reconstruction. We show that the NN-FDK reconstruction algorithm is substantially faster in computing a reconstruction than all the tested alternative methods except for the standard FDK algorithm and we show it can compute accurate CCB CT reconstructions in cases of high noise, a low number of projection angles or large cone angles. Moreover, we show that the training time of an NN-FDK network is orders of magnitude lower than the considered deep neural networks, with only a slight reduction in reconstruction accuracy.
Noise2Filter: fast, self-supervised learning and real-time reconstruction for 3D Computed Tomography
Jul 03, 2020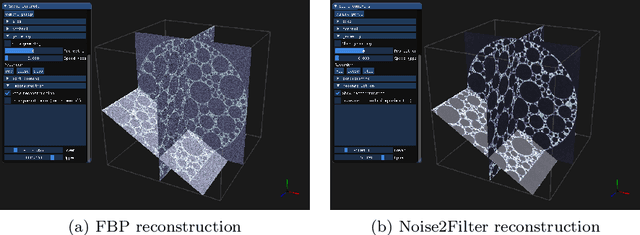
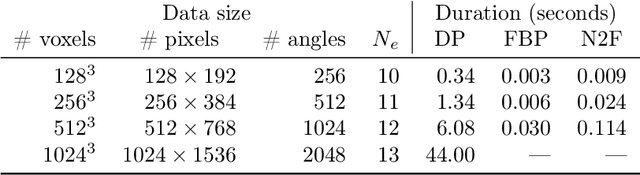
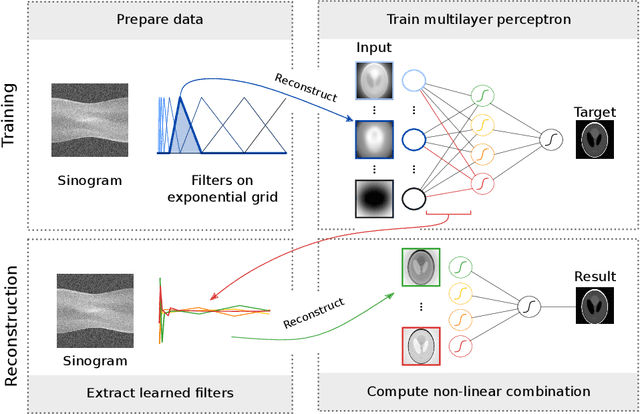
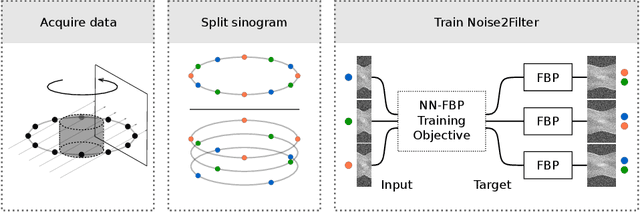
Abstract:At X-ray beamlines of synchrotron light sources, the achievable time-resolution for 3D tomographic imaging of the interior of an object has been reduced to a fraction of a second, enabling rapidly changing structures to be examined. The associated data acquisition rates require sizable computational resources for reconstruction. Therefore, full 3D reconstruction of the object is usually performed after the scan has completed. Quasi-3D reconstruction -- where several interactive 2D slices are computed instead of a 3D volume -- has been shown to be significantly more efficient, and can enable the real-time reconstruction and visualization of the interior. However, quasi-3D reconstruction relies on filtered backprojection type algorithms, which are typically sensitive to measurement noise. To overcome this issue, we propose Noise2Filter, a learned filter method that can be trained using only the measured data, and does not require any additional training data. This method combines quasi-3D reconstruction, learned filters, and self-supervised learning to derive a tomographic reconstruction method that can be trained in under a minute and evaluated in real-time. We show limited loss of accuracy compared to training with additional training data, and improved accuracy compared to standard filter-based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge