Maria J. Cardoso
An inpainting approach to manipulate asymmetry in pre-operative breast images
Feb 08, 2025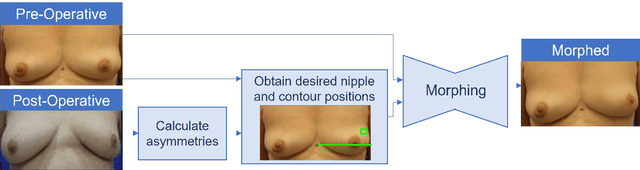
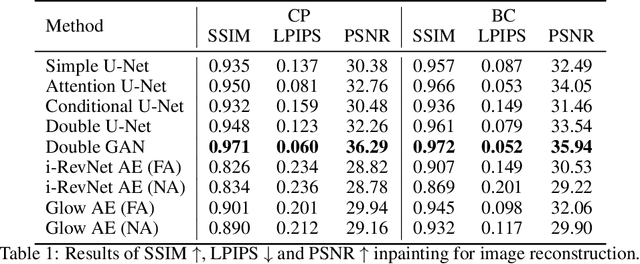
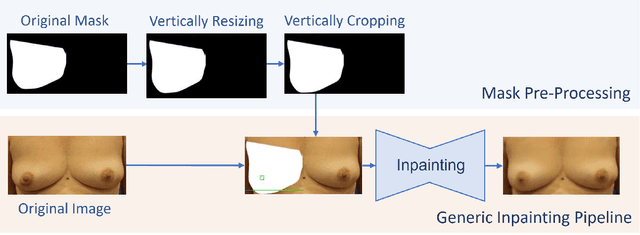

Abstract:One of the most frequent modalities of breast cancer treatment is surgery. Breast surgery can cause visual alterations to the breasts, due to scars and asymmetries. To enable an informed choice of treatment, the patient must be adequately informed of the aesthetic outcomes of each treatment plan. In this work, we propose an inpainting approach to manipulate breast shape and nipple position in breast images, for the purpose of predicting the aesthetic outcomes of breast cancer treatment. We perform experiments with various model architectures for the inpainting task, including invertible networks capable of manipulating breasts in the absence of ground-truth breast contour and nipple annotations. Experiments on two breast datasets show the proposed models' ability to realistically alter a patient's breasts, enabling a faithful reproduction of breast asymmetries of post-operative patients in pre-operative images.
Deep Aesthetic Assessment and Retrieval of Breast Cancer Treatment Outcomes
May 25, 2022Abstract:Treatments for breast cancer have continued to evolve and improve in recent years, resulting in a substantial increase in survival rates, with approximately 80\% of patients having a 10-year survival period. Given the serious impact that breast cancer treatments can have on a patient's body image, consequently affecting her self-confidence and sexual and intimate relationships, it is paramount to ensure that women receive the treatment that optimizes both survival and aesthetic outcomes. Currently, there is no gold standard for evaluating the aesthetic outcome of breast cancer treatment. In addition, there is no standard way to show patients the potential outcome of surgery. The presentation of similar cases from the past would be extremely important to manage women's expectations of the possible outcome. In this work, we propose a deep neural network to perform the aesthetic evaluation. As a proof-of-concept, we focus on a binary aesthetic evaluation. Besides its use for classification, this deep neural network can also be used to find the most similar past cases by searching for nearest neighbours in the highly semantic space before classification. We performed the experiments on a dataset consisting of 143 photos of women after conservative treatment for breast cancer. The results for accuracy and balanced accuracy showed the superior performance of our proposed model compared to the state of the art in aesthetic evaluation of breast cancer treatments. In addition, the model showed a good ability to retrieve similar previous cases, with the retrieved cases having the same or adjacent class (in the 4-class setting) and having similar types of asymmetry. Finally, a qualitative interpretability assessment was also performed to analyse the robustness and trustworthiness of the model.
Computer Aided Detection of Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforators in Computed Tomography Angiography scans
Jul 24, 2019



Abstract:The deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEAP) flap is the most common free flap used for breast reconstruction after a mastectomy. It makes use of the skin and fat of the lower abdomen to build a new breast mound either at the same time of the mastectomy or in a second surgery. This operation requires preoperative imaging studies to evaluate the branches - the perforators - that irrigate the tissue that will be used to reconstruct the breast mound. These branches will support tissue viability after the microsurgical ligation of the inferior epigastric vessels to the receptor vessels in the thorax. Usually through a Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA), each perforator, diameter and direction is manually identified by the imaging team, who will subsequently draw a map for the identification of the best vascular support for the reconstruction. In the current work we propose a semi-automatic methodology that aims at reducing the time and subjectivity inherent to the manual annotation. In 21 CTAs from patients proposed for breast reconstruction with DIEAP flaps, the subcutaneous region of each perforator was extracted, by means of a tracking procedure, whereas the intramuscular portion was detected through a minimum cost approach. Both were subsequently compared with the radiologist manual annotation. Results showed that the semi-automatic procedure was able to correctly detect the course of the DIEAPs with a minimum error (average error of 0.64 mm and 0.50 mm regarding the extraction of subcutaneous and intramuscular paths, respectively). The objective methodology is a promising tool in the automatic detection of perforators in CTA and can contribute to spare human resources and reduce subjectivity in the aforementioned task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge