Margaux Zaffran
EDF R&D, CRISAM, CMAP, PARIETAL
Conformal Prediction with Missing Values
Jun 05, 2023



Abstract:Conformal prediction is a theoretically grounded framework for constructing predictive intervals. We study conformal prediction with missing values in the covariates -- a setting that brings new challenges to uncertainty quantification. We first show that the marginal coverage guarantee of conformal prediction holds on imputed data for any missingness distribution and almost all imputation functions. However, we emphasize that the average coverage varies depending on the pattern of missing values: conformal methods tend to construct prediction intervals that under-cover the response conditionally to some missing patterns. This motivates our novel generalized conformalized quantile regression framework, missing data augmentation, which yields prediction intervals that are valid conditionally to the patterns of missing values, despite their exponential number. We then show that a universally consistent quantile regression algorithm trained on the imputed data is Bayes optimal for the pinball risk, thus achieving valid coverage conditionally to any given data point. Moreover, we examine the case of a linear model, which demonstrates the importance of our proposal in overcoming the heteroskedasticity induced by missing values. Using synthetic and data from critical care, we corroborate our theory and report improved performance of our methods.
Adaptive Conformal Predictions for Time Series
Feb 15, 2022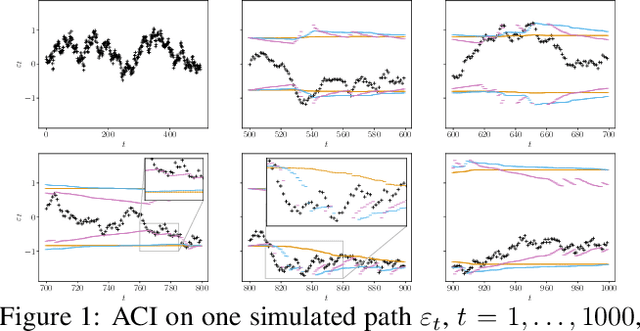
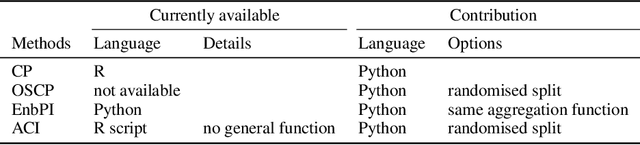
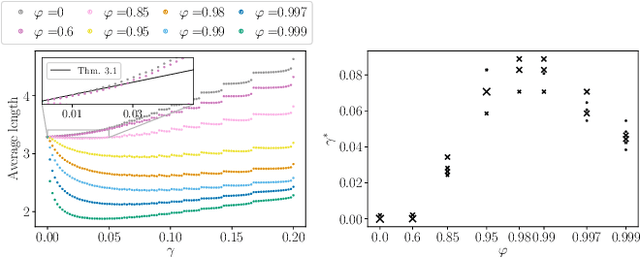
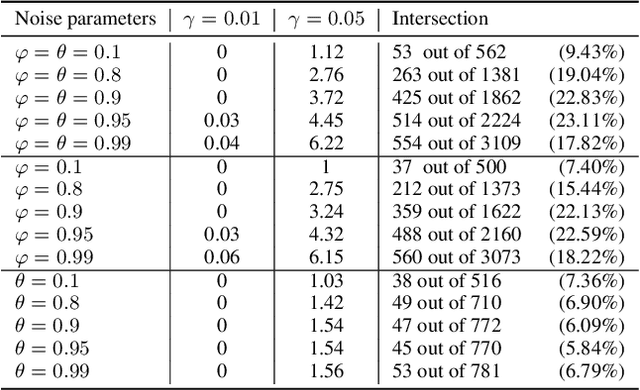
Abstract:Uncertainty quantification of predictive models is crucial in decision-making problems. Conformal prediction is a general and theoretically sound answer. However, it requires exchangeable data, excluding time series. While recent works tackled this issue, we argue that Adaptive Conformal Inference (ACI, Gibbs and Cand{\`e}s, 2021), developed for distribution-shift time series, is a good procedure for time series with general dependency. We theoretically analyse the impact of the learning rate on its efficiency in the exchangeable and auto-regressive case. We propose a parameter-free method, AgACI, that adaptively builds upon ACI based on online expert aggregation. We lead extensive fair simulations against competing methods that advocate for ACI's use in time series. We conduct a real case study: electricity price forecasting. The proposed aggregation algorithm provides efficient prediction intervals for day-ahead forecasting. All the code and data to reproduce the experiments is made available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge