Marco R. Spruit
Theory of Mind in Large Language Models: Examining Performance of 11 State-of-the-Art models vs. Children Aged 7-10 on Advanced Tests
Oct 31, 2023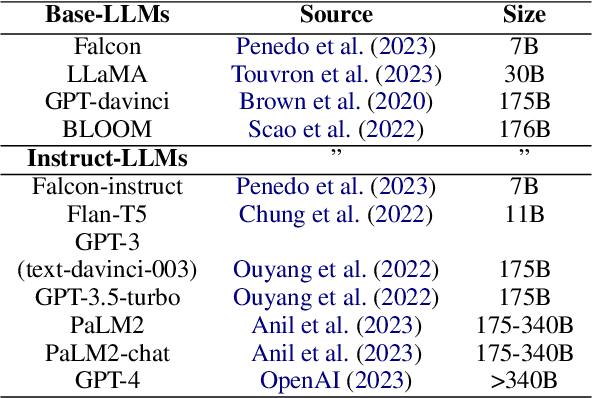

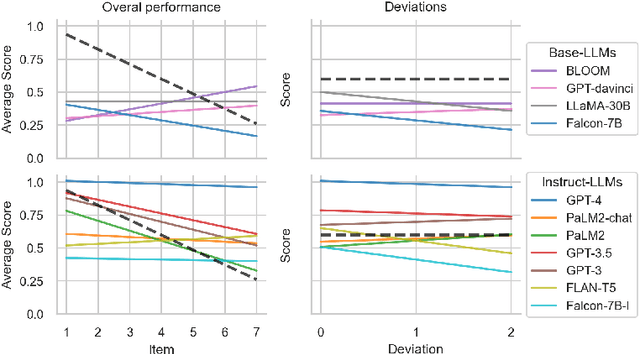

Abstract:To what degree should we ascribe cognitive capacities to Large Language Models (LLMs), such as the ability to reason about intentions and beliefs known as Theory of Mind (ToM)? Here we add to this emerging debate by (i) testing 11 base- and instruction-tuned LLMs on capabilities relevant to ToM beyond the dominant false-belief paradigm, including non-literal language usage and recursive intentionality; (ii) using newly rewritten versions of standardized tests to gauge LLMs' robustness; (iii) prompting and scoring for open besides closed questions; and (iv) benchmarking LLM performance against that of children aged 7-10 on the same tasks. We find that instruction-tuned LLMs from the GPT family outperform other models, and often also children. Base-LLMs are mostly unable to solve ToM tasks, even with specialized prompting. We suggest that the interlinked evolution and development of language and ToM may help explain what instruction-tuning adds: rewarding cooperative communication that takes into account interlocutor and context. We conclude by arguing for a nuanced perspective on ToM in LLMs.
Large Language Models: The Need for Nuance in Current Debates and a Pragmatic Perspective on Understanding
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Current Large Language Models (LLMs) are unparalleled in their ability to generate grammatically correct, fluent text. LLMs are appearing rapidly, and debates on LLM capacities have taken off, but reflection is lagging behind. Thus, in this position paper, we first zoom in on the debate and critically assess three points recurring in critiques of LLM capacities: i) that LLMs only parrot statistical patterns in the training data; ii) that LLMs master formal but not functional language competence; and iii) that language learning in LLMs cannot inform human language learning. Drawing on empirical and theoretical arguments, we show that these points need more nuance. Second, we outline a pragmatic perspective on the issue of `real' understanding and intentionality in LLMs. Understanding and intentionality pertain to unobservable mental states we attribute to other humans because they have pragmatic value: they allow us to abstract away from complex underlying mechanics and predict behaviour effectively. We reflect on the circumstances under which it would make sense for humans to similarly attribute mental states to LLMs, thereby outlining a pragmatic philosophical context for LLMs as an increasingly prominent technology in society.
ChiSCor: A Corpus of Freely Told Fantasy Stories by Dutch Children for Computational Linguistics and Cognitive Science
Oct 31, 2023



Abstract:In this resource paper we release ChiSCor, a new corpus containing 619 fantasy stories, told freely by 442 Dutch children aged 4-12. ChiSCor was compiled for studying how children render character perspectives, and unravelling language and cognition in development, with computational tools. Unlike existing resources, ChiSCor's stories were produced in natural contexts, in line with recent calls for more ecologically valid datasets. ChiSCor hosts text, audio, and annotations for character complexity and linguistic complexity. Additional metadata (e.g. education of caregivers) is available for one third of the Dutch children. ChiSCor also includes a small set of 62 English stories. This paper details how ChiSCor was compiled and shows its potential for future work with three brief case studies: i) we show that the syntactic complexity of stories is strikingly stable across children's ages; ii) we extend work on Zipfian distributions in free speech and show that ChiSCor obeys Zipf's law closely, reflecting its social context; iii) we show that even though ChiSCor is relatively small, the corpus is rich enough to train informative lemma vectors that allow us to analyse children's language use. We end with a reflection on the value of narrative datasets in computational linguistics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge