Marcia Hon
Transfer Learning with intelligent training data selection for prediction of Alzheimer's Disease
Jun 04, 2019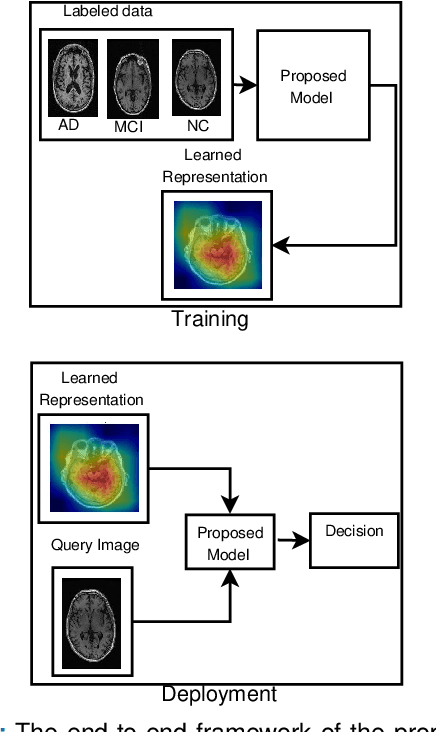
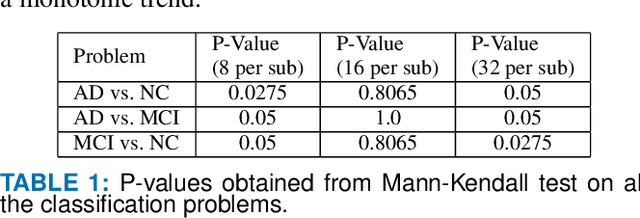
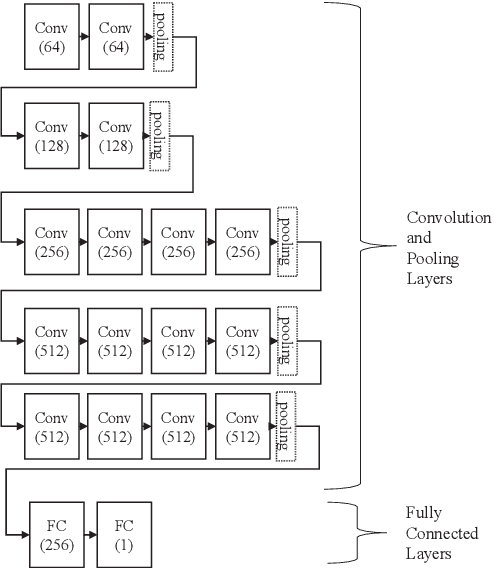
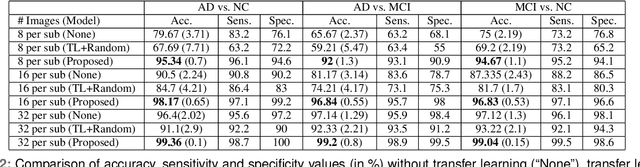
Abstract:Detection of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) from neuroimaging data such as MRI through machine learning has been a subject of intense research in recent years. Recent success of deep learning in computer vision has progressed such research further. However, common limitations with such algorithms are reliance on a large number of training images, and requirement of careful optimization of the architecture of deep networks. In this paper, we attempt solving these issues with transfer learning, where the state-of-the-art VGG architecture is initialized with pre-trained weights from large benchmark datasets consisting of natural images. The network is then fine-tuned with layer-wise tuning, where only a pre-defined group of layers are trained on MRI images. To shrink the training data size, we employ image entropy to select the most informative slices. Through experimentation on the ADNI dataset, we show that with training size of 10 to 20 times smaller than the other contemporary methods, we reach state-of-the-art performance in AD vs. NC, AD vs. MCI, and MCI vs. NC classification problems, with a 4% and a 7% increase in accuracy over the state-of-the-art for AD vs. MCI and MCI vs. NC, respectively. We also provide detailed analysis of the effect of the intelligent training data selection method, changing the training size, and changing the number of layers to be fine-tuned. Finally, we provide Class Activation Maps (CAM) that demonstrate how the proposed model focuses on discriminative image regions that are neuropathologically relevant, and can help the healthcare practitioner in interpreting the model's decision making process.
Towards Alzheimer's Disease Classification through Transfer Learning
Nov 29, 2017


Abstract:Detection of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) from neuroimaging data such as MRI through machine learning have been a subject of intense research in recent years. Recent success of deep learning in computer vision have progressed such research further. However, common limitations with such algorithms are reliance on a large number of training images, and requirement of careful optimization of the architecture of deep networks. In this paper, we attempt solving these issues with transfer learning, where state-of-the-art architectures such as VGG and Inception are initialized with pre-trained weights from large benchmark datasets consisting of natural images, and the fully-connected layer is re-trained with only a small number of MRI images. We employ image entropy to select the most informative slices for training. Through experimentation on the OASIS MRI dataset, we show that with training size almost 10 times smaller than the state-of-the-art, we reach comparable or even better performance than current deep-learning based methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge