Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Marc Dalmasso
Human-robot Collaborative Navigation Search using Social Reward Sources
Sep 10, 2019Figures and Tables: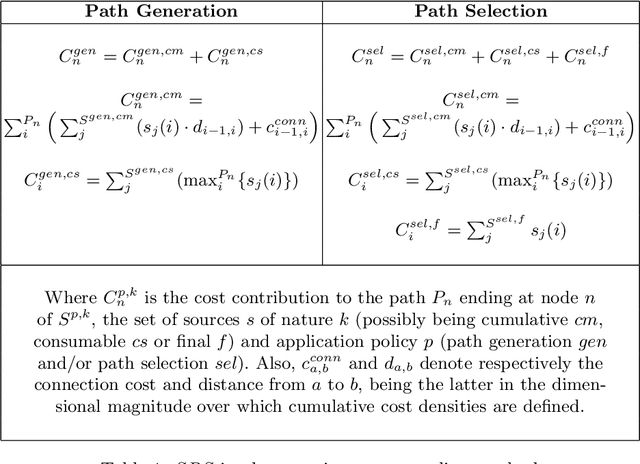
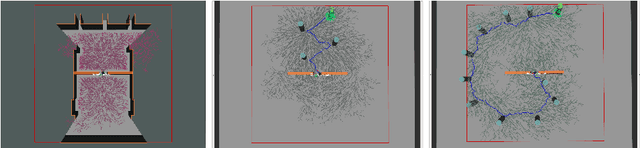
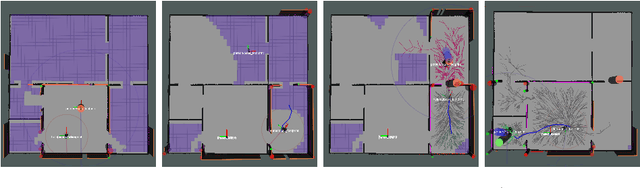
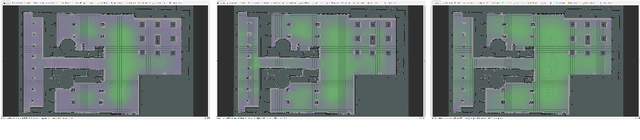




Abstract:This paper proposes a Social Reward Sources (SRS) design for a Human-Robot Collaborative Navigation (HRCN) task: human-robot collaborative search. It is a flexible approach capable of handling the collaborative task, human-robot interaction and environment restrictions, all integrated on a common environment. We modelled task rewards based on unexplored area observability and isolation and evaluated the model through different levels of human-robot communication. The models are validated through quantitative evaluation against both agents' individual performance and qualitative surveying of participants' perception. After that, the three proposed communication levels are compared against each other using the previous metrics.
* Preprint, accepted to the fourth Iberian Robotics Conference (Robot
2019)
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge