Manuel Watter
Early Seizure Detection with an Energy-Efficient Convolutional Neural Network on an Implantable Microcontroller
Jun 12, 2018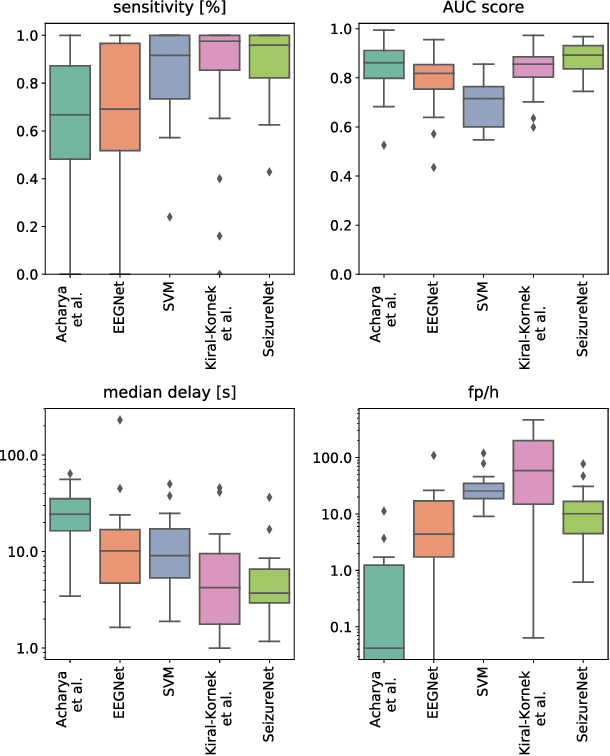
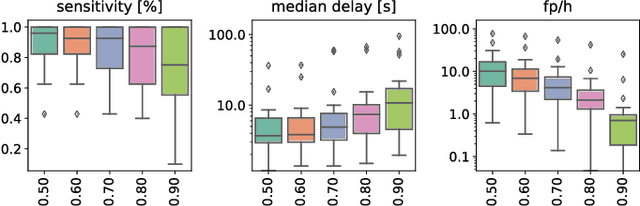
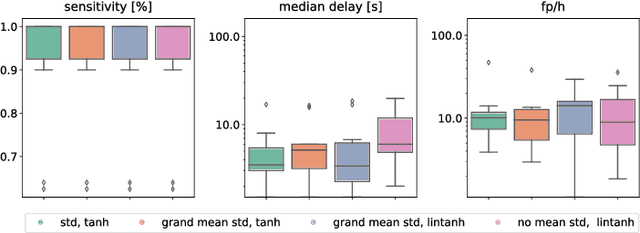
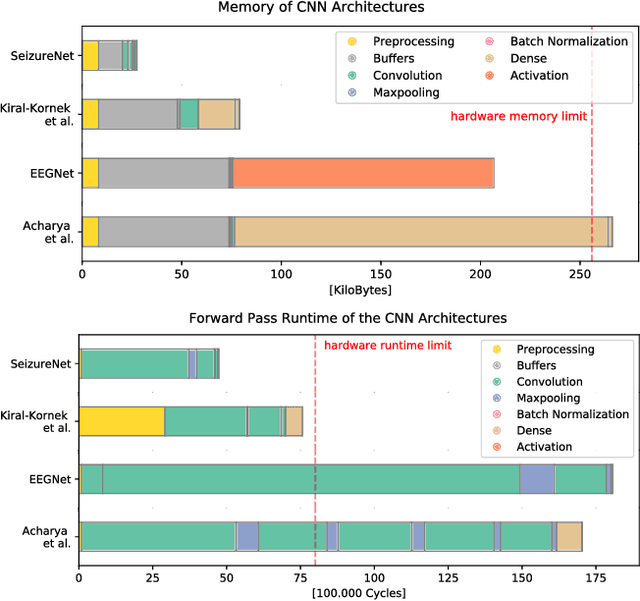
Abstract:Implantable, closed-loop devices for automated early detection and stimulation of epileptic seizures are promising treatment options for patients with severe epilepsy that cannot be treated with traditional means. Most approaches for early seizure detection in the literature are, however, not optimized for implementation on ultra-low power microcontrollers required for long-term implantation. In this paper we present a convolutional neural network for the early detection of seizures from intracranial EEG signals, designed specifically for this purpose. In addition, we investigate approximations to comply with hardware limits while preserving accuracy. We compare our approach to three previously proposed convolutional neural networks and a feature-based SVM classifier with respect to detection accuracy, latency and computational needs. Evaluation is based on a comprehensive database with long-term EEG recordings. The proposed method outperforms the other detectors with a median sensitivity of 0.96, false detection rate of 10.1 per hour and median detection delay of 3.7 seconds, while being the only approach suited to be realized on a low power microcontroller due to its parsimonious use of computational and memory resources.
Embed to Control: A Locally Linear Latent Dynamics Model for Control from Raw Images
Nov 20, 2015



Abstract:We introduce Embed to Control (E2C), a method for model learning and control of non-linear dynamical systems from raw pixel images. E2C consists of a deep generative model, belonging to the family of variational autoencoders, that learns to generate image trajectories from a latent space in which the dynamics is constrained to be locally linear. Our model is derived directly from an optimal control formulation in latent space, supports long-term prediction of image sequences and exhibits strong performance on a variety of complex control problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge