Manolis Pitsikalis
Logic Rules Meet Deep Learning: A Novel Approach for Ship Type Classification
Nov 01, 2021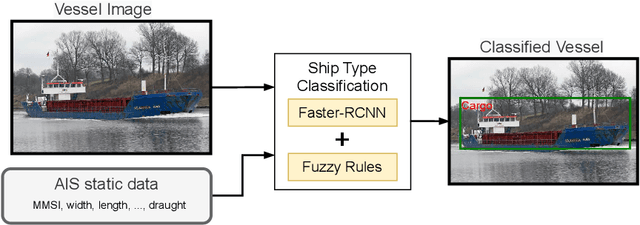


Abstract:The shipping industry is an important component of the global trade and economy, however in order to ensure law compliance and safety it needs to be monitored. In this paper, we present a novel Ship Type classification model that combines vessel transmitted data from the Automatic Identification System, with vessel imagery. The main components of our approach are the Faster R-CNN Deep Neural Network and a Neuro-Fuzzy system with IF-THEN rules. We evaluate our model using real world data and showcase the advantages of this combination while also compare it with other methods. Results show that our model can increase prediction scores by up to 15.4\% when compared with the next best model we considered, while also maintaining a level of explainability as opposed to common black box approaches.
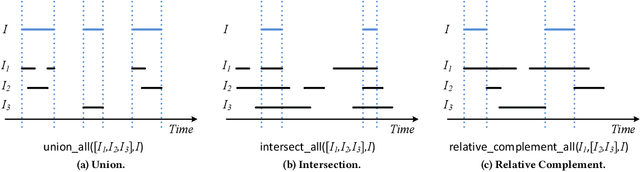
Representation and Processing of Instantaneous and Durative Temporal Phenomena
Aug 27, 2021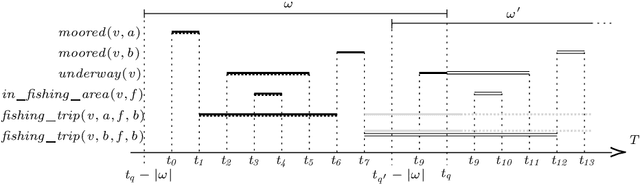

Abstract:Event definitions in Complex Event Processing systems are constrained by the expressiveness of each system's language. Some systems allow the definition of instantaneous complex events, while others allow the definition of durative complex events. While there are exceptions that offer both options, they often lack of intervals relations such as those specified by the Allen's interval algebra. In this paper, we propose a new logic based temporal phenomena definition language, specifically tailored for Complex Event Processing, that allows the representation of both instantaneous and durative phenomena and the temporal relations between them. Moreover, we demonstrate the expressiveness of our proposed language by employing a maritime use case where we define maritime events of interest. Finally, we analyse the execution semantics of our proposed language for stream processing and introduce the `Phenesthe' implementation prototype.
Composite Event Recognition for Maritime Monitoring
Mar 08, 2019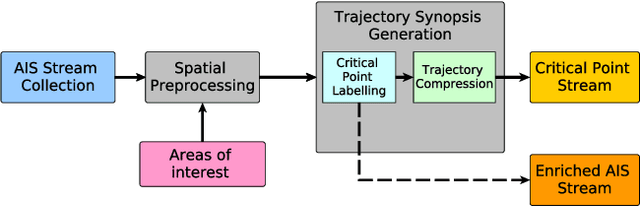


Abstract:Maritime monitoring systems support safe shipping as they allow for the real-time detection of dangerous, suspicious and illegal vessel activities. We present such a system using the Run-Time Event Calculus, a composite event recognition system with formal, declarative semantics. For effective recognition, we developed a library of maritime patterns in close collaboration with domain experts. We present a thorough evaluation of the system and the patterns both in terms of predictive accuracy and computational efficiency, using real-world datasets of vessel position streams and contextual geographical information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge