Manish Joshi
KBCNMUJAL@HASOC-Dravidian-CodeMix-FIRE2020: Using Machine Learning for Detection of Hate Speech and Offensive Code-Mixed Social Media text
Feb 19, 2021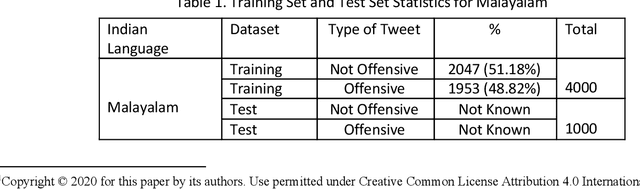
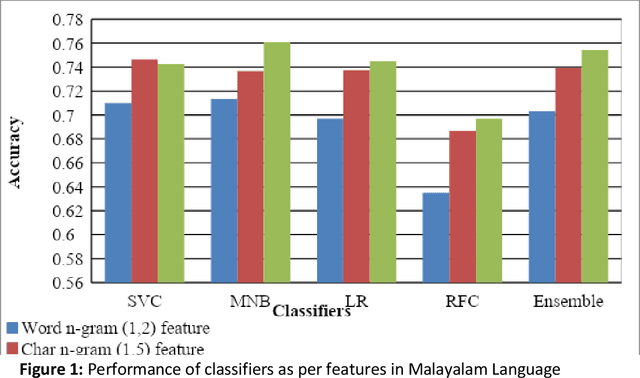

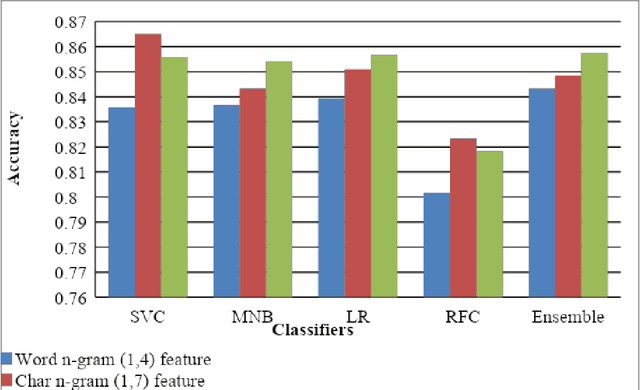
Abstract:This paper describes the system submitted by our team, KBCNMUJAL, for Task 2 of the shared task Hate Speech and Offensive Content Identification in Indo-European Languages (HASOC), at Forum for Information Retrieval Evaluation, December 16-20, 2020, Hyderabad, India. The datasets of two Dravidian languages Viz. Malayalam and Tamil of size 4000 observations, each were shared by the HASOC organizers. These datasets are used to train the machine using different machine learning algorithms, based on classification and regression models. The datasets consist of tweets or YouTube comments with two class labels offensive and not offensive. The machine is trained to classify such social media messages in these two categories. Appropriate n-gram feature sets are extracted to learn the specific characteristics of the Hate Speech text messages. These feature models are based on TFIDF weights of n-gram. The referred work and respective experiments show that the features such as word, character and combined model of word and character n-grams could be used to identify the term patterns of offensive text contents. As a part of the HASOC shared task, the test data sets are made available by the HASOC track organizers. The best performing classification models developed for both languages are applied on test datasets. The model which gives the highest accuracy result on training dataset for Malayalam language was experimented to predict the categories of respective test data. This system has obtained an F1 score of 0.77. Similarly the best performing model for Tamil language has obtained an F1 score of 0.87. This work has received 2nd and 3rd rank in this shared Task 2 for Malayalam and Tamil language respectively. The proposed system is named HASOC_kbcnmujal.
Descriptive analysis of computational methods for automating mammograms with practical applications
Oct 06, 2020
Abstract:Mammography is a vital screening technique for early revealing and identification of breast cancer in order to assist to decrease mortality rate. Practical applications of mammograms are not limited to breast cancer revealing, identification ,but include task based lens design, image compression, image classification, content based image retrieval and a host of others. Mammography computational analysis methods are a useful tool for specialists to reveal hidden features and extract significant information in mammograms. Digital mammograms are mammography images available along with the conventional screen-film mammography to make automation of mammograms easier. In this paper, we descriptively discuss computational advancement in digital mammograms to serve as a compass for research and practice in the domain of computational mammography and related fields. The discussion focuses on research aiming at a variety of applications and automations of mammograms. It covers different perspectives on image pre-processing, feature extraction, application of mammograms, screen-film mammogram, digital mammogram and development of benchmark corpora for experimenting with digital mammograms.
An Extensive Review of Computational Dance Automation Techniques and Applications
Jun 03, 2019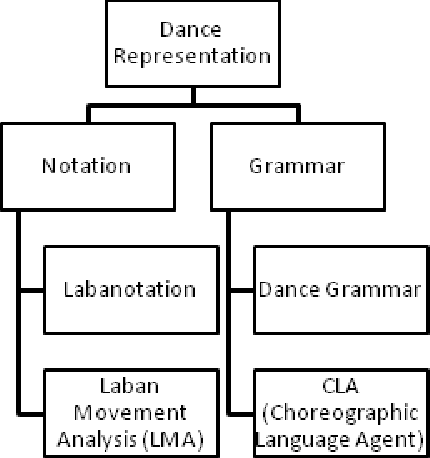
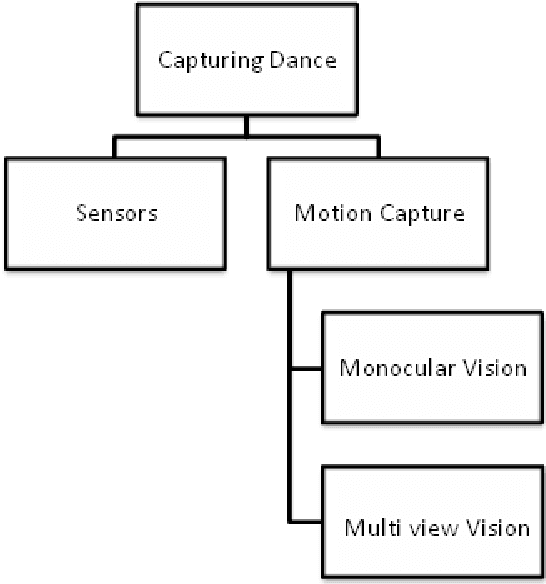
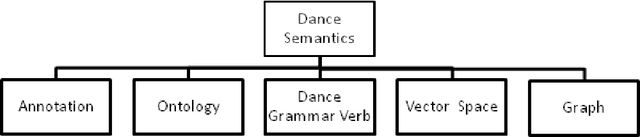
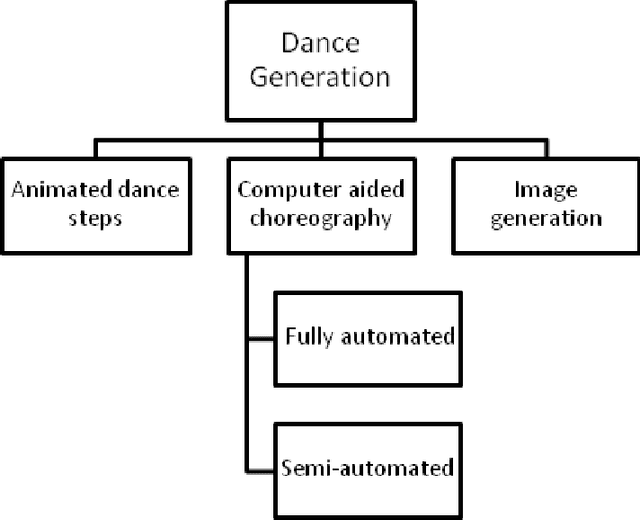
Abstract:Dance is an art and when technology meets this kind of art, it's a novel attempt in itself. Several researchers have attempted to automate several aspects of dance, right from dance notation to choreography. Furthermore, we have encountered several applications of dance automation like e-learning, heritage preservation, etc. Despite several attempts by researchers for more than two decades in various styles of dance all round the world, we found a review paper that portrays the research status in this area dating to 1990 \cite{politis1990computers}. Hence, we decide to come up with a comprehensive review article that showcases several aspects of dance automation. This paper is an attempt to review research work reported in the literature, categorize and group all research work completed so far in the field of automating dance. We have explicitly identified six major categories corresponding to the use of computers in dance automation namely dance representation, dance capturing, dance semantics, dance generation, dance processing approaches and applications of dance automation systems. We classified several research papers under these categories according to their research approach and functionality. With the help of proposed categories and subcategories one can easily determine the state of research and the new avenues left for exploration in the field of dance automation.
A Review of Network Traffic Analysis and Prediction Techniques
Jul 27, 2015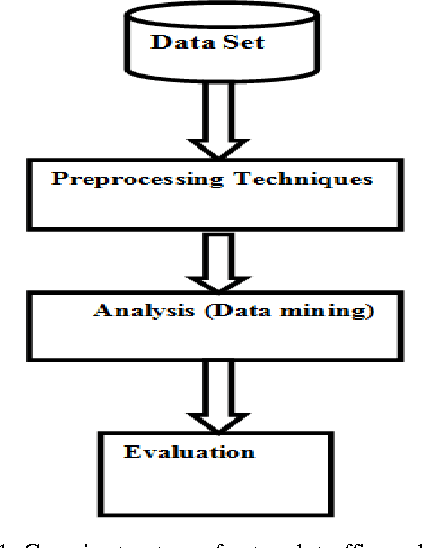
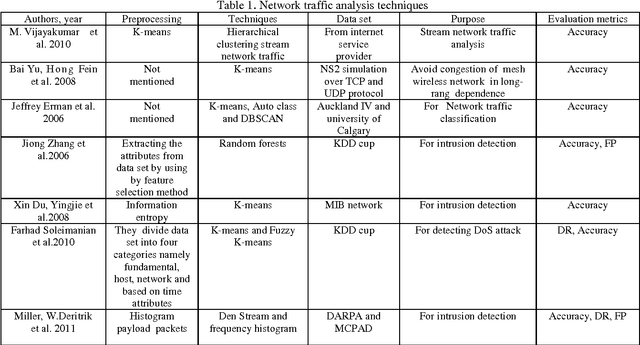
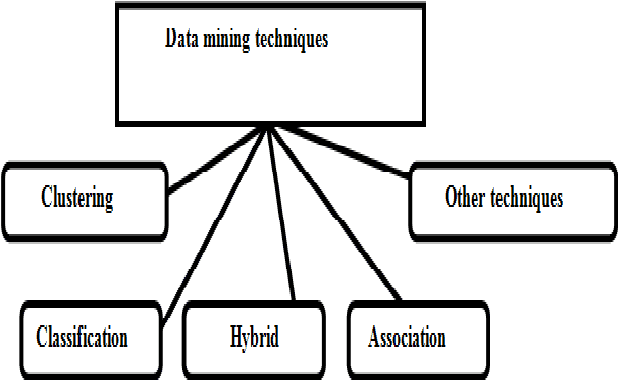
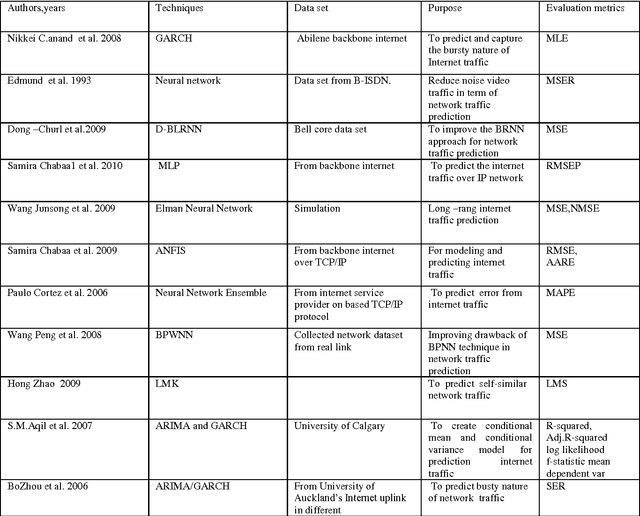
Abstract:Analysis and prediction of network traffic has applications in wide comprehensive set of areas and has newly attracted significant number of studies. Different kinds of experiments are conducted and summarized to identify various problems in existing computer network applications. Network traffic analysis and prediction is a proactive approach to ensure secure, reliable and qualitative network communication. Various techniques are proposed and experimented for analyzing network traffic including neural network based techniques to data mining techniques. Similarly, various Linear and non-linear models are proposed for network traffic prediction. Several interesting combinations of network analysis and prediction techniques are implemented to attain efficient and effective results. This paper presents a survey on various such network analysis and traffic prediction techniques. The uniqueness and rules of previous studies are investigated. Moreover, various accomplished areas of analysis and prediction of network traffic have been summed.
Automated Matchmaking to Improve Accuracy of Applicant Selection for University Education System
Jul 09, 2015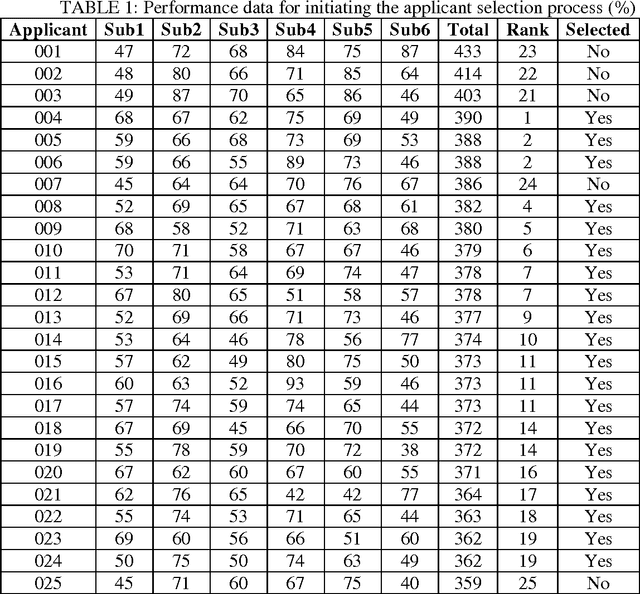
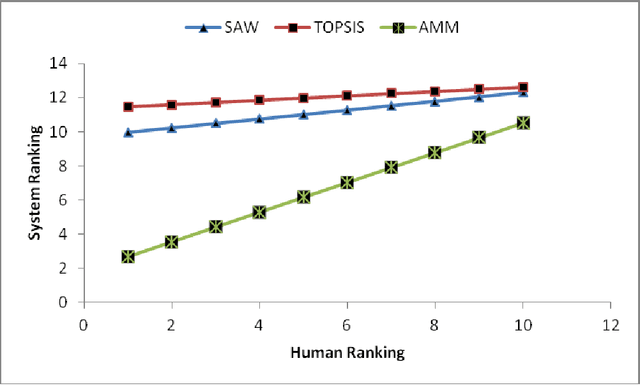
Abstract:The accurate applicant selection for university education is imperative to ensure fairness and optimal use of institutional resources. Although various approaches are operational in tertiary educational institutions for selecting applicants, a novel method of automated matchmaking is explored in the current study. The method functions by matching a prospective students skills profile to a programmes requisites profile. Empirical comparisons of the results, calculated by automated matchmaking and two other selection methods, show matchmaking to be a viable alternative for accurate selection of applicants. Matchmaking offers a unique advantage that it neither requires data from other applicants nor compares applicants with each other. Instead, it emphasises norms that define admissibility to a programme. We have proposed the use of technology to minimize the gap between students aspirations, skill sets and course requirements. It is a solution to minimize the number of students who get frustrated because of mismatched course selection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge