Manfred Schmidt-Schauß
Nominal Unification and Matching of Higher Order Expressions with Recursive Let
Feb 16, 2021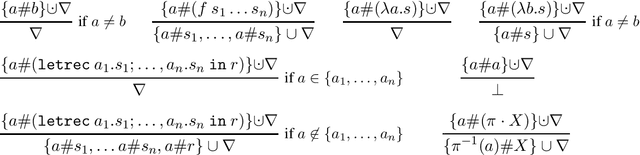
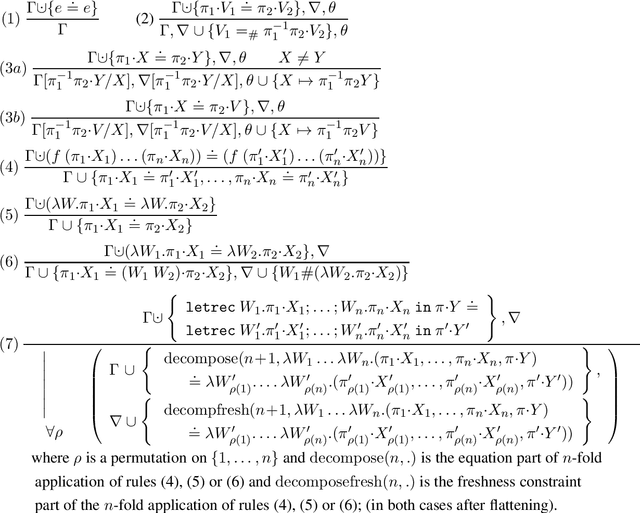

Abstract:A sound and complete algorithm for nominal unification of higher-order expressions with a recursive let is described, and shown to run in nondeterministic polynomial time. We also explore specializations like nominal letrec-matching for expressions, for DAGs, and for garbage-free expressions and determine their complexity. Finally, we also provide a nominal unification algorithm for higher-order expressions with recursive let and atom-variables, where we show that it also runs in nondeterministic polynomial time.
A Lambda-Calculus with letrec, case, constructors and non-determinism
Nov 06, 2000
Abstract:A non-deterministic call-by-need lambda-calculus \calc with case, constructors, letrec and a (non-deterministic) erratic choice, based on rewriting rules is investigated. A standard reduction is defined as a variant of left-most outermost reduction. The semantics is defined by contextual equivalence of expressions instead of using $\alpha\beta(\eta)$-equivalence. It is shown that several program transformations are correct, for example all (deterministic) rules of the calculus, and in addition the rules for garbage collection, removing indirections and unique copy. This shows that the combination of a context lemma and a meta-rewriting on reductions using complete sets of commuting (forking, resp.) diagrams is a useful and successful method for providing a semantics of a functional programming language and proving correctness of program transformations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge