Manas Bundele
AlerTiger: Deep Learning for AI Model Health Monitoring at LinkedIn
Jun 03, 2023Abstract:Data-driven companies use AI models extensively to develop products and intelligent business solutions, making the health of these models crucial for business success. Model monitoring and alerting in industries pose unique challenges, including a lack of clear model health metrics definition, label sparsity, and fast model iterations that result in short-lived models and features. As a product, there are also requirements for scalability, generalizability, and explainability. To tackle these challenges, we propose AlerTiger, a deep-learning-based MLOps model monitoring system that helps AI teams across the company monitor their AI models' health by detecting anomalies in models' input features and output score over time. The system consists of four major steps: model statistics generation, deep-learning-based anomaly detection, anomaly post-processing, and user alerting. Our solution generates three categories of statistics to indicate AI model health, offers a two-stage deep anomaly detection solution to address label sparsity and attain the generalizability of monitoring new models, and provides holistic reports for actionable alerts. This approach has been deployed to most of LinkedIn's production AI models for over a year and has identified several model issues that later led to significant business metric gains after fixing.
An Interactive Medical Image Segmentation Framework Using Iterative Refinement
Jun 05, 2016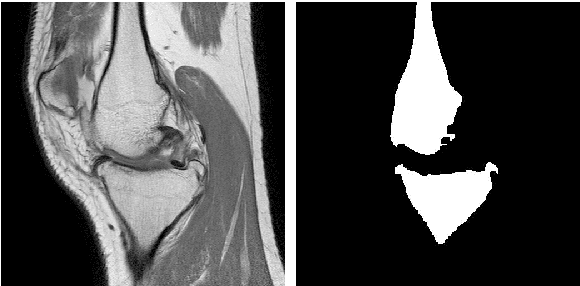


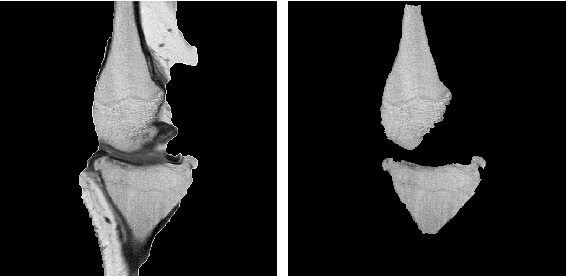
Abstract:Image segmentation is often performed on medical images for identifying diseases in clinical evaluation. Hence it has become one of the major research areas. Conventional image segmentation techniques are unable to provide satisfactory segmentation results for medical images as they contain irregularities. They need to be pre-processed before segmentation. In order to obtain the most suitable method for medical image segmentation, we propose a two stage algorithm. The first stage automatically generates a binary marker image of the region of interest using mathematical morphology. This marker serves as the mask image for the second stage which uses GrabCut on the input image thus resulting in an efficient segmented result. The obtained result can be further refined by user interaction which can be done using the Graphical User Interface (GUI). Experimental results show that the proposed method is accurate and provides satisfactory segmentation results with minimum user interaction on medical as well as natural images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge