Mahmoud Melkemi
SuperpixelGridCut, SuperpixelGridMean and SuperpixelGridMix Data Augmentation
Apr 11, 2022
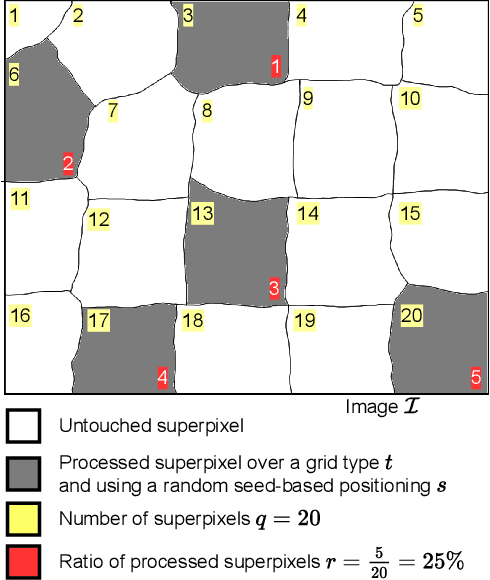
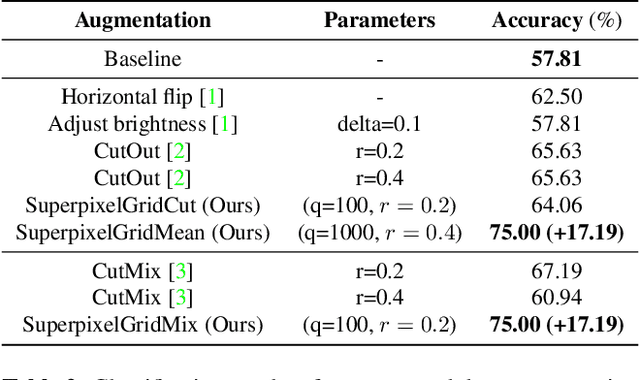
Abstract:A novel approach of data augmentation based on irregular superpixel decomposition is proposed. This approach called SuperpixelGridMasks permits to extend original image datasets that are required by training stages of machine learning-related analysis architectures towards increasing their performances. Three variants named SuperpixelGridCut, SuperpixelGridMean and SuperpixelGridMix are presented. These grid-based methods produce a new style of image transformations using the dropping and fusing of information. Extensive experiments using various image classification models and datasets show that baseline performances can be significantly outperformed using our methods. The comparative study also shows that our methods can overpass the performances of other data augmentations. Experimental results obtained over image recognition datasets of varied natures show the efficiency of these new methods. SuperpixelGridCut, SuperpixelGridMean and SuperpixelGridMix codes are publicly available at https://github.com/hammoudiproject/SuperpixelGridMasks
MaskedFace-Net -- A Dataset of Correctly/Incorrectly Masked Face Images in the Context of COVID-19
Aug 18, 2020
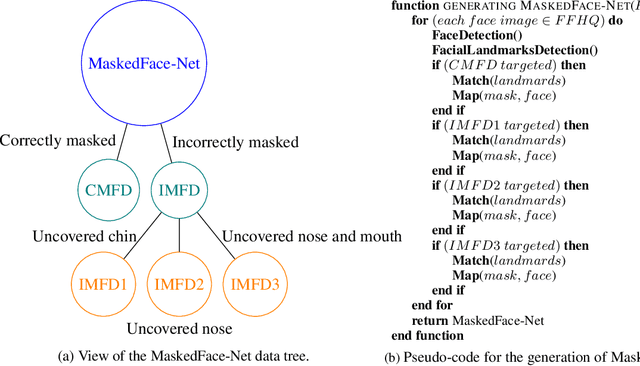
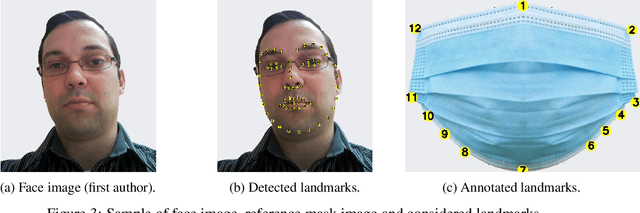
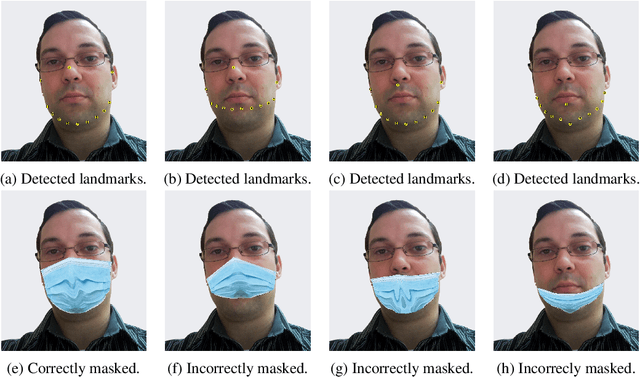
Abstract:The wearing of the face masks appears as a solution for limiting the spread of COVID-19. In this context, efficient recognition systems are expected for checking that people faces are masked in regulated areas. To perform this task, a large dataset of masked faces is necessary for training deep learning models towards detecting people wearing masks and those not wearing masks. Some large datasets of masked faces are available in the literature. However, at the moment, there are no available large dataset of masked face images that permits to check if detected masked faces are correctly worn or not. Indeed, many people are not correctly wearing their masks due to bad practices, bad behaviors or vulnerability of individuals (e.g., children, old people). For these reasons, several mask wearing campaigns intend to sensitize people about this problem and good practices. In this sense, this work proposes three types of masked face detection dataset; namely, the Correctly Masked Face Dataset (CMFD), the Incorrectly Masked Face Dataset (IMFD) and their combination for the global masked face detection (MaskedFace-Net). Realistic masked face datasets are proposed with a twofold objective: i) to detect people having their faces masked or not masked, ii) to detect faces having their masks correctly worn or incorrectly worn (e.g.; at airport portals or in crowds). To the best of our knowledge, no large dataset of masked faces provides such a granularity of classification towards permitting mask wearing analysis. Moreover, this work globally presents the applied mask-to-face deformable model for permitting the generation of other masked face images, notably with specific masks. Our datasets of masked face images (137,016 images) are available at https://github.com/cabani/MaskedFace-Net.
Deep Learning on Chest X-ray Images to Detect and Evaluate Pneumonia Cases at the Era of COVID-19
Apr 05, 2020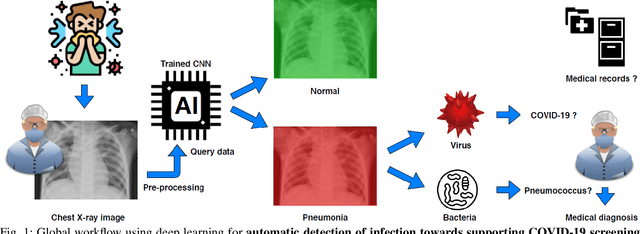
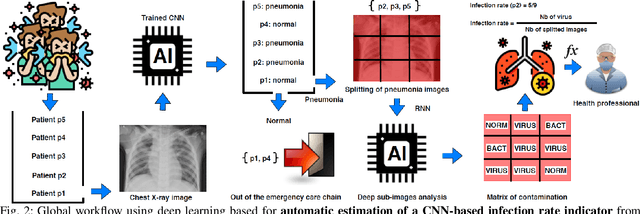
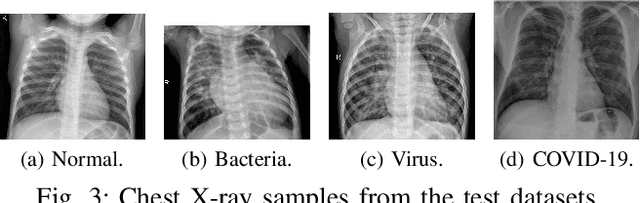
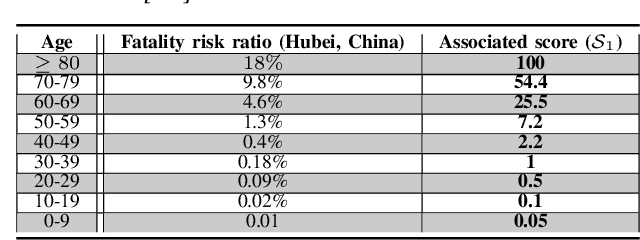
Abstract:Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease with first symptoms similar to the flu. COVID-19 appeared first in China and very quickly spreads to the rest of the world, causing then the 2019-20 coronavirus pandemic. In many cases, this disease causes pneumonia. Since pulmonary infections can be observed through radiography images, this paper investigates deep learning methods for automatically analyzing query chest X-ray images with the hope to bring precision tools to health professionals towards screening the COVID-19 and diagnosing confirmed patients. In this context, training datasets, deep learning architectures and analysis strategies have been experimented from publicly open sets of chest X-ray images. Tailored deep learning models are proposed to detect pneumonia infection cases, notably viral cases. It is assumed that viral pneumonia cases detected during an epidemic COVID-19 context have a high probability to presume COVID-19 infections. Moreover, easy-to-apply health indicators are proposed for estimating infection status and predicting patient status from the detected pneumonia cases. Experimental results show possibilities of training deep learning models over publicly open sets of chest X-ray images towards screening viral pneumonia. Chest X-ray test images of COVID-19 infected patients are successfully diagnosed through detection models retained for their performances. The efficiency of proposed health indicators is highlighted through simulated scenarios of patients presenting infections and health problems by combining real and synthetic health data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge