Mahdi Erfanian
Needle: A Generative-AI Powered Monte Carlo Method for Answering Complex Natural Language Queries on Multi-modal Data
Dec 01, 2024Abstract:Multi-modal data, such as image data sets, often miss the detailed descriptions that properly capture the rich information encoded in them. This makes answering complex natural language queries a major challenge in these domains. In particular, unlike the traditional nearest-neighbor search, where the tuples and the query are modeled as points in a data cube, the query and the tuples are of different natures, making the traditional query answering solutions not directly applicable for such settings. Existing literature addresses this challenge for image data through vector representations jointly trained on natural language and images. This technique, however, underperforms for complex queries due to various reasons. This paper takes a step towards addressing this challenge by introducing a Generative-AI (GenAI) powered Monte Carlo method that utilizes foundation models to generate synthetic samples that capture the complexity of the natural language query and transform it to the same space of the multi-modal data. Following this method, we develop a system for image data retrieval and propose practical solutions that enable leveraging future advancements in GenAI and vector representations for improving our system's performance. Our comprehensive experiments on various benchmark datasets verify that our system significantly outperforms state-of-the-art techniques.
Optimized Inference for 1.58-bit LLMs: A Time and Memory-Efficient Algorithm for Binary and Ternary Matrix Multiplication
Nov 10, 2024



Abstract:Despite their tremendous success and versatility, Large Language Models (LLMs) suffer from inference inefficiency while relying on advanced computational infrastructure. To address these challenges and make LLMs more accessible and cost-effective, in this paper, we propose algorithms to improve the inference time and memory efficiency of 1.58-bit LLMs with ternary weight matrices. Particularly focusing on matrix multiplication as the bottle-neck operation of inference, we observe that, once trained, the weight matrices of a model no longer change. This allows us to preprocess these matrices and create indices that help reduce the storage requirements by a logarithmic factor while enabling our efficient inference algorithms. Specifically, for a $n$ by $n$ weight matrix, our efficient algorithm guarantees a time complexity of $O(\frac{n^2}{\log n})$, a logarithmic factor improvement over the standard $O(n^2)$ vector-matrix multiplication. Besides theoretical analysis, we conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the practical efficiency of our algorithms. Our results confirm the superiority of the approach both with respect to time and memory, as we observed a reduction in inference time up to 29x and memory usage up to 6x.
FairEM360: A Suite for Responsible Entity Matching
Apr 10, 2024Abstract:Entity matching is one the earliest tasks that occur in the big data pipeline and is alarmingly exposed to unintentional biases that affect the quality of data. Identifying and mitigating the biases that exist in the data or are introduced by the matcher at this stage can contribute to promoting fairness in downstream tasks. This demonstration showcases FairEM360, a framework for 1) auditing the output of entity matchers across a wide range of fairness measures and paradigms, 2) providing potential explanations for the underlying reasons for unfairness, and 3) providing resolutions for the unfairness issues through an exploratory process with human-in-the-loop feedback, utilizing an ensemble of matchers. We aspire for FairEM360 to contribute to the prioritization of fairness as a key consideration in the evaluation of EM pipelines.
Chameleon: Foundation Models for Fairness-aware Multi-modal Data Augmentation to Enhance Coverage of Minorities
Feb 02, 2024
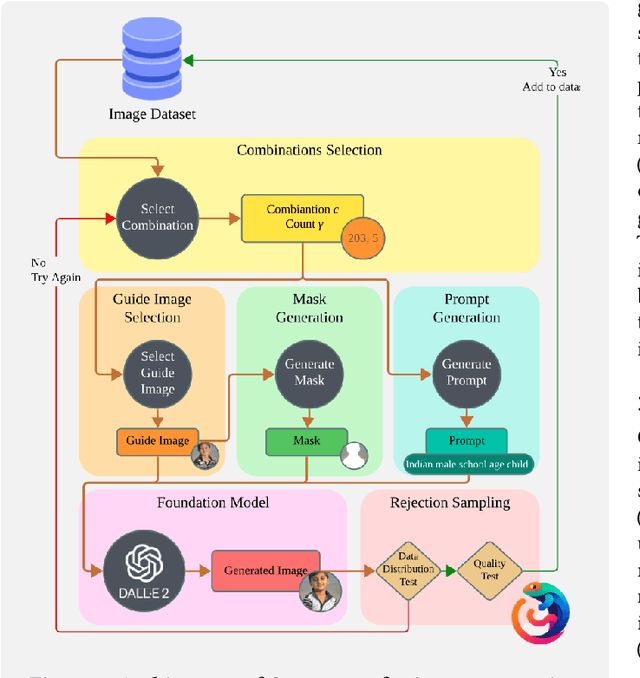

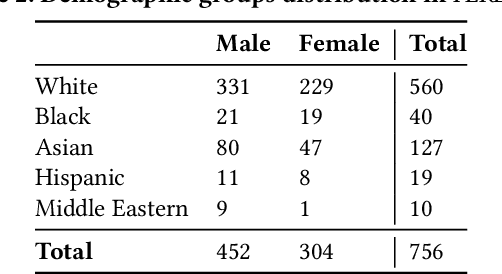
Abstract:The potential harms of the under-representation of minorities in training data, particularly in multi-modal settings, is a well-recognized concern. While there has been extensive effort in detecting such under-representation, resolution has remained a challenge. With recent advancements in generative AI, large language models and foundation models have emerged as versatile tools across various domains. In this paper, we propose Chameleon, a system that efficiently utilizes these tools to augment a data set with a minimal addition of synthetically generated tuples, in order to enhance the coverage of the under-represented groups. Our system follows a rejection sampling approach to ensure the generated tuples have a high quality and follow the underlying distribution. In order to minimize the rejection chance of the generated tuples, we propose multiple strategies for providing a guide for the foundation model. Our experiment results, in addition to confirming the efficiency of our proposed algorithms, illustrate the effectiveness of our approach, as the unfairness of the model in a downstream task significantly dropped after data repair using Chameleon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge