Fatemeh Nargesian
FairEM360: A Suite for Responsible Entity Matching
Apr 10, 2024Abstract:Entity matching is one the earliest tasks that occur in the big data pipeline and is alarmingly exposed to unintentional biases that affect the quality of data. Identifying and mitigating the biases that exist in the data or are introduced by the matcher at this stage can contribute to promoting fairness in downstream tasks. This demonstration showcases FairEM360, a framework for 1) auditing the output of entity matchers across a wide range of fairness measures and paradigms, 2) providing potential explanations for the underlying reasons for unfairness, and 3) providing resolutions for the unfairness issues through an exploratory process with human-in-the-loop feedback, utilizing an ensemble of matchers. We aspire for FairEM360 to contribute to the prioritization of fairness as a key consideration in the evaluation of EM pipelines.
Through the Fairness Lens: Experimental Analysis and Evaluation of Entity Matching
Jul 06, 2023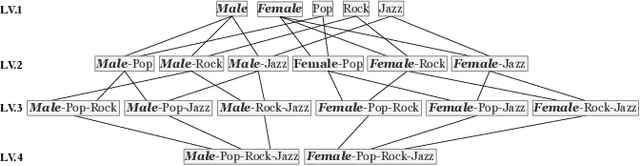
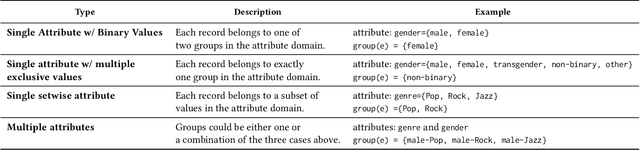
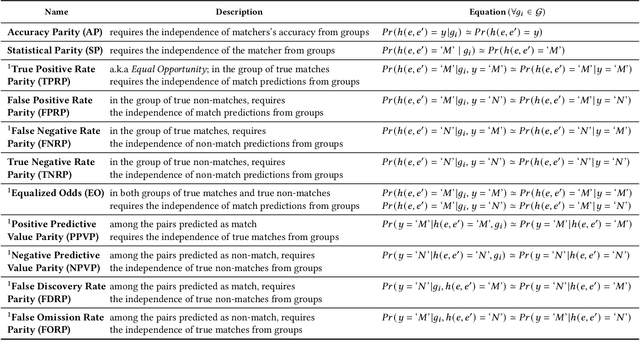
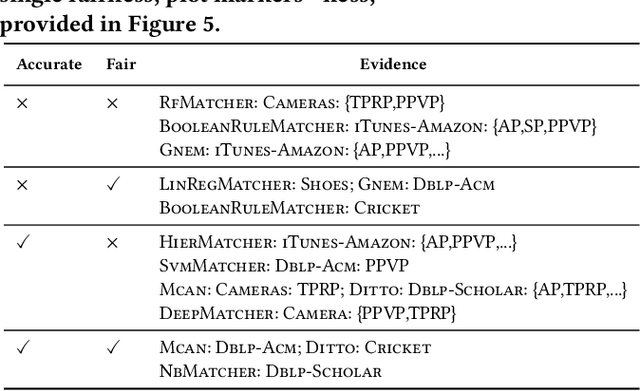
Abstract:Entity matching (EM) is a challenging problem studied by different communities for over half a century. Algorithmic fairness has also become a timely topic to address machine bias and its societal impacts. Despite extensive research on these two topics, little attention has been paid to the fairness of entity matching. Towards addressing this gap, we perform an extensive experimental evaluation of a variety of EM techniques in this paper. We generated two social datasets from publicly available datasets for the purpose of auditing EM through the lens of fairness. Our findings underscore potential unfairness under two common conditions in real-world societies: (i) when some demographic groups are overrepresented, and (ii) when names are more similar in some groups compared to others. Among our many findings, it is noteworthy to mention that while various fairness definitions are valuable for different settings, due to EM's class imbalance nature, measures such as positive predictive value parity and true positive rate parity are, in general, more capable of revealing EM unfairness.
Pylon: Semantic Table Union Search in Data Lakes
Jan 13, 2023Abstract:The large size and fast growth of data repositories, such as data lakes, has spurred the need for data discovery to help analysts find related data. The problem has become challenging as (i) a user typically does not know what datasets exist in an enormous data repository; and (ii) there is usually a lack of a unified data model to capture the interrelationships between heterogeneous datasets from disparate sources. In this work, we address one important class of discovery needs: finding union-able tables. The task is to find tables in a data lake that can be unioned with a given query table. The challenge is to recognize union-able columns even if they are represented differently. In this paper, we propose a data-driven learning approach: specifically, an unsupervised representation learning and embedding retrieval task. Our key idea is to exploit self-supervised contrastive learning to learn an embedding model that takes into account the indexing/search data structure and produces embeddings close by for columns with semantically similar values while pushing apart columns with semantically dissimilar values. We then find union-able tables based on similarities between their constituent columns in embedding space. On a real-world data lake, we demonstrate that our best-performing model achieves significant improvements in precision ($16\% \uparrow$), recall ($17\% \uparrow $), and query response time (7x faster) compared to the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge