Maggie Delano
Sex Trouble: Common pitfalls in incorporating sex/gender in medical machine learning and how to avoid them
Mar 15, 2022

Abstract:False assumptions about sex and gender are deeply embedded in the medical system, including that they are binary, static, and concordant. Machine learning researchers must understand the nature of these assumptions in order to avoid perpetuating them. In this perspectives piece, we identify three common mistakes that researchers make when dealing with sex/gender data: "sex confusion", the failure to identity what sex in a dataset does or doesn't mean; "sex obsession", the belief that sex, specifically sex assigned at birth, is the relevant variable for most applications; and "sex/gender slippage", the conflation of sex and gender even in contexts where only one or the other is known. We then discuss how these pitfalls show up in machine learning studies based on electronic health record data, which is commonly used for everything from retrospective analysis of patient outcomes to the development of algorithms to predict risk and administer care. Finally, we offer a series of recommendations about how machine learning researchers can produce both research and algorithms that more carefully engage with questions of sex/gender, better serving all patients, including transgender people.
Adversarial for Good? How the Adversarial ML Community's Values Impede Socially Beneficial Uses of Attacks
Jul 11, 2021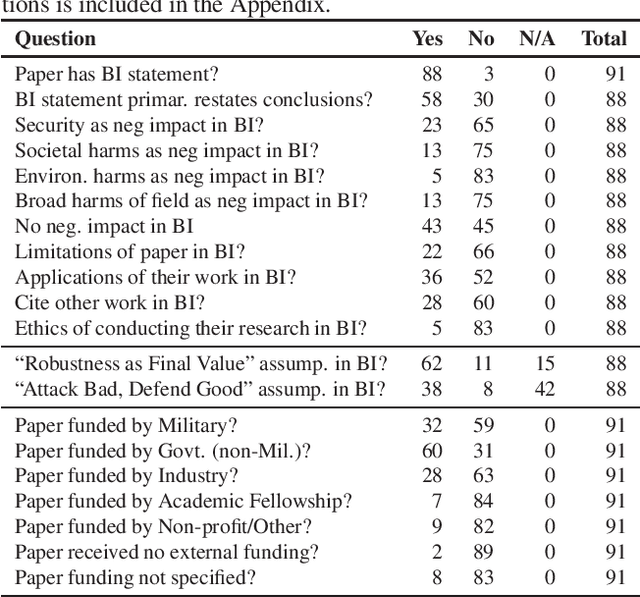
Abstract:Attacks from adversarial machine learning (ML) have the potential to be used "for good": they can be used to run counter to the existing power structures within ML, creating breathing space for those who would otherwise be the targets of surveillance and control. But most research on adversarial ML has not engaged in developing tools for resistance against ML systems. Why? In this paper, we review the broader impact statements that adversarial ML researchers wrote as part of their NeurIPS 2020 papers and assess the assumptions that authors have about the goals of their work. We also collect information about how authors view their work's impact more generally. We find that most adversarial ML researchers at NeurIPS hold two fundamental assumptions that will make it difficult for them to consider socially beneficial uses of attacks: (1) it is desirable to make systems robust, independent of context, and (2) attackers of systems are normatively bad and defenders of systems are normatively good. That is, despite their expressed and supposed neutrality, most adversarial ML researchers believe that the goal of their work is to secure systems, making it difficult to conceptualize and build tools for disrupting the status quo.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge