Maciej Eder
Scalable handwritten text recognition system for lexicographic sources of under-resourced languages and alphabets
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:The paper discusses an approach to decipher large collections of handwritten index cards of historical dictionaries. Our study provides a working solution that reads the cards, and links their lemmas to a searchable list of dictionary entries, for a large historical dictionary entitled the Dictionary of the 17th- and 18th-century Polish, which comprizes 2.8 million index cards. We apply a tailored handwritten text recognition (HTR) solution that involves (1) an optimized detection model; (2) a recognition model to decipher the handwritten content, designed as a spatial transformer network (STN) followed by convolutional neural network (RCNN) with a connectionist temporal classification layer (CTC), trained using a synthetic set of 500,000 generated Polish words of different length; (3) a post-processing step using constrained Word Beam Search (WBC): the predictions were matched against a list of dictionary entries known in advance. Our model achieved the accuracy of 0.881 on the word level, which outperforms the base RCNN model. Within this study we produced a set of 20,000 manually annotated index cards that can be used for future benchmarks and transfer learning HTR applications.
From stage to page: language independent bootstrap measures of distinctiveness in fictional speech
Jan 13, 2023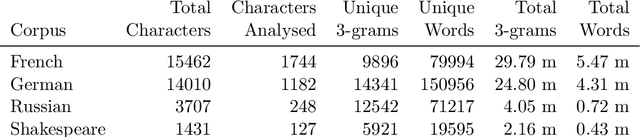
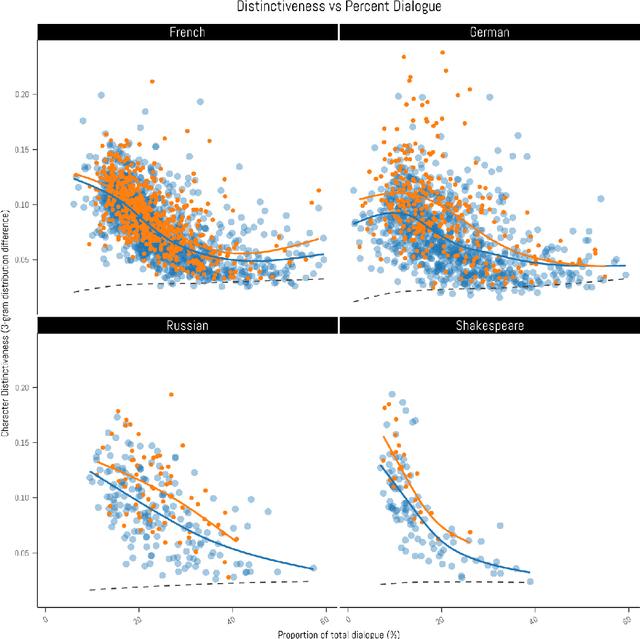
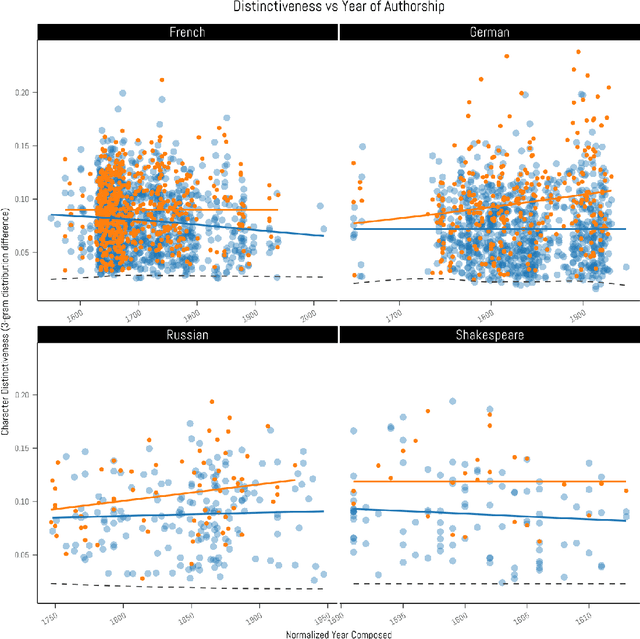
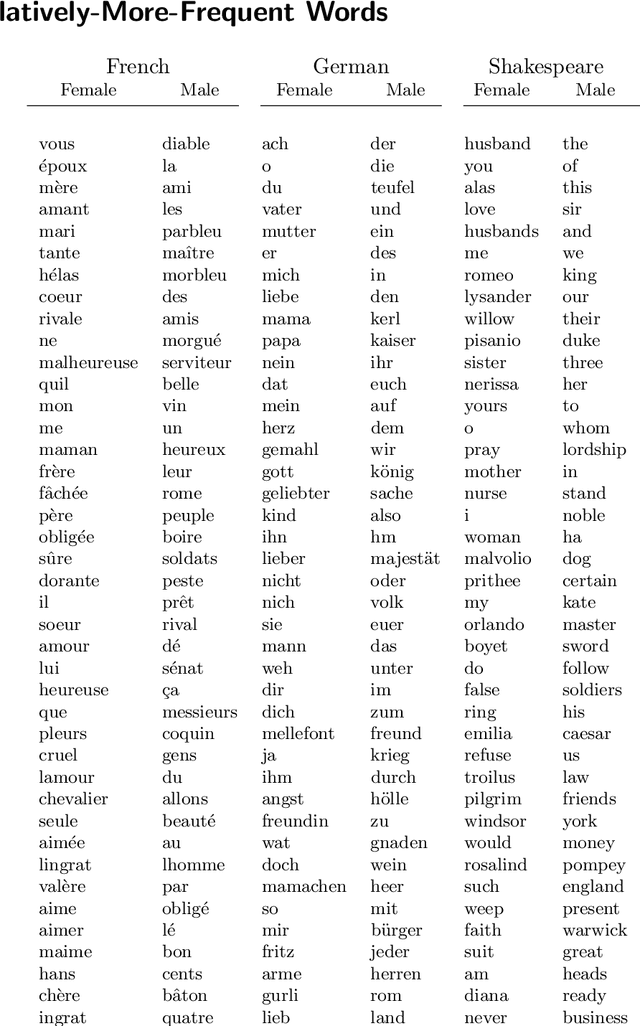
Abstract:Stylometry is mostly applied to authorial style. Recently, researchers have begun investigating the style of characters, finding that the variation remains within authorial bounds. We address the stylistic distinctiveness of characters in drama. Our primary contribution is methodological; we introduce and evaluate two non-parametric methods to produce a summary statistic for character distinctiveness that can be usefully applied and compared across languages and times. Our first method is based on bootstrap distances between 3-gram probability distributions, the second (reminiscent of 'unmasking' techniques) on word keyness curves. Both methods are validated and explored by applying them to a reasonably large corpus (a subset of DraCor): we analyse 3301 characters drawn from 2324 works, covering five centuries and four languages (French, German, Russian, and the works of Shakespeare). Both methods appear useful; the 3-gram method is statistically more powerful but the word keyness method offers rich interpretability. Both methods are able to capture phonological differences such as accent or dialect, as well as broad differences in topic and lexical richness. Based on exploratory analysis, we find that smaller characters tend to be more distinctive, and that women are cross-linguistically more distinctive than men, with this latter finding carefully interrogated using multiple regression. This greater distinctiveness stems from a historical tendency for female characters to be restricted to an 'internal narrative domain' covering mainly direct discourse and family/romantic themes. It is hoped that direct, comparable statistical measures will form a basis for more sophisticated future studies, and advances in theory.
Boosting word frequencies in authorship attribution
Nov 02, 2022Abstract:In this paper, I introduce a simple method of computing relative word frequencies for authorship attribution and similar stylometric tasks. Rather than computing relative frequencies as the number of occurrences of a given word divided by the total number of tokens in a text, I argue that a more efficient normalization factor is the total number of relevant tokens only. The notion of relevant words includes synonyms and, usually, a few dozen other words in some ways semantically similar to a word in question. To determine such a semantic background, one of word embedding models can be used. The proposed method outperforms classical most-frequent-word approaches substantially, usually by a few percentage points depending on the input settings.
Stylistic Fingerprints, POS-tags and Inflected Languages: A Case Study in Polish
Jun 05, 2022



Abstract:In stylometric investigations, frequencies of the most frequent words (MFWs) and character n-grams outperform other style-markers, even if their performance varies significantly across languages. In inflected languages, word endings play a prominent role, and hence different word forms cannot be recognized using generic text tokenization. Countless inflected word forms make frequencies sparse, making most statistical procedures complicated. Presumably, applying one of the NLP techniques, such as lemmatization and/or parsing, might increase the performance of classification. The aim of this paper is to examine the usefulness of grammatical features (as assessed via POS-tag n-grams) and lemmatized forms in recognizing authorial profiles, in order to address the underlying issue of the degree of freedom of choice within lexis and grammar. Using a corpus of Polish novels, we performed a series of supervised authorship attribution benchmarks, in order to compare the classification accuracy for different types of lexical and syntactic style-markers. Even if the performance of POS-tags as well as lemmatized forms was notoriously worse than that of lexical markers, the difference was not substantial and never exceeded ca. 15%.
Modeling the dynamics of language change: logistic regression, Piotrowski's law, and a handful of examples in Polish
Apr 28, 2021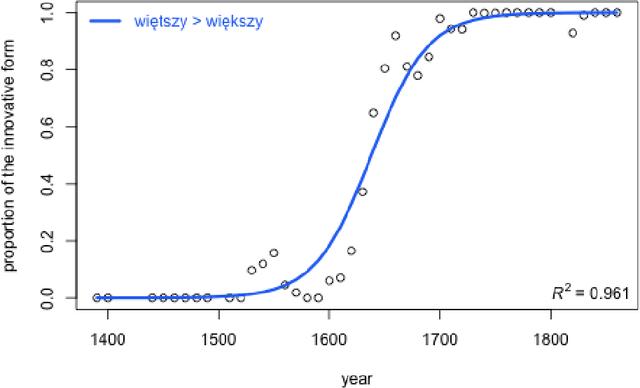
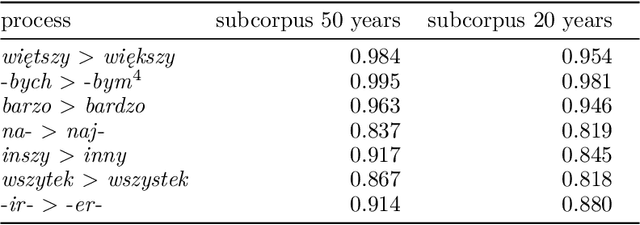
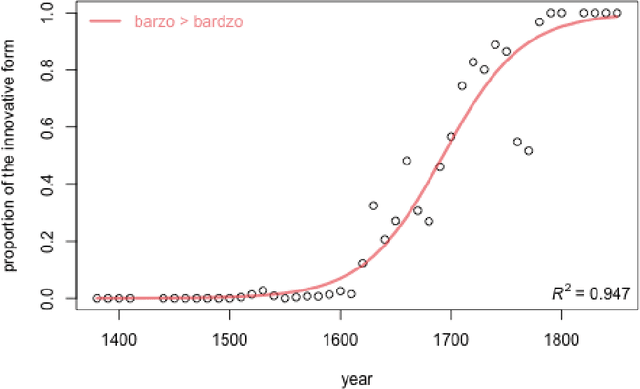
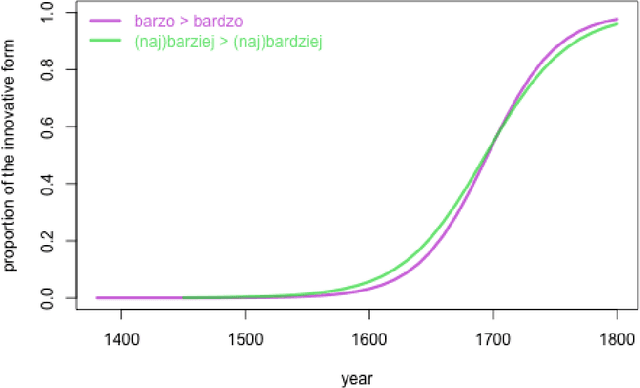
Abstract:The study discusses modeling diachronic processes by logistic regression. Such an approach was suggested by Raimund Piotrowski (hence labelled as Piotrowski's law), even if actual linguistic evidence usually speaks against using the notion of a "law" in this context. In our study, we apply logistic regression models to 9 changes which occurred between 15th and 18th century in the Polish language. The attested course of the majority of these changes closely follow the expected values, which proves that the language change might indeed resemble a nonlinear phase change scenario. We also extend the original Piotrowski's approach by proposing polynomial logistic regression for these cases which can hardly be described by its standard version. Also, we propose to consider individual language change cases jointly, in order to inspect their possible collinearity or, more likely, their different dynamics in the function of time. Last but not least, we evaluate our results by testing the influence of the subcorpus size on the model's goodness-of-fit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge