Lukas König
Single-Agent Actor Critic for Decentralized Cooperative Driving
Mar 18, 2024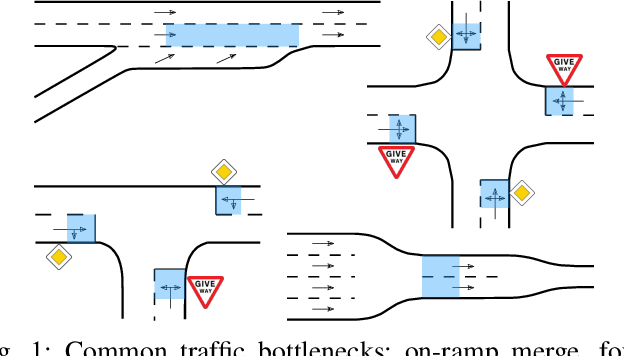
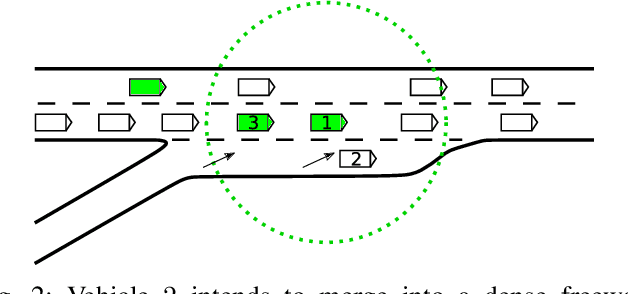
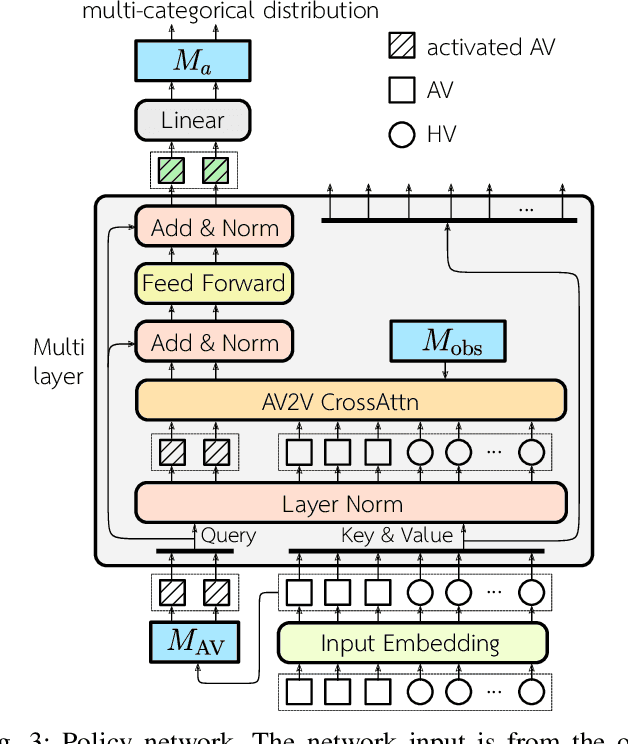
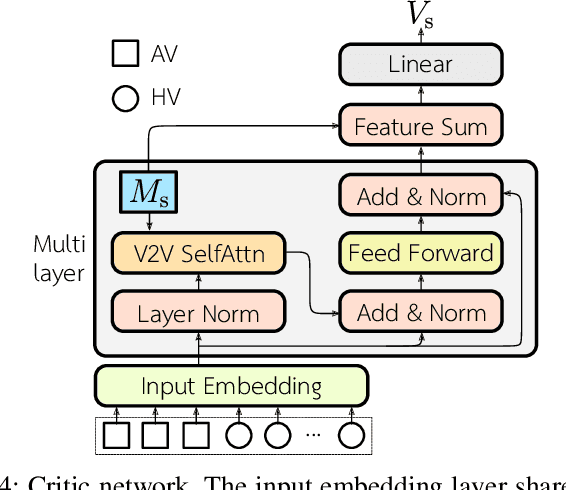
Abstract:Active traffic management incorporating autonomous vehicles (AVs) promises a future with diminished congestion and enhanced traffic flow. However, developing algorithms for real-world application requires addressing the challenges posed by continuous traffic flow and partial observability. To bridge this gap and advance the field of active traffic management towards greater decentralization, we introduce a novel asymmetric actor-critic model aimed at learning decentralized cooperative driving policies for autonomous vehicles using single-agent reinforcement learning. Our approach employs attention neural networks with masking to handle the dynamic nature of real-world traffic flow and partial observability. Through extensive evaluations against baseline controllers across various traffic scenarios, our model shows great potential for improving traffic flow at diverse bottleneck locations within the road system. Additionally, we explore the challenge associated with the conservative driving behaviors of autonomous vehicles that adhere strictly to traffic regulations. The experiment results illustrate that our proposed cooperative policy can mitigate potential traffic slowdowns without compromising safety.
Building a Knowledge Graph of Distributed Ledger Technologies
Mar 29, 2023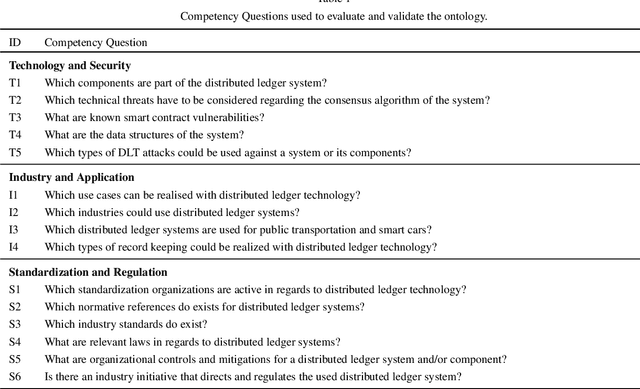
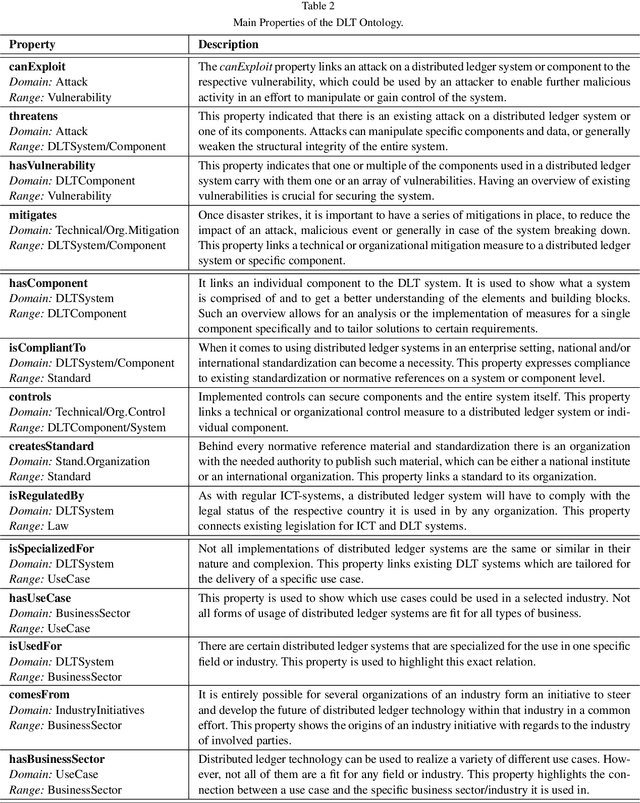
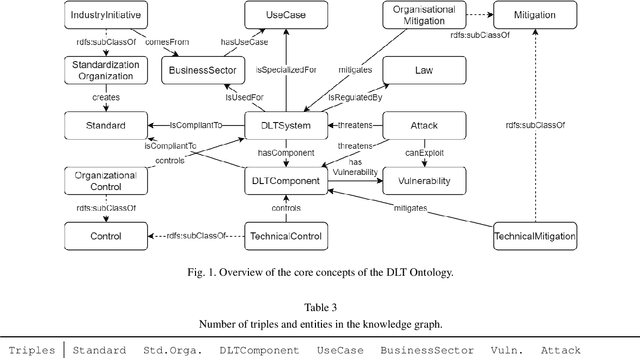
Abstract:Distributed ledger systems have become more prominent and successful in recent years, with a focus on blockchains and cryptocurrency. This has led to various misunderstandings about both the technology itself and its capabilities, as in many cases blockchain and cryptocurrency is used synonymously and other applications are often overlooked. Therefore, as a whole, the view of distributed ledger technology beyond blockchains and cryptocurrencies is very limited. Existing vocabularies and ontologies often focus on single aspects of the technology, or in some cases even just on one product. This potentially leads to other types of distributed ledgers and their possible use cases being neglected. In this paper, we present a knowledge graph and an ontology for distributed ledger technologies, which includes security considerations to model aspects such as threats and vulnerabilities, application domains, as well as relevant standards and regulations. Such a knowledge graph improves the overall understanding of distributed ledgers, reveals their strengths, and supports the work of security personnel, i.e. analysts and system architects. We discuss potential uses and follow semantic web best practices to evaluate and publish the ontology and knowledge graph.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge