Luka Grbčić
Reconstruction and analysis of negatively buoyant jets with interpretable machine learning
Nov 10, 2022Abstract:In this paper, negatively inclined buoyant jets, which appear during the discharge of wastewater from processes such as desalination, are observed. To minimize harmful effects and assess environmental impact, a detailed numerical investigation is necessary. The selection of appropriate geometry and working conditions for minimizing such effects often requires numerous experiments and numerical simulations. For this reason, the application of machine learning models is proposed. Several models including Support Vector Regression, Artificial Neural Networks, Random Forests, XGBoost, CatBoost and LightGBM were trained. The dataset was built with numerous OpenFOAM simulations, which were validated by experimental data from previous research. The best prediction was obtained by Artificial Neural Network with an average of R2 0.98 and RMSE 0.28. In order to understand the working of the machine learning model and the influence of all parameters on the geometrical characteristics of inclined buoyant jets, the SHAP feature interpretation method was used.
Machine learning based surrogate models for microchannel heat sink optimization
Aug 20, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, microchannel designs with secondary channels and with ribs are investigated using computational fluid dynamics and are coupled with a multi-objective optimization algorithm to determine and propose optimal solutions based on observed thermal resistance and pumping power. A workflow that combines Latin hypercube sampling, machine learning-based surrogate modeling and multi-objective optimization is proposed. Random forests, gradient boosting algorithms and neural networks were considered during the search for the best surrogate. We demonstrated that tuned neural networks can make accurate predictions and be used to create an acceptable surrogate model. Optimized solutions show a negligible difference in overall performance when compared to the conventional optimization approach. Additionally, solutions are calculated in one-fifth of the original time. Generated designs attain temperatures that are lower by more than 10% under the same pressure limits as a convectional microchannel design. When limited by temperature, pressure drops are reduced by more than 25%. Finally, the influence of each design variable on the thermal resistance and pumping power was investigated by employing the SHapley Additive exPlanations technique. Overall, we have demonstrated that the proposed framework has merit and can be used as a viable methodology in microchannel heat sink design optimization.
Multi-UAV trajectory planning for 3D visual inspection of complex structures
Apr 21, 2022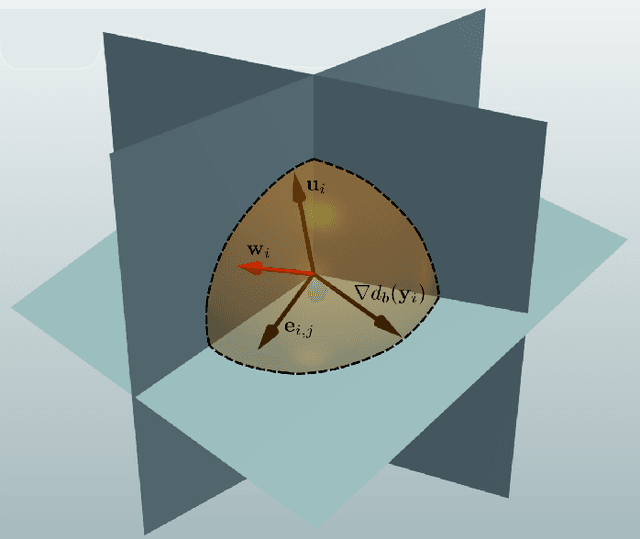
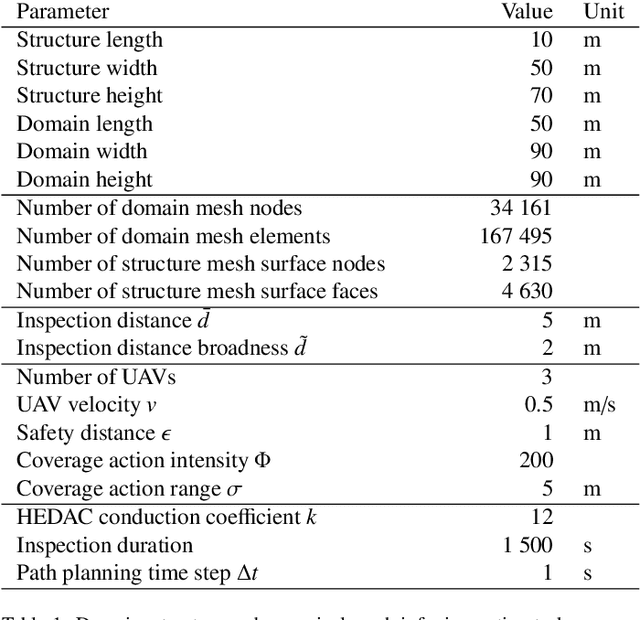
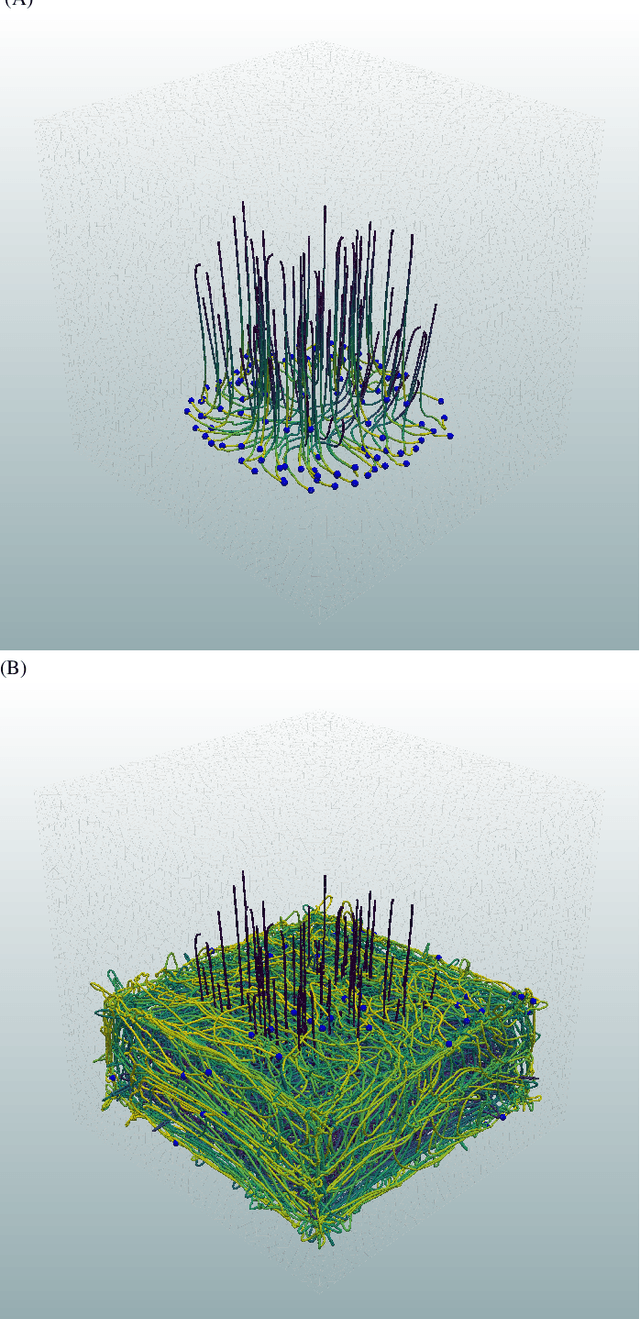
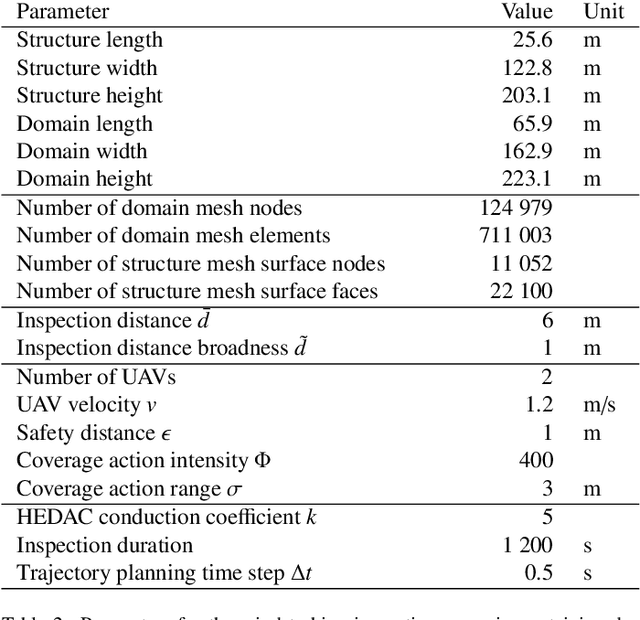
Abstract:This paper presents a new trajectory planning algorithm for 3D autonomous UAV volume coverage and visual inspection. The algorithm is an extension of a state-of-the-art Heat Equation Driven Area Coverage (HEDAC) multi-agent area coverage algorithm for 3D domains. With a given target exploration density field, the algorithm designs a potential field and directs UAVs to the regions of higher potential, i.e., higher values of remaining density. Collisions between the agents and agents with domain boundaries are prevented by implementing the distance field and correcting the agent's directional vector when the distance threshold is reached. A unit cube test case is considered to evaluate this trajectory planning strategy for volume coverage. For visual inspection applications, the algorithm is supplemented with camera direction control. A field containing the nearest distance from any point in the domain to the structure surface is designed. The gradient of this field is calculated to obtain the camera orientation throughout the trajectory. Three different test cases of varying complexities are considered to validate the proposed method for visual inspection. The simplest scenario is a synthetic portal-like structure inspected using three UAVs. The other two inspection scenarios are based on realistic structures where UAVs are commonly utilized: a wind turbine and a bridge. When deployed to a wind turbine inspection, two simulated UAVs traversing smooth spiral trajectories have successfully explored the entire turbine structure while cameras are directed to the curved surfaces of the turbine's blades. In the bridge test case an efficacious visual inspection of a complex structure is demonstrated by employing a single UAV and five UAVs. The proposed methodology is successful, flexible and applicable in real-world UAV inspection tasks.
Predictive modeling of microbiological seawater quality classification in karst region using cascade model
Feb 11, 2022Abstract:In this paper, an in-depth analysis of Escherichia coli seawater measurements during the bathing season in the city of Rijeka, Croatia was conducted. Submerged sources of groundwater were observed at several measurement locations which could be the cause for increased E. coli values. This specificity of karst terrain is usually not considered during the monitoring process, thus a novel measurement methodology is proposed. A cascade machine learning model is used to predict coastal water quality based on meteorological data, which improves the level of accuracy due to data imbalance resulting from rare occurrences of measurements with reduced water quality. Currently, the cascade model is employed as a filter method, where measurements not classified as excellent quality need to be further analyzed. However, with improvements proposed in the paper, the cascade model could be ultimately used as a standalone method.
Coastal water quality prediction based on machine learning with feature interpretation and spatio-temporal analysis
Jul 09, 2021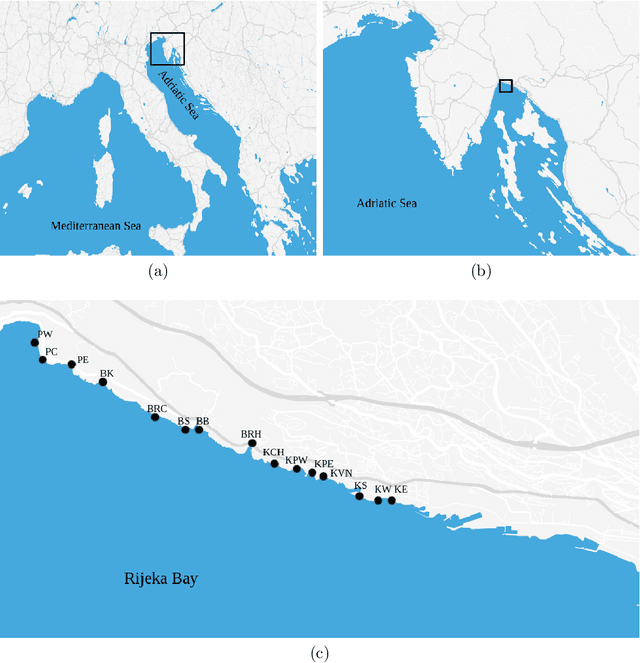
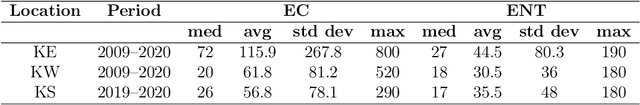
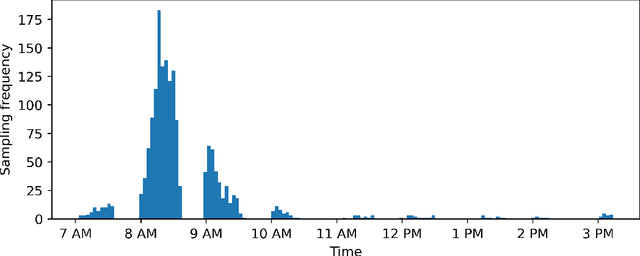
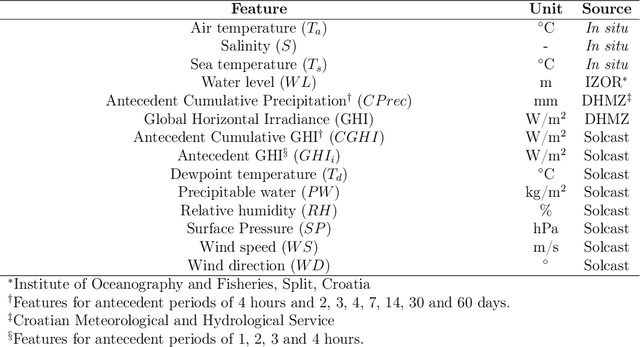
Abstract:Coastal water quality management is a public health concern, as poor coastal water quality can harbor pathogens that are dangerous to human health. Tourism-oriented countries need to actively monitor the condition of coastal water at tourist popular sites during the summer season. In this study, routine monitoring data of $Escherichia\ Coli$ and enterococci across 15 public beaches in the city of Rijeka, Croatia, were used to build machine learning models for predicting their levels based on environmental parameters as well as to investigate their relationships with environmental stressors. Gradient Boosting (Catboost, Xgboost), Random Forests, Support Vector Regression and Artificial Neural Networks were trained with measurements from all sampling sites and used to predict $E.\ Coli$ and enterococci values based on environmental features. The evaluation of stability and generalizability with 10-fold cross validation analysis of the machine learning models, showed that the Catboost algorithm performed best with R$^2$ values of 0.71 and 0.68 for predicting $E.\ Coli$ and enterococci, respectively, compared to other evaluated ML algorithms including Xgboost, Random Forests, Support Vector Regression and Artificial Neural Networks. We also use the SHapley Additive exPlanations technique to identify and interpret which features have the most predictive power. The results show that site salinity measured is the most important feature for forecasting both $E.\ Coli$ and enterococci levels. Finally, the spatial and temporal accuracy of both ML models were examined at sites with the lowest coastal water quality. The spatial $E. Coli$ and enterococci models achieved strong R$^2$ values of 0.85 and 0.83, while the temporal models achieved R$^2$ values of 0.74 and 0.67. The temporal model also achieved moderate R$^2$ values of 0.44 and 0.46 at a site with high coastal water quality.
Introducing languid particle dynamics to a selection of PSO variants
Jun 06, 2019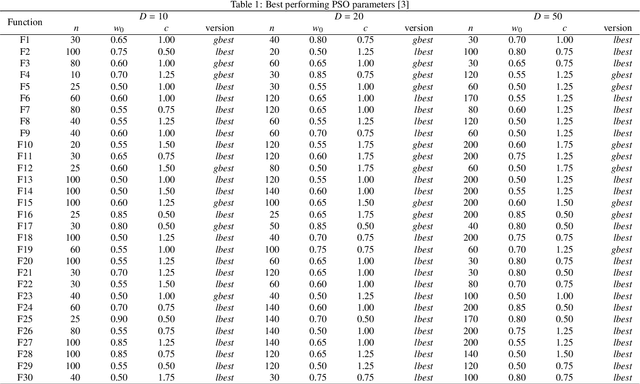
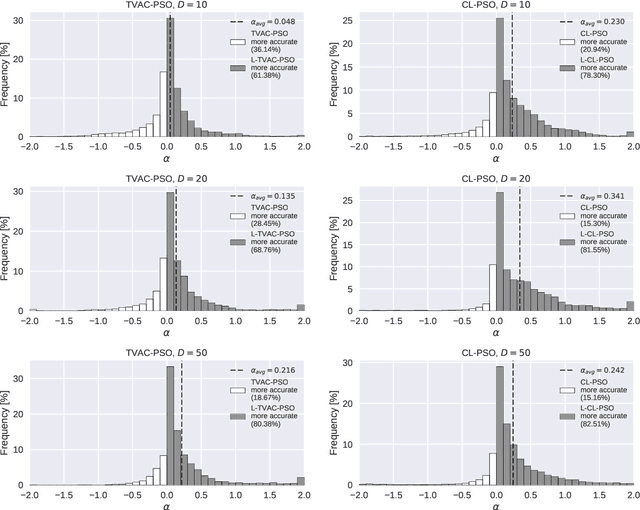
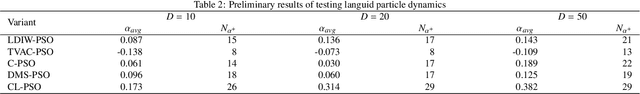
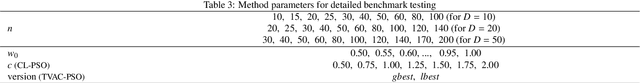
Abstract:Previous research showed that conditioning a PSO agent's movement based on its personal fitness improvement enhances the standard PSO method. In this article, languid particle dynamics (LPD) technique is used on five adequate and widely used PSO variants. Five unmodified PSO variants were tested against their LPD-implemented counterparts on three search space dimensionalities (10, 20, and 50 dimensions) and 30 test functions of the CEC 2014 benchmark test. In the preliminary phase of the testing four of the five tested PSO variants showed improvement in accuracy. The worst and best-achieving variants from preliminary test went through detailed investigation on 220 and 770 combinations of method parameters, where both variants showed overall gains in accuracy when enhanced with LPD. Finally, the results obtained with best achieving PSO parameters were subject to statistical analysis which showed that the two variants give statistically significant improvements in accuracy for 13-50% of the test functions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge