Luigi Tommaso Luppino
A robust and versatile deep learning model for prediction of the arterial input function in dynamic small animal $\left[^{18}\text{F}\right]$FDG PET imaging
Jul 03, 2025![Figure 1 for A robust and versatile deep learning model for prediction of the arterial input function in dynamic small animal $\left[^{18}\text{F}\right]$FDG PET imaging](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2Faeedac3751b9e214478a1237ed9043e09178057f%2F5-Figure1-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 2 for A robust and versatile deep learning model for prediction of the arterial input function in dynamic small animal $\left[^{18}\text{F}\right]$FDG PET imaging](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2Faeedac3751b9e214478a1237ed9043e09178057f%2F6-Figure2-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 3 for A robust and versatile deep learning model for prediction of the arterial input function in dynamic small animal $\left[^{18}\text{F}\right]$FDG PET imaging](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2Faeedac3751b9e214478a1237ed9043e09178057f%2F7-Figure3-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 4 for A robust and versatile deep learning model for prediction of the arterial input function in dynamic small animal $\left[^{18}\text{F}\right]$FDG PET imaging](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Ffigures.semanticscholar.org%2Faeedac3751b9e214478a1237ed9043e09178057f%2F9-Figure4-1.png&w=640&q=75)
Abstract:Dynamic positron emission tomography (PET) and kinetic modeling are pivotal in advancing tracer development research in small animal studies. Accurate kinetic modeling requires precise input function estimation, traditionally achieved via arterial blood sampling. However, arterial cannulation in small animals like mice, involves intricate, time-consuming, and terminal procedures, precluding longitudinal studies. This work proposes a non-invasive, fully convolutional deep learning-based approach (FC-DLIF) to predict input functions directly from PET imaging, potentially eliminating the need for blood sampling in dynamic small-animal PET. The proposed FC-DLIF model includes a spatial feature extractor acting on the volumetric time frames of the PET sequence, extracting spatial features. These are subsequently further processed in a temporal feature extractor that predicts the arterial input function. The proposed approach is trained and evaluated using images and arterial blood curves from [$^{18}$F]FDG data using cross validation. Further, the model applicability is evaluated on imaging data and arterial blood curves collected using two additional radiotracers ([$^{18}$F]FDOPA, and [$^{68}$Ga]PSMA). The model was further evaluated on data truncated and shifted in time, to simulate shorter, and shifted, PET scans. The proposed FC-DLIF model reliably predicts the arterial input function with respect to mean squared error and correlation. Furthermore, the FC-DLIF model is able to predict the arterial input function even from truncated and shifted samples. The model fails to predict the AIF from samples collected using different radiotracers, as these are not represented in the training data. Our deep learning-based input function offers a non-invasive and reliable alternative to arterial blood sampling, proving robust and flexible to temporal shifts and different scan durations.
Filling of incomplete sinograms from sparse PET detector configurations using a residual U-Net
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Long axial field-of-view PET scanners offer increased field-of-view and sensitivity compared to traditional PET scanners. However, a significant cost is associated with the densely packed photodetectors required for the extended-coverage systems, limiting clinical utilisation. To mitigate the cost limitations, alternative sparse system configurations have been proposed, allowing an extended field-of-view PET design with detector costs similar to a standard PET system, albeit at the expense of image quality. In this work, we propose a deep sinogram restoration network to fill in the missing sinogram data. Our method utilises a modified Residual U-Net, trained on clinical PET scans from a GE Signa PET/MR, simulating the removal of 50% of the detectors in a chessboard pattern (retaining only 25% of all lines of response). The model successfully recovers missing counts, with a mean absolute error below two events per pixel, outperforming 2D interpolation in both sinogram and reconstructed image domain. Notably, the predicted sinograms exhibit a smoothing effect, leading to reconstructed images lacking sharpness in finer details. Despite these limitations, the model demonstrates a substantial capacity for compensating for the undersampling caused by the sparse detector configuration. This proof-of-concept study suggests that sparse detector configurations, combined with deep learning techniques, offer a viable alternative to conventional PET scanner designs. This approach supports the development of cost-effective, total body PET scanners, allowing a significant step forward in medical imaging technology.
Postoperative glioblastoma segmentation: Development of a fully automated pipeline using deep convolutional neural networks and comparison with currently available models
Apr 17, 2024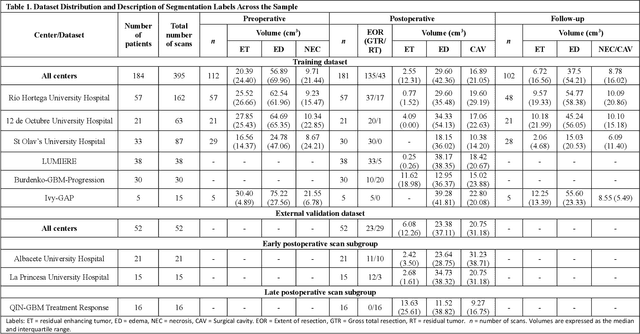
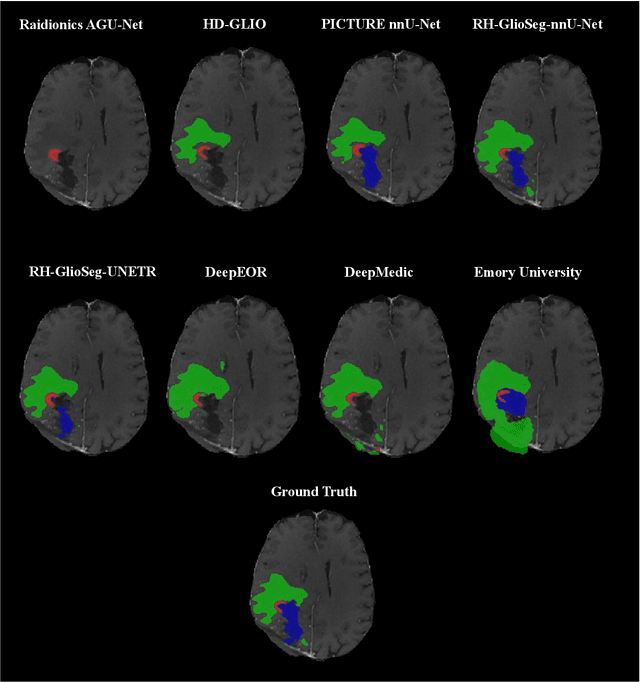
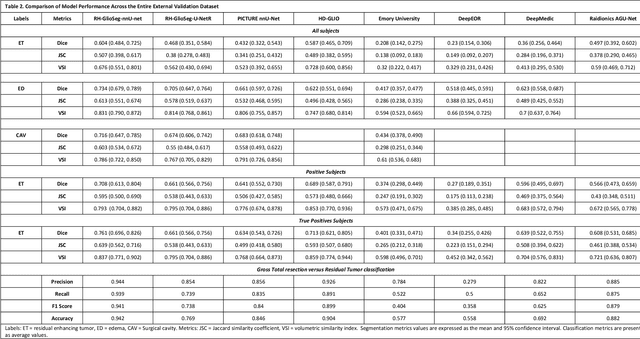
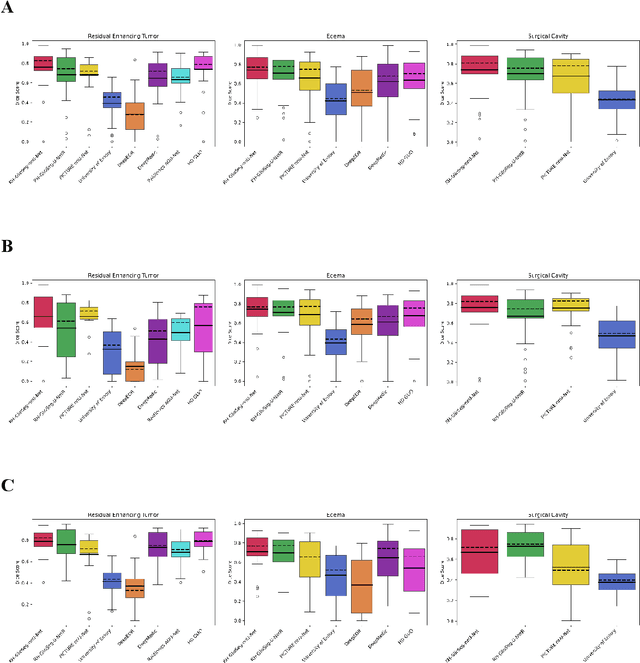
Abstract:Accurately assessing tumor removal is paramount in the management of glioblastoma. We developed a pipeline using MRI scans and neural networks to segment tumor subregions and the surgical cavity in postoperative images. Our model excels in accurately classifying the extent of resection, offering a valuable tool for clinicians in assessing treatment effectiveness.
Deep Image Translation with an Affinity-Based Change Prior for Unsupervised Multimodal Change Detection
Jan 13, 2020



Abstract:Image translation with convolutional neural networks has recently been used as an approach to multimodal change detection. Existing approaches train the networks by exploiting supervised information of the change areas, which, however, is not always available. A main challenge in the unsupervised problem setting is to avoid that change pixels affect the learning of the translation function. We propose two new network architectures trained with loss functions weighted by priors that reduce the impact of change pixels on the learning objective. The change prior is derived in an unsupervised fashion from relational pixel information captured by domain-specific affinity matrices. Specifically, we use the vertex degrees associated with an absolute affinity difference matrix and demonstrate their utility in combination with cycle consistency and adversarial training. The proposed neural networks are compared with state-of-the-art algorithms. Experiments conducted on two real datasets show the effectiveness of our methodology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge