Lucas Jarnac
KGPrune: a Web Application to Extract Subgraphs of Interest from Wikidata with Analogical Pruning
Aug 26, 2024Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have become ubiquitous publicly available knowledge sources, and are nowadays covering an ever increasing array of domains. However, not all knowledge represented is useful or pertaining when considering a new application or specific task. Also, due to their increasing size, handling large KGs in their entirety entails scalability issues. These two aspects asks for efficient methods to extract subgraphs of interest from existing KGs. To this aim, we introduce KGPrune, a Web Application that, given seed entities of interest and properties to traverse, extracts their neighboring subgraphs from Wikidata. To avoid topical drift, KGPrune relies on a frugal pruning algorithm based on analogical reasoning to only keep relevant neighbors while pruning irrelevant ones. The interest of KGPrune is illustrated by two concrete applications, namely, bootstrapping an enterprise KG and extracting knowledge related to looted artworks.
Uncertainty Management in the Construction of Knowledge Graphs: a Survey
May 27, 2024
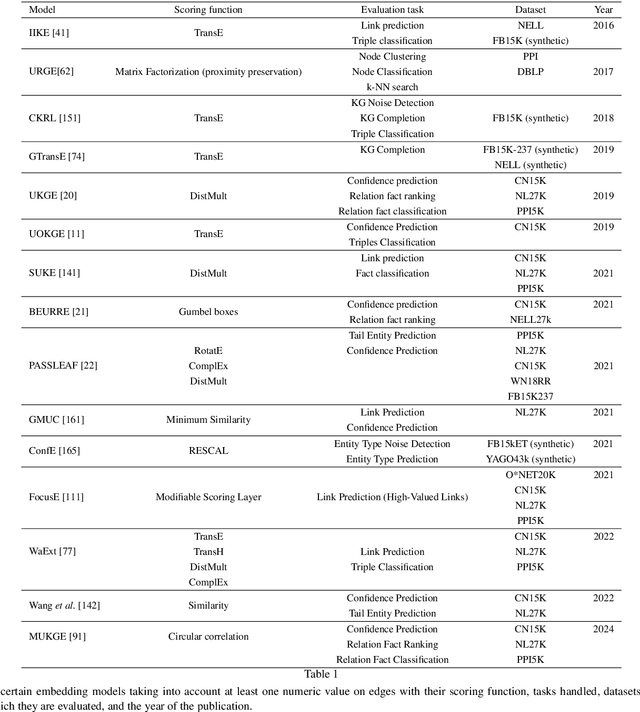
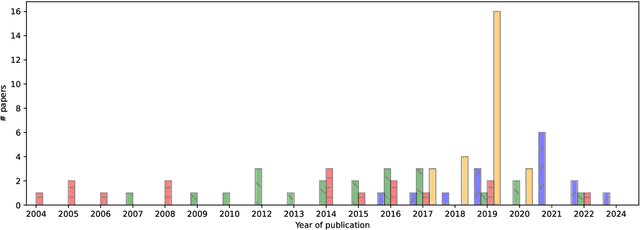
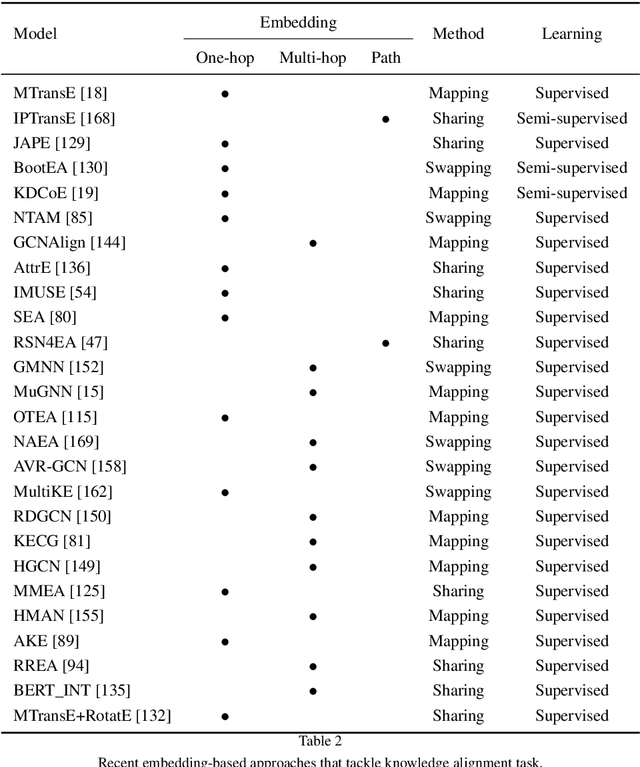
Abstract:Knowledge Graphs (KGs) are a major asset for companies thanks to their great flexibility in data representation and their numerous applications, e.g., vocabulary sharing, Q/A or recommendation systems. To build a KG it is a common practice to rely on automatic methods for extracting knowledge from various heterogeneous sources. But in a noisy and uncertain world, knowledge may not be reliable and conflicts between data sources may occur. Integrating unreliable data would directly impact the use of the KG, therefore such conflicts must be resolved. This could be done manually by selecting the best data to integrate. This first approach is highly accurate, but costly and time-consuming. That is why recent efforts focus on automatic approaches, which represents a challenging task since it requires handling the uncertainty of extracted knowledge throughout its integration into the KG. We survey state-of-the-art approaches in this direction and present constructions of both open and enterprise KGs and how their quality is maintained. We then describe different knowledge extraction methods, introducing additional uncertainty. We also discuss downstream tasks after knowledge acquisition, including KG completion using embedding models, knowledge alignment, and knowledge fusion in order to address the problem of knowledge uncertainty in KG construction. We conclude with a discussion on the remaining challenges and perspectives when constructing a KG taking into account uncertainty.
Relevant Entity Selection: Knowledge Graph Bootstrapping via Zero-Shot Analogical Pruning
Jun 28, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge Graph Construction (KGC) can be seen as an iterative process starting from a high quality nucleus that is refined by knowledge extraction approaches in a virtuous loop. Such a nucleus can be obtained from knowledge existing in an open KG like Wikidata. However, due to the size of such generic KGs, integrating them as a whole may entail irrelevant content and scalability issues. We propose an analogy-based approach that starts from seed entities of interest in a generic KG, and keeps or prunes their neighboring entities. We evaluate our approach on Wikidata through two manually labeled datasets that contain either domain-homogeneous or -heterogeneous seed entities. We empirically show that our analogy-based approach outperforms LSTM, Random Forest, SVM, and MLP, with a drastically lower number of parameters. We also evaluate its generalization potential in a transfer learning setting. These results advocate for the further integration of analogy-based inference in tasks related to the KG lifecycle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge