Luca Ghiani
Improving fingerprint presentation attack detection by an approach integrated into the personal verification stage
Apr 15, 2025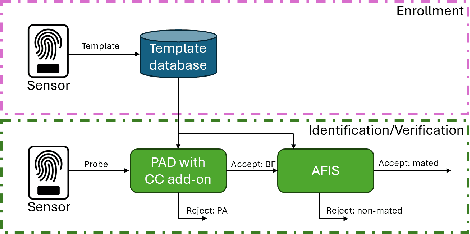
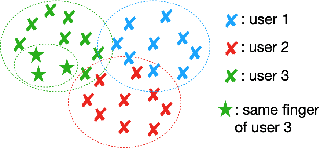
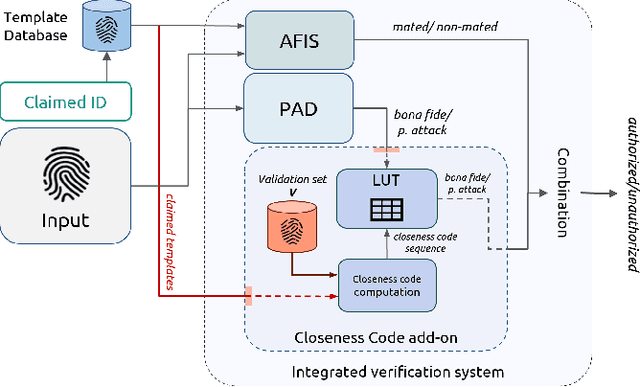
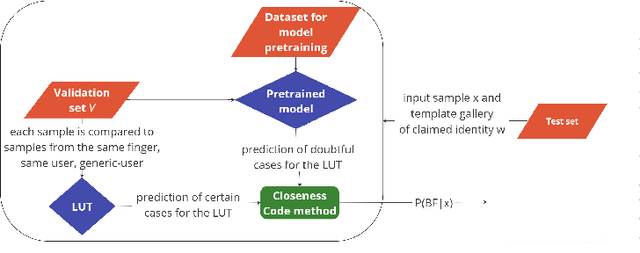
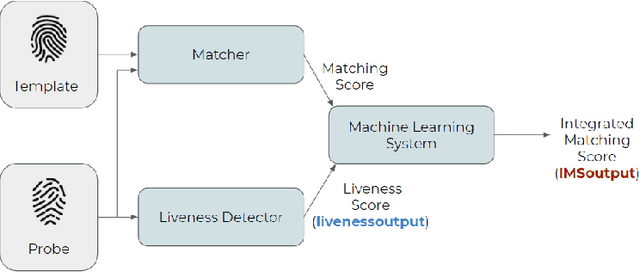
Abstract:Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) systems are usually designed independently of the fingerprint verification system. While this can be acceptable for use cases where specific user templates are not predetermined, it represents a missed opportunity to enhance security in scenarios where integrating PAD with the fingerprint verification system could significantly leverage users' templates, which are the real target of a potential presentation attack. This does not mean that a PAD should be specifically designed for such users; that would imply the availability of many enrolled users' PAI and, consequently, complexity, time, and cost increase. On the contrary, we propose to equip a basic PAD, designed according to the state of the art, with an innovative add-on module called the Closeness Binary Code (CC) module. The term "closeness" refers to a peculiar property of the bona fide-related features: in an Euclidean feature space, genuine fingerprints tend to cluster in a specific pattern. First, samples from the same finger are close to each other, then samples from other fingers of the same user and finally, samples from fingers of other users. This property is statistically verified in our previous publication, and further confirmed in this paper. It is independent of the user population and the feature set class, which can be handcrafted or deep network-based (embeddings). Therefore, the add-on can be designed without the need for the targeted user samples; moreover, it exploits her/his samples' "closeness" property during the verification stage. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets and state-of-the-art PAD methods confirm the benefits of the proposed add-on, which can be easily coupled with the main PAD module integrated into the fingerprint verification system.
Analysis of "User-Specific Effect" and Impact of Operator Skills on Fingerprint PAD Systems
Jul 18, 2019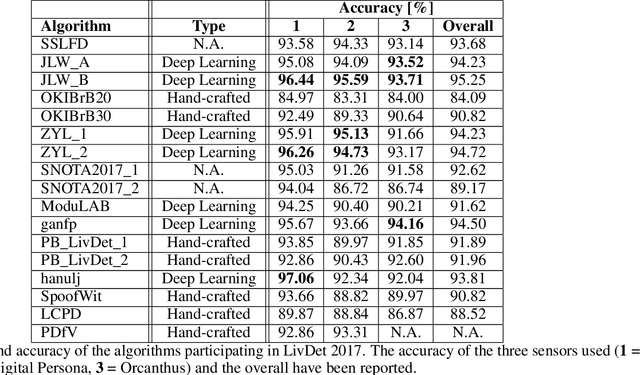
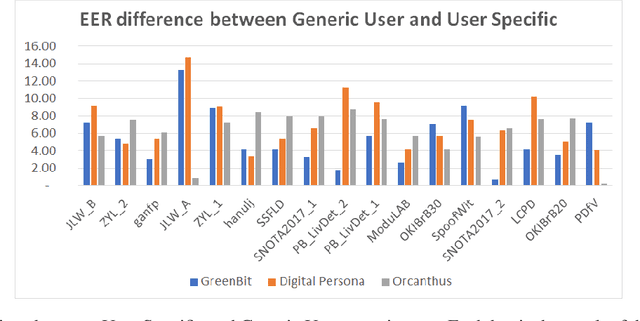
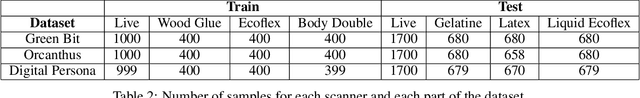
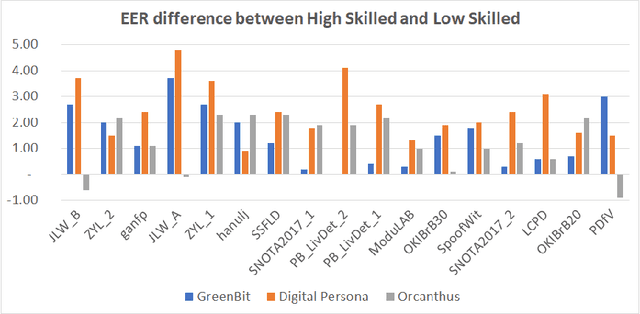
Abstract:Fingerprint Liveness detection, or presentation attacks detection (PAD), that is, the ability of detecting if a fingerprint submitted to an electronic capture device is authentic or made up of some artificial materials, boosted the attention of the scientific community and recently machine learning approaches based on deep networks opened novel scenarios. A significant step ahead was due thanks to the public availability of large sets of data; in particular, the ones released during the International Fingerprint Liveness Detection Competition (LivDet). Among others, the fifth edition carried on in 2017, challenged the participants in two more challenges which were not detailed in the official report. In this paper, we want to extend that report by focusing on them: the first one was aimed at exploring the case in which the PAD is integrated into a fingerprint verification systems, where templates of users are available too and the designer is not constrained to refer only to a generic users population for the PAD settings. The second one faces with the exploitation ability of attackers of the provided fakes, and how this ability impacts on the final performance. These two challenges together may set at which extent the fingerprint presentation attacks are an actual threat and how to exploit additional information to make the PAD more effective.
LivDet in Action - Fingerprint Liveness Detection Competition 2019
May 02, 2019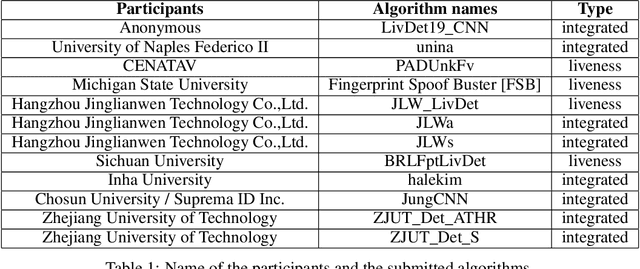

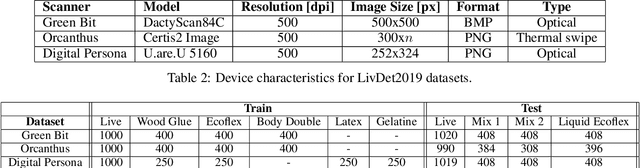
Abstract:The International Fingerprint liveness Detection Competition (LivDet) is an open and well-acknowledged meeting point of academies and private companies that deal with the problem of distinguishing images coming from reproductions of fingerprints made of artificial materials and images relative to real fingerprints. In this edition of LivDet we invited the competitors to propose integrated algorithms with matching systems. The goal was to investigate at which extent this integration impact on the whole performance. Twelve algorithms were submitted to the competition, eight of which worked on integrated systems.
LivDet 2017 Fingerprint Liveness Detection Competition 2017
Mar 14, 2018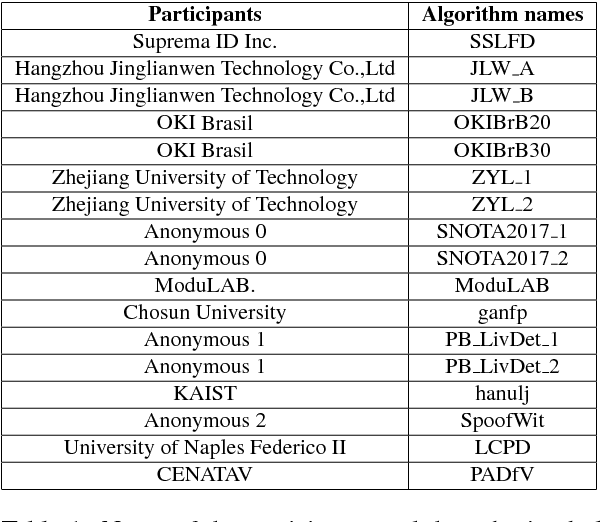
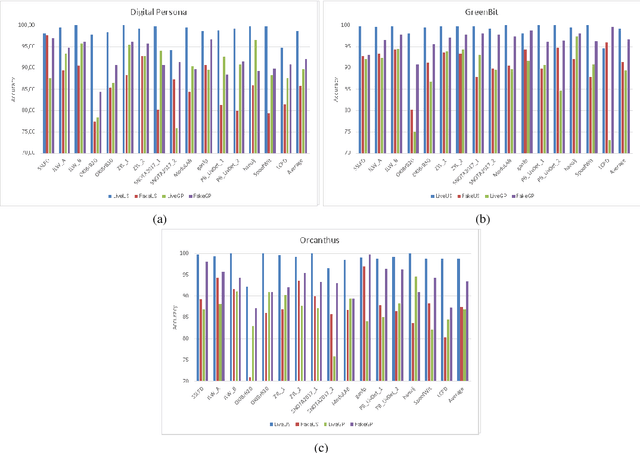
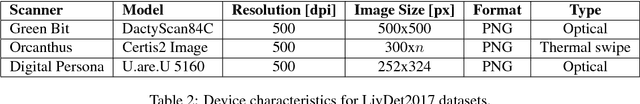
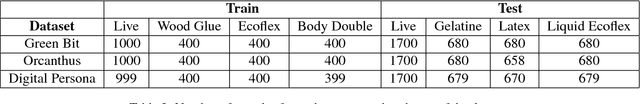
Abstract:Fingerprint Presentation Attack Detection (FPAD) deals with distinguishing images coming from artificial replicas of the fingerprint characteristic, made up of materials like silicone, gelatine or latex, and images coming from alive fingerprints. Images are captured by modern scanners, typically relying on solid-state or optical technologies. Since from 2009, the Fingerprint Liveness Detection Competition (LivDet) aims to assess the performance of the state-of-the-art algorithms according to a rigorous experimental protocol and, at the same time, a simple overview of the basic achievements. The competition is open to all academics research centers and all companies that work in this field. The positive, increasing trend of the participants number, which supports the success of this initiative, is confirmed even this year: 17 algorithms were submitted to the competition, with a larger involvement of companies and academies. This means that the topic is relevant for both sides, and points out that a lot of work must be done in terms of fundamental and applied research.
Review of the Fingerprint Liveness Detection competition series: 2009 to 2015
Sep 06, 2016
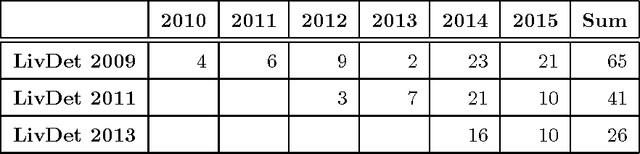

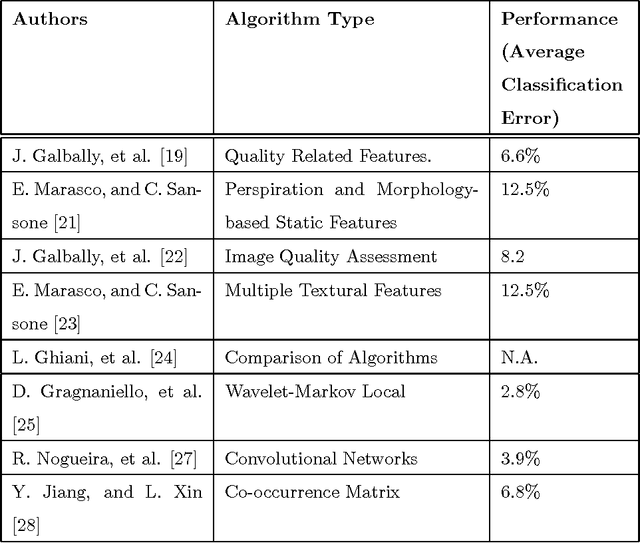
Abstract:A spoof attack, a subset of presentation attacks, is the use of an artificial replica of a biometric in an attempt to circumvent a biometric sensor. Liveness detection, or presentation attack detection, distinguishes between live and fake biometric traits and is based on the principle that additional information can be garnered above and beyond the data procured by a standard authentication system to determine if a biometric measure is authentic. The goals for the Liveness Detection (LivDet) competitions are to compare software-based fingerprint liveness detection and artifact detection algorithms (Part 1), as well as fingerprint systems which incorporate liveness detection or artifact detection capabilities (Part 2), using a standardized testing protocol and large quantities of spoof and live tests. The competitions are open to all academic and industrial institutions which have a solution for either softwarebased or system-based fingerprint liveness detection. The LivDet competitions have been hosted in 2009, 2011, 2013 and 2015 and have shown themselves to provide a crucial look at the current state of the art in liveness detection schemes. There has been a noticeable increase in the number of participants in LivDet competitions as well as a noticeable decrease in error rates across competitions. Participants have grown from four to the most recent thirteen submissions for Fingerprint Part 1. Fingerprints Part 2 has held steady at two submissions each competition in 2011 and 2013 and only one for the 2015 edition. The continuous increase of competitors demonstrates a growing interest in the topic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge