Luca Caltagirone
Lidar-Camera Co-Training for Semi-Supervised Road Detection
Nov 28, 2019
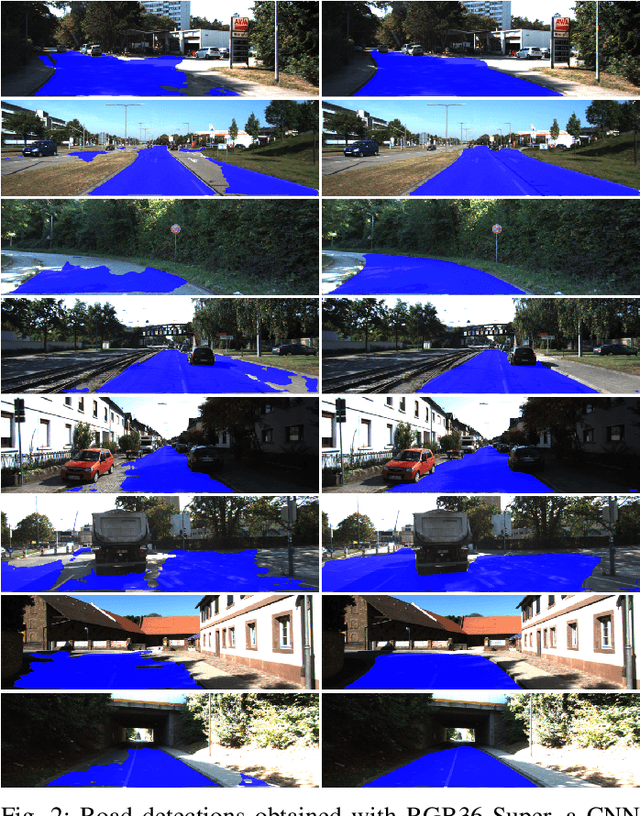
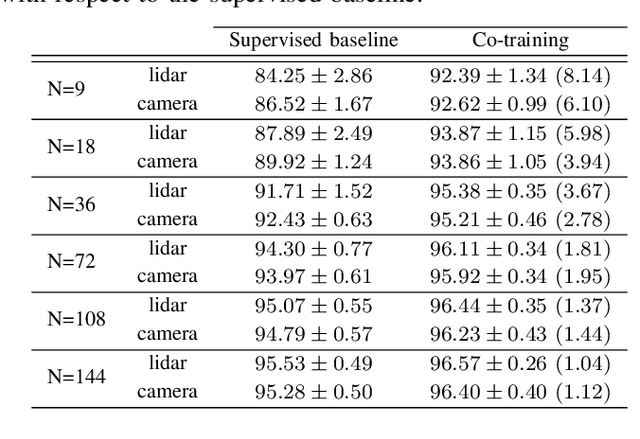
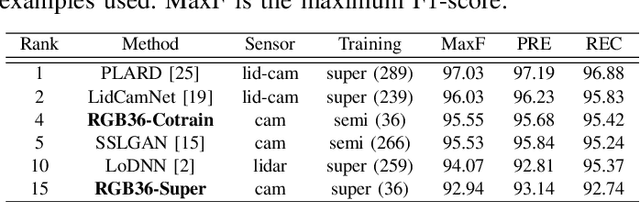
Abstract:Recent advances in the field of machine learning and computer vision have enabled the development of fast and accurate road detectors. Commonly such systems are trained within a supervised learning paradigm where both an input sensor's data and the corresponding ground truth label must be provided. The task of generating labels is commonly carried out by human annotators and it is notoriously time consuming and expensive. In this work, it is shown that a semi-supervised approach known as co-training can provide significant F1-score average improvements compared to supervised learning. In co-training, two classifiers acting on different views of the data cooperatively improve each other's performance by leveraging unlabeled examples. Depending on the amount of labeled data used, the improvements ranged from 1.12 to 6.10 percentage points for a camera-based road detector and from 1.04 to 8.14 percentage points for a lidar-based road detector. Lastly, the co-training algorithm is validated on the KITTI road benchmark, achieving high performance using only 36 labeled training examples together with several thousands unlabeled ones.
LIDAR-Camera Fusion for Road Detection Using Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Sep 21, 2018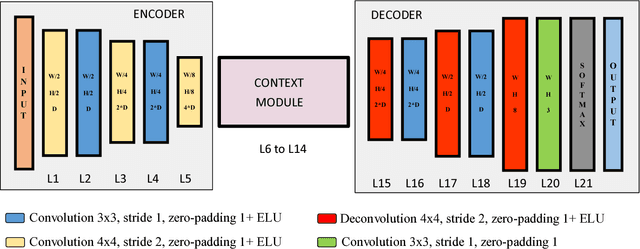
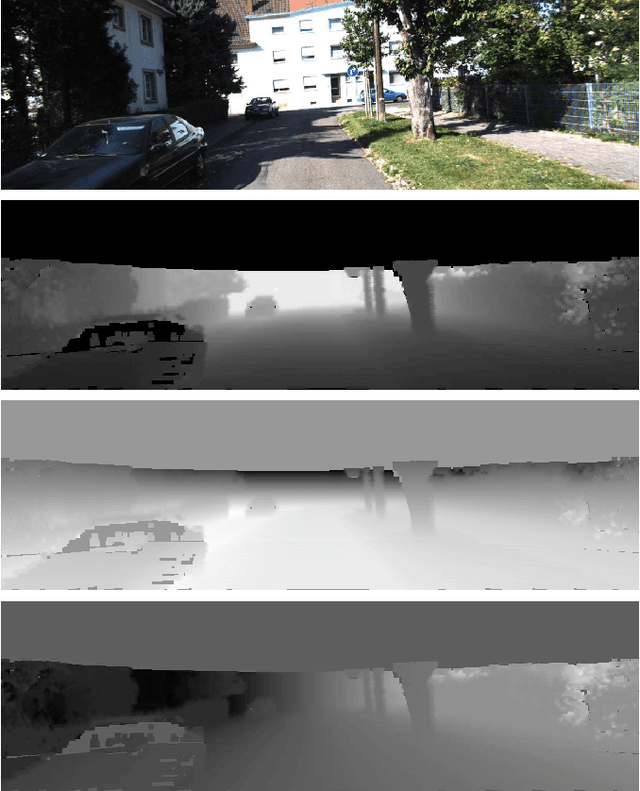
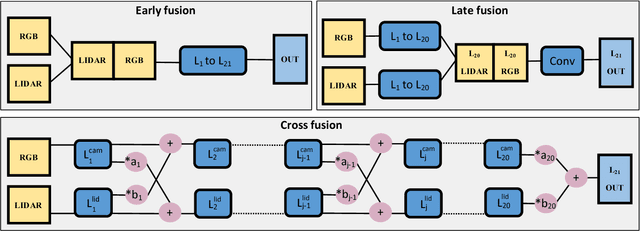

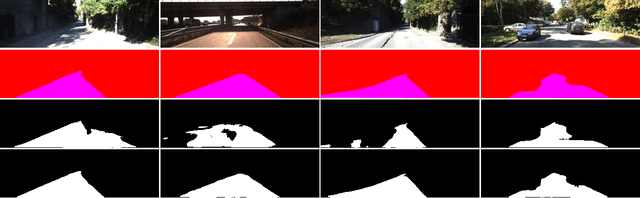
Abstract:In this work, a deep learning approach has been developed to carry out road detection by fusing LIDAR point clouds and camera images. An unstructured and sparse point cloud is first projected onto the camera image plane and then upsampled to obtain a set of dense 2D images encoding spatial information. Several fully convolutional neural networks (FCNs) are then trained to carry out road detection, either by using data from a single sensor, or by using three fusion strategies: early, late, and the newly proposed cross fusion. Whereas in the former two fusion approaches, the integration of multimodal information is carried out at a predefined depth level, the cross fusion FCN is designed to directly learn from data where to integrate information; this is accomplished by using trainable cross connections between the LIDAR and the camera processing branches. To further highlight the benefits of using a multimodal system for road detection, a data set consisting of visually challenging scenes was extracted from driving sequences of the KITTI raw data set. It was then demonstrated that, as expected, a purely camera-based FCN severely underperforms on this data set. A multimodal system, on the other hand, is still able to provide high accuracy. Finally, the proposed cross fusion FCN was evaluated on the KITTI road benchmark where it achieved excellent performance, with a MaxF score of 96.03%, ranking it among the top-performing approaches.
LIDAR-based Driving Path Generation Using Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Apr 03, 2017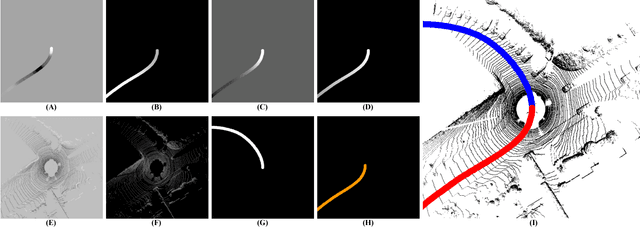
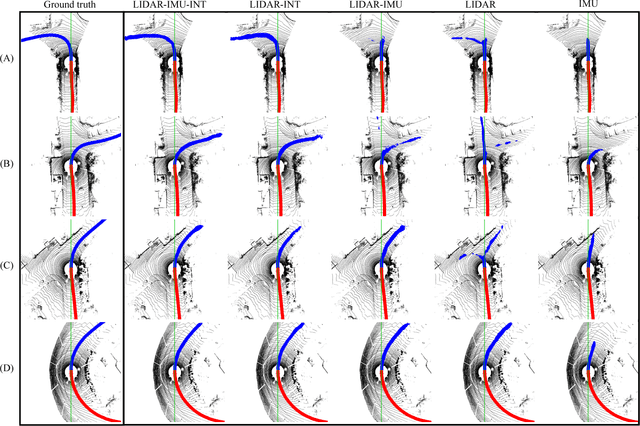
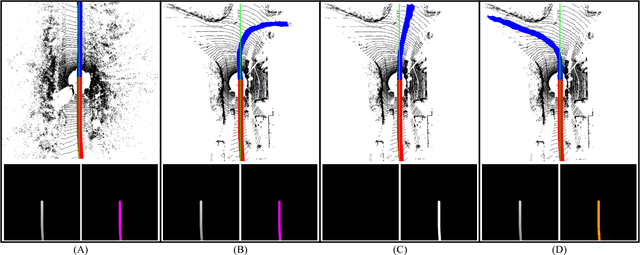
Abstract:In this work, a novel learning-based approach has been developed to generate driving paths by integrating LIDAR point clouds, GPS-IMU information, and Google driving directions. The system is based on a fully convolutional neural network that jointly learns to carry out perception and path generation from real-world driving sequences and that is trained using automatically generated training examples. Several combinations of input data were tested in order to assess the performance gain provided by specific information modalities. The fully convolutional neural network trained using all the available sensors together with driving directions achieved the best MaxF score of 88.13% when considering a region of interest of 60x60 meters. By considering a smaller region of interest, the agreement between predicted paths and ground-truth increased to 92.60%. The positive results obtained in this work indicate that the proposed system may help fill the gap between low-level scene parsing and behavior-reflex approaches by generating outputs that are close to vehicle control and at the same time human-interpretable.
Fast LIDAR-based Road Detection Using Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
Mar 29, 2017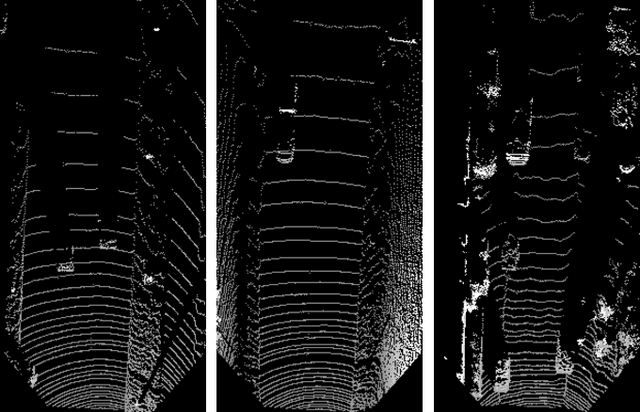
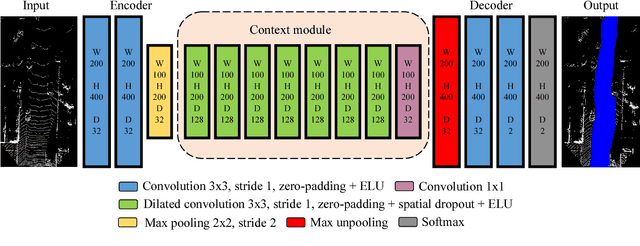
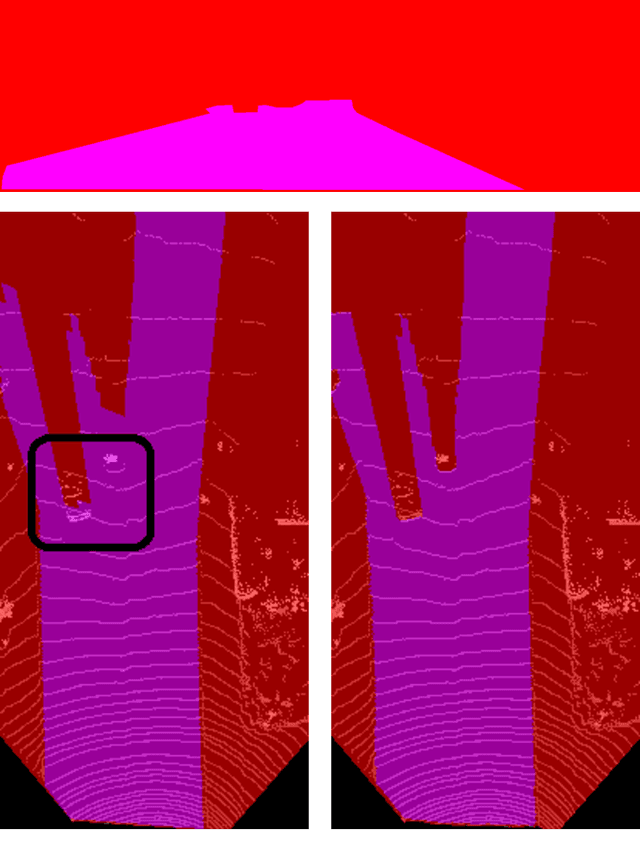
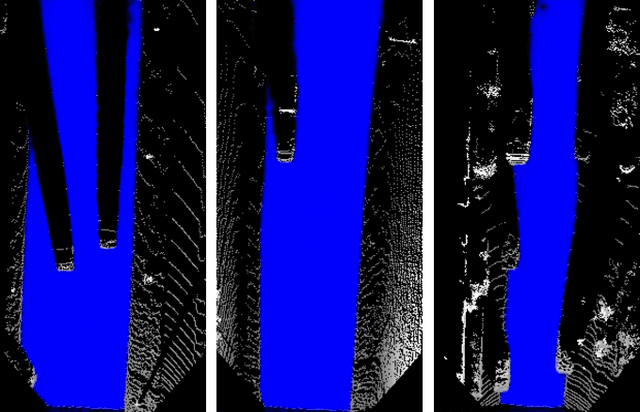
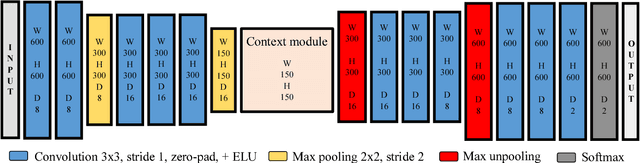
Abstract:In this work, a deep learning approach has been developed to carry out road detection using only LIDAR data. Starting from an unstructured point cloud, top-view images encoding several basic statistics such as mean elevation and density are generated. By considering a top-view representation, road detection is reduced to a single-scale problem that can be addressed with a simple and fast fully convolutional neural network (FCN). The FCN is specifically designed for the task of pixel-wise semantic segmentation by combining a large receptive field with high-resolution feature maps. The proposed system achieved excellent performance and it is among the top-performing algorithms on the KITTI road benchmark. Its fast inference makes it particularly suitable for real-time applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge