Lorenzo Paleari
Affordable AI Assistants with Knowledge Graph of Thoughts
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing the development of AI assistants capable of performing diverse tasks across domains. However, current state-of-the-art LLM-driven agents face significant challenges, including high operational costs and limited success rates on complex benchmarks like GAIA. To address these issues, we propose the Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT), an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. For example, KGoT achieves a 29% improvement in task success rates on the GAIA benchmark compared to Hugging Face Agents with GPT-4o mini, while reducing costs by over 36x compared to GPT-4o. Improvements for recent reasoning models are similar, e.g., 36% and 37.5% for Qwen2.5-32B and Deepseek-R1-70B, respectively. KGoT offers a scalable, affordable, and high-performing solution for AI assistants.
CheckEmbed: Effective Verification of LLM Solutions to Open-Ended Tasks
Jun 04, 2024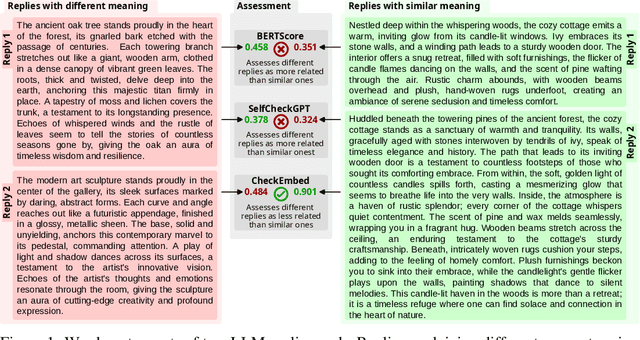
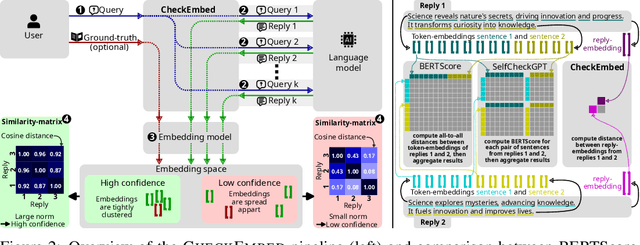
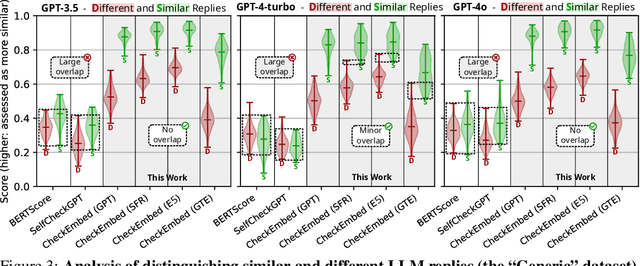
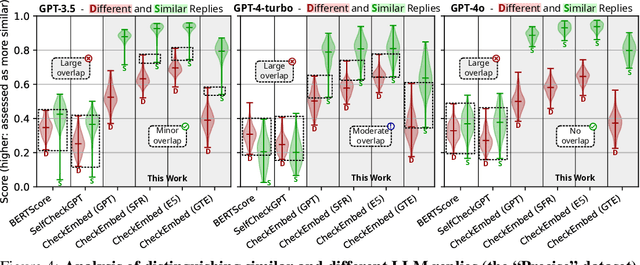
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing various domains, yet verifying their answers remains a significant challenge, especially for intricate open-ended tasks such as consolidation, summarization, and extraction of knowledge. In this work, we propose CheckEmbed: an accurate, scalable, and simple LLM verification approach. CheckEmbed is driven by a straightforward yet powerful idea: in order to compare LLM solutions to one another or to the ground-truth, compare their corresponding answer-level embeddings obtained with a model such as GPT Text Embedding Large. This reduces a complex textual answer to a single embedding, facilitating straightforward, fast, and meaningful verification. We develop a comprehensive verification pipeline implementing the CheckEmbed methodology. The CheckEmbed pipeline also comes with metrics for assessing the truthfulness of the LLM answers, such as embedding heatmaps and their summaries. We show how to use these metrics for deploying practical engines that decide whether an LLM answer is satisfactory or not. We apply the pipeline to real-world document analysis tasks, including term extraction and document summarization, showcasing significant improvements in accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and runtime performance compared to existing token-, sentence-, and fact-level schemes such as BERTScore or SelfCheckGPT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge