Lluis Padro
Dept LSI, Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya
Integrating Multiple Knowledge Sources for Robust Semantic Parsing
Sep 17, 2001
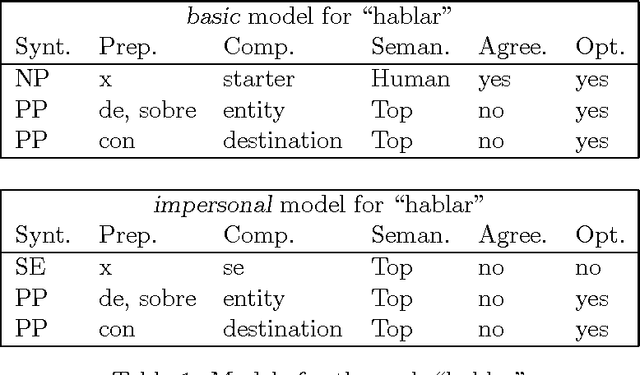


Abstract:This work explores a new robust approach for Semantic Parsing of unrestricted texts. Our approach considers Semantic Parsing as a Consistent Labelling Problem (CLP), allowing the integration of several knowledge types (syntactic and semantic) obtained from different sources (linguistic and statistic). The current implementation obtains 95% accuracy in model identification and 72% in case-role filling.
A Hybrid Environment for Syntax-Semantic Tagging
Feb 11, 1998



Abstract:The thesis describes the application of the relaxation labelling algorithm to NLP disambiguation. Language is modelled through context constraint inspired on Constraint Grammars. The constraints enable the use of a real value statind "compatibility". The technique is applied to POS tagging, Shallow Parsing and Word Sense Disambigation. Experiments and results are reported. The proposed approach enables the use of multi-feature constraint models, the simultaneous resolution of several NL disambiguation tasks, and the collaboration of linguistic and statistical models.
A Flexible POS tagger Using an Automatically Acquired Language Model
Jul 11, 1997



Abstract:We present an algorithm that automatically learns context constraints using statistical decision trees. We then use the acquired constraints in a flexible POS tagger. The tagger is able to use information of any degree: n-grams, automatically learned context constraints, linguistically motivated manually written constraints, etc. The sources and kinds of constraints are unrestricted, and the language model can be easily extended, improving the results. The tagger has been tested and evaluated on the WSJ corpus.
* 8 pages, aclap.sty, 2 eps figures. Appears in (E)ACL'97
Developing a hybrid NP parser
Apr 24, 1997

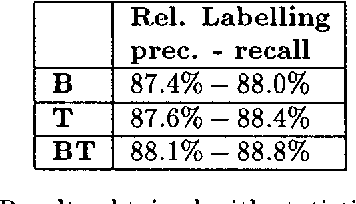
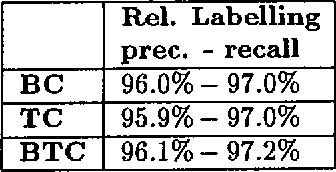
Abstract:We describe the use of energy function optimization in very shallow syntactic parsing. The approach can use linguistic rules and corpus-based statistics, so the strengths of both linguistic and statistical approaches to NLP can be combined in a single framework. The rules are contextual constraints for resolving syntactic ambiguities expressed as alternative tags, and the statistical language model consists of corpus-based n-grams of syntactic tags. The success of the hybrid syntactic disambiguator is evaluated against a held-out benchmark corpus. Also the contributions of the linguistic and statistical language models to the hybrid model are estimated.
* 8 pages, uses aclap.sty, epsf.sty
POS Tagging Using Relaxation Labelling
Oct 02, 1995

Abstract:Relaxation labelling is an optimization technique used in many fields to solve constraint satisfaction problems. The algorithm finds a combination of values for a set of variables such that satisfies -to the maximum possible degree- a set of given constraints. This paper describes some experiments performed applying it to POS tagging, and the results obtained. It also ponders the possibility of applying it to word sense disambiguation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge