Liviu Marina
NeuroTrajectory: A Neuroevolutionary Approach to Local State Trajectory Learning for Autonomous Vehicles
Jun 26, 2019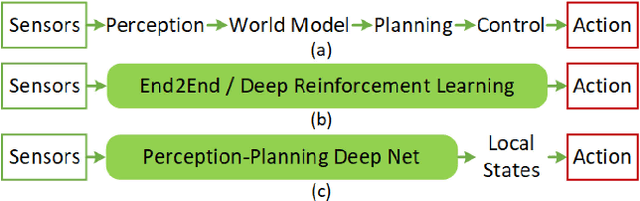
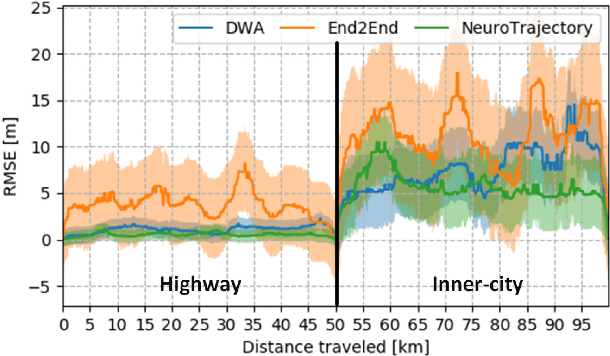
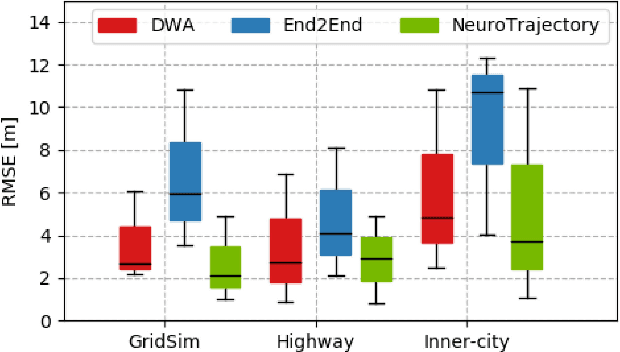
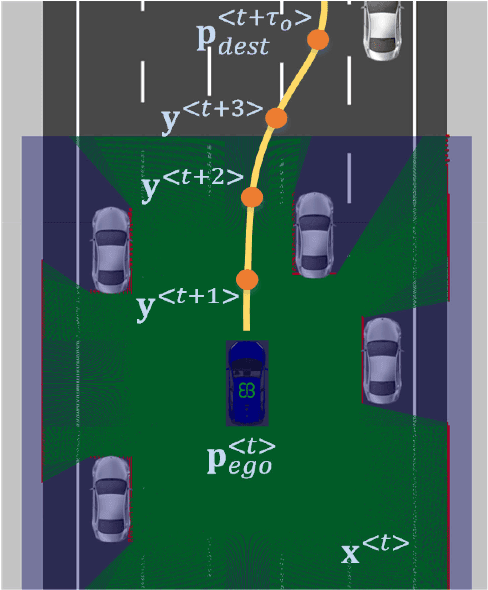
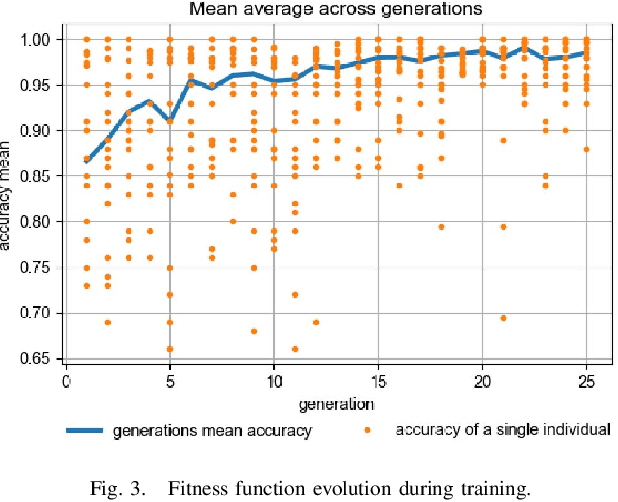
Abstract:Autonomous vehicles are controlled today either based on sequences of decoupled perception-planning-action operations, either based on End2End or Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) systems. Current deep learning solutions for autonomous driving are subject to several limitations (e.g. they estimate driving actions through a direct mapping of sensors to actuators, or require complex reward shaping methods). Although the cost function used for training can aggregate multiple weighted objectives, the gradient descent step is computed by the backpropagation algorithm using a single-objective loss. To address these issues, we introduce NeuroTrajectory, which is a multi-objective neuroevolutionary approach to local state trajectory learning for autonomous driving, where the desired state trajectory of the ego-vehicle is estimated over a finite prediction horizon by a perception-planning deep neural network. In comparison to DRL methods, which predict optimal actions for the upcoming sampling time, we estimate a sequence of optimal states that can be used for motion control. We propose an approach which uses genetic algorithms for training a population of deep neural networks, where each network individual is evaluated based on a multi-objective fitness vector, with the purpose of establishing a so-called Pareto front of optimal deep neural networks. The performance of an individual is given by a fitness vector composed of three elements. Each element describes the vehicle's travel path, lateral velocity and longitudinal speed, respectively. The same network structure can be trained on synthetic, as well as on real-world data sequences. We have benchmarked our system against a baseline Dynamic Window Approach (DWA), as well as against an End2End supervised learning method.
Deep Grid Net : A Deep Learning System for Real-Time Driving Context Understanding
Jan 16, 2019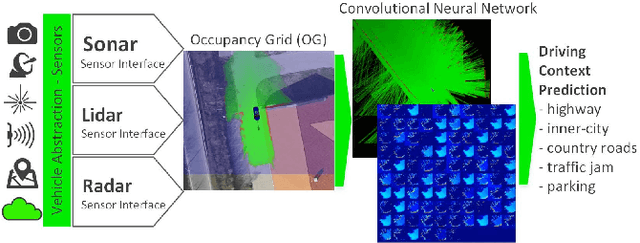
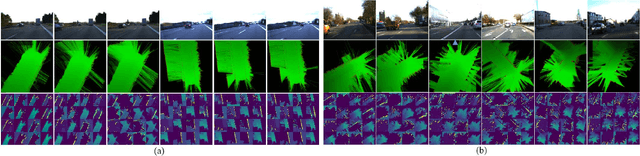
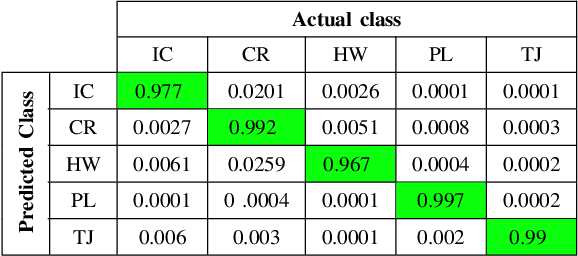
Abstract:Grid maps obtained from fused sensory information are nowadays among the most popular approaches for motion planning for autonomous driving cars. In this paper, we introduce Deep Grid Net (DGN), a deep learning (DL) system designed for understanding the context in which an autonomous car is driving. DGN incorporates a learned driving environment representation based on Occupancy Grids (OG) obtained from raw Lidar data and constructed on top of the Dempster-Shafer (DS) theory. The predicted driving context is further used for switching between different driving strategies implemented within EB robinos, Elektrobit's Autonomous Driving (AD) software platform. Based on genetic algorithms (GAs), we also propose a neuroevolutionary approach for learning the tuning hyperparameters of DGN. The performance of the proposed deep network has been evaluated against similar competing driving context estimation classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge