Lingzi Hong
Q-realign: Piggybacking Realignment on Quantization for Safe and Efficient LLM Deployment
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Public large language models (LLMs) are typically safety-aligned during pretraining, yet task-specific fine-tuning required for deployment often erodes this alignment and introduces safety risks. Existing defenses either embed safety recovery into fine-tuning or rely on fine-tuning-derived priors for post-hoc correction, leaving safety recovery tightly coupled with training and incurring high computational overhead and a complex workflow. To address these challenges, we propose \texttt{Q-realign}, a post-hoc defense method based on post-training quantization, guided by an analysis of representational structure. By reframing quantization as a dual-objective procedure for compression and safety, \texttt{Q-realign} decouples safety alignment from fine-tuning and naturally piggybacks into modern deployment pipelines. Experiments across multiple models and datasets demonstrate that our method substantially reduces unsafe behaviors while preserving task performance, with significant reductions in memory usage and GPU hours. Notably, our approach can recover the safety alignment of a fine-tuned 7B LLM on a single RTX 4090 within 40 minutes. Overall, our work provides a practical, turnkey solution for safety-aware deployment.
Multi-Agent Retrieval-Augmented Framework for Evidence-Based Counterspeech Against Health Misinformation
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) incorporated with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) have demonstrated powerful capabilities in generating counterspeech against misinformation. However, current studies rely on limited evidence and offer less control over final outputs. To address these challenges, we propose a Multi-agent Retrieval-Augmented Framework to generate counterspeech against health misinformation, incorporating multiple LLMs to optimize knowledge retrieval, evidence enhancement, and response refinement. Our approach integrates both static and dynamic evidence, ensuring that the generated counterspeech is relevant, well-grounded, and up-to-date. Our method outperforms baseline approaches in politeness, relevance, informativeness, and factual accuracy, demonstrating its effectiveness in generating high-quality counterspeech. To further validate our approach, we conduct ablation studies to verify the necessity of each component in our framework. Furthermore, human evaluations reveal that refinement significantly enhances counterspeech quality and obtains human preference.
Echoes of Discord: Forecasting Hater Reactions to Counterspeech
Jan 27, 2025
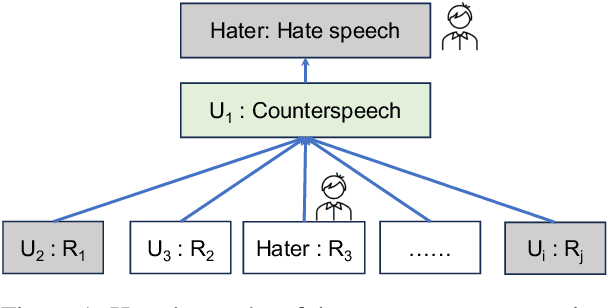
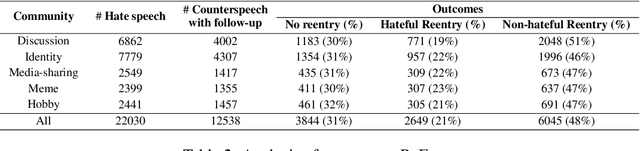
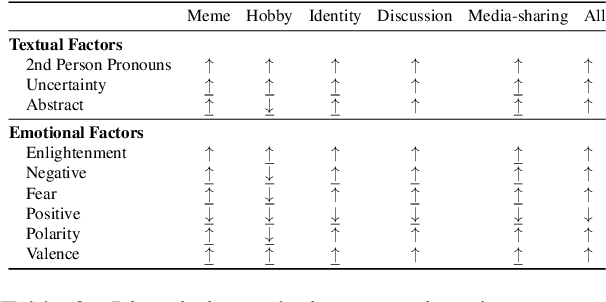
Abstract:Hate speech (HS) erodes the inclusiveness of online users and propagates negativity and division. Counterspeech has been recognized as a way to mitigate the harmful consequences. While some research has investigated the impact of user-generated counterspeech on social media platforms, few have examined and modeled haters' reactions toward counterspeech, despite the immediate alteration of haters' attitudes being an important aspect of counterspeech. This study fills the gap by analyzing the impact of counterspeech from the hater's perspective, focusing on whether the counterspeech leads the hater to reenter the conversation and if the reentry is hateful. We compile the Reddit Echoes of Hate dataset (ReEco), which consists of triple-turn conversations featuring haters' reactions, to assess the impact of counterspeech. The linguistic analysis sheds insights on the language of counterspeech to hate eliciting different haters' reactions. Experimental results demonstrate that the 3-way classification model outperforms the two-stage reaction predictor, which first predicts reentry and then determines the reentry type. We conclude the study with an assessment showing the most common errors identified by the best-performing model.
Assessing the Human Likeness of AI-Generated Counterspeech
Oct 14, 2024
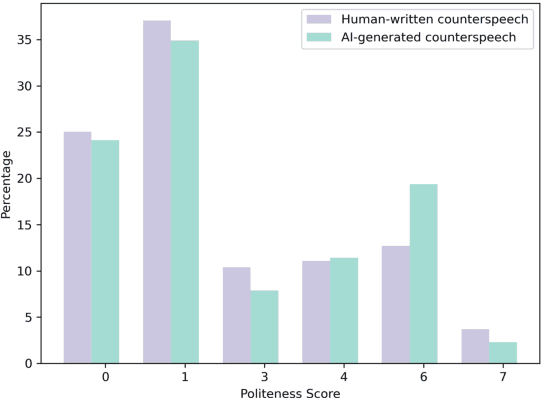
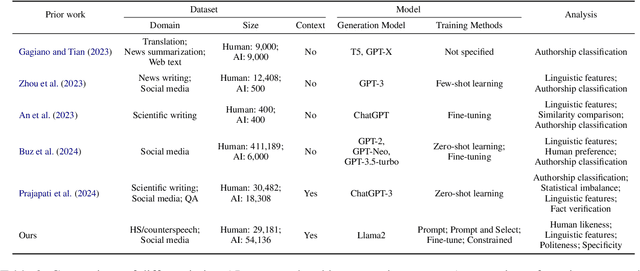
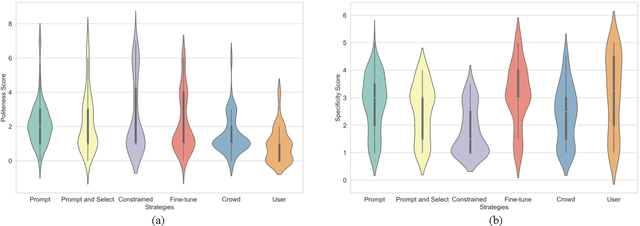
Abstract:Counterspeech is a targeted response to counteract and challenge abusive or hateful content. It can effectively curb the spread of hatred and foster constructive online communication. Previous studies have proposed different strategies for automatically generated counterspeech. Evaluations, however, focus on the relevance, surface form, and other shallow linguistic characteristics. In this paper, we investigate the human likeness of AI-generated counterspeech, a critical factor influencing effectiveness. We implement and evaluate several LLM-based generation strategies, and discover that AI-generated and human-written counterspeech can be easily distinguished by both simple classifiers and humans. Further, we reveal differences in linguistic characteristics, politeness, and specificity.
Outcome-Constrained Large Language Models for Countering Hate Speech
Mar 25, 2024Abstract:Counterspeech that challenges or responds to hate speech has been seen as an alternative to mitigate the negative impact of hate speech and foster productive online communications. Research endeavors have been directed to using language models for the automatic generation of counterspeech to assist efforts in combating online hate. Existing research focuses on the generation of counterspeech with certain linguistic attributes, such as being polite, informative, and intent-driven. However, it remains unclear what impact the counterspeech might have in an online environment. We first explore methods that utilize large language models (LLM) to generate counterspeech constrained by potential conversation outcomes. We build two conversation outcome classifiers that predict the incivility level and the hater reentry behavior following replies to hate with Reddit data, then propose four methods to incorporate the desired outcomes, i.e., low conversation incivility and non-hateful hater reentry, into the text generation process, including Prompt with Instructions, Prompt and Select, LLM finetune, and LLM transformer reinforcement learning (TRL). Evaluation results show effective strategies to generate outcome-constrained counterspeech and the linguistic characteristics of texts generated by different methods.
Hate Cannot Drive out Hate: Forecasting Conversation Incivility following Replies to Hate Speech
Dec 08, 2023Abstract:User-generated replies to hate speech are promising means to combat hatred, but questions about whether they can stop incivility in follow-up conversations linger. We argue that effective replies stop incivility from emerging in follow-up conversations - replies that elicit more incivility are counterproductive. This study introduces the task of predicting the incivility of conversations following replies to hate speech. We first propose a metric to measure conversation incivility based on the number of civil and uncivil comments as well as the unique authors involved in the discourse. Our metric approximates human judgments more accurately than previous metrics. We then use the metric to evaluate the outcomes of replies to hate speech. A linguistic analysis uncovers the differences in the language of replies that elicit follow-up conversations with high and low incivility. Experimental results show that forecasting incivility is challenging. We close with a qualitative analysis shedding light into the most common errors made by the best model.
Hate Speech and Counter Speech Detection: Conversational Context Does Matter
Jun 13, 2022
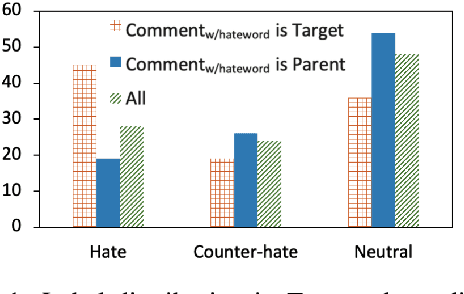
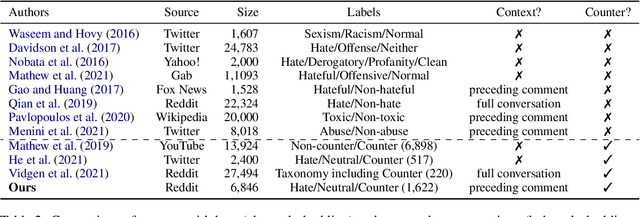
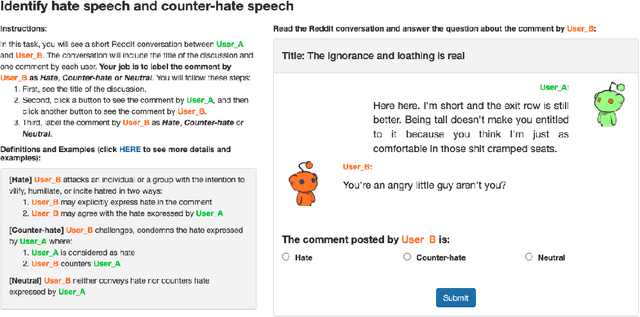
Abstract:Hate speech is plaguing the cyberspace along with user-generated content. This paper investigates the role of conversational context in the annotation and detection of online hate and counter speech, where context is defined as the preceding comment in a conversation thread. We created a context-aware dataset for a 3-way classification task on Reddit comments: hate speech, counter speech, or neutral. Our analyses indicate that context is critical to identify hate and counter speech: human judgments change for most comments depending on whether we show annotators the context. A linguistic analysis draws insights into the language people use to express hate and counter speech. Experimental results show that neural networks obtain significantly better results if context is taken into account. We also present qualitative error analyses shedding light into (a) when and why context is beneficial and (b) the remaining errors made by our best model when context is taken into account.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge