Liming Shi
Bayesian Pitch Tracking Based on the Harmonic Model
May 21, 2019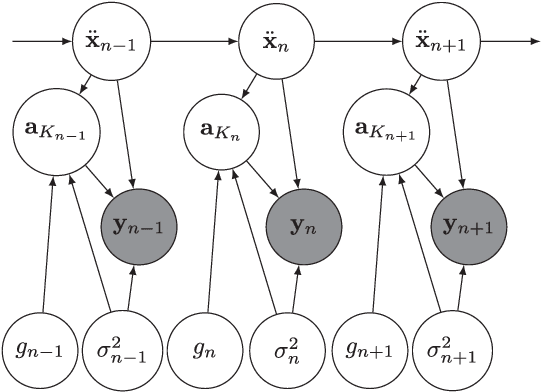
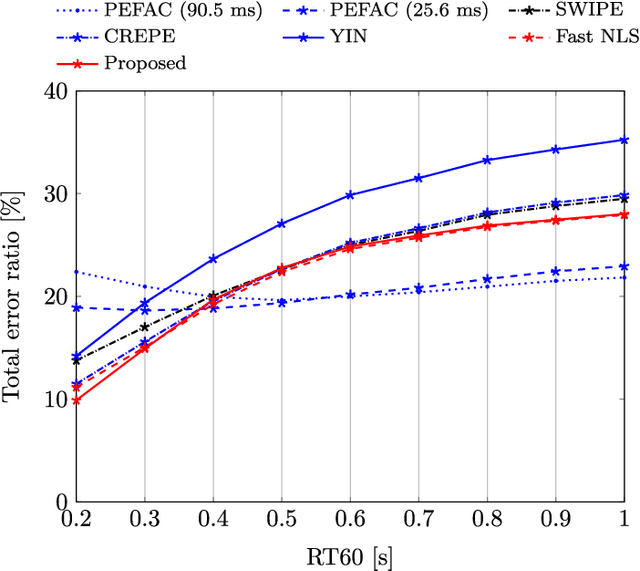
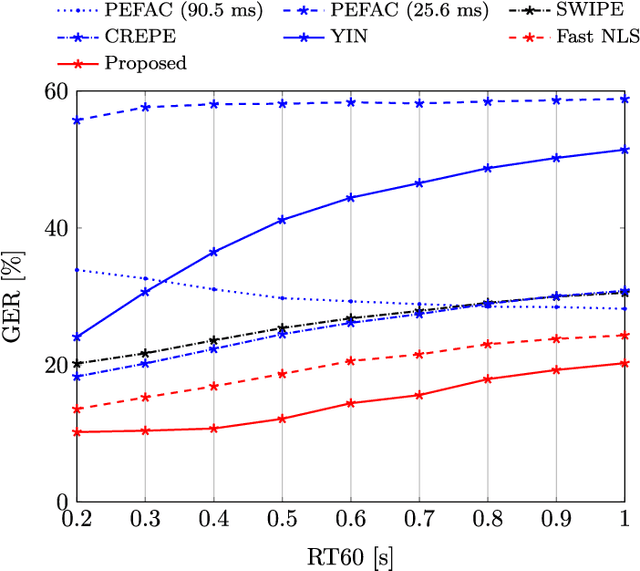
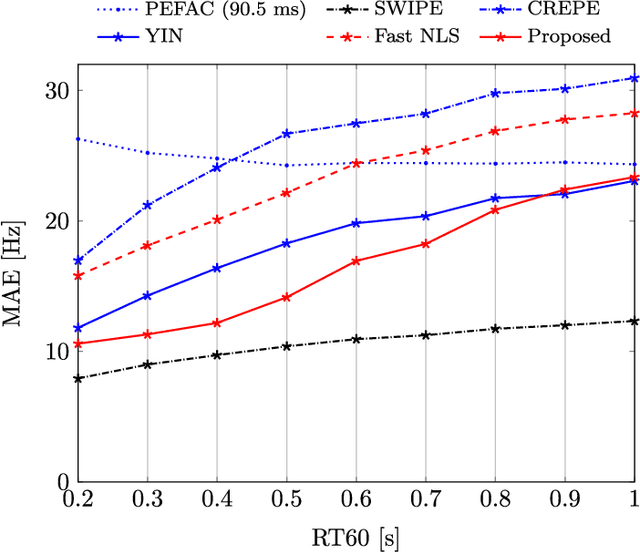
Abstract:Fundamental frequency is one of the most important characteristics of speech and audio signals. Harmonic model-based fundamental frequency estimators offer a higher estimation accuracy and robustness against noise than the widely used autocorrelation-based methods. However, the traditional harmonic model-based estimators do not take the temporal smoothness of the fundamental frequency, the model order, and the voicing into account as they process each data segment independently. In this paper, a fully Bayesian fundamental frequency tracking algorithm based on the harmonic model and a first-order Markov process model is proposed. Smoothness priors are imposed on the fundamental frequencies, model orders, and voicing using first-order Markov process models. Using these Markov models, fundamental frequency estimation and voicing detection errors can be reduced. Using the harmonic model, the proposed fundamental frequency tracker has an improved robustness to noise. An analytical form of the likelihood function, which can be computed efficiently, is derived. Compared to the state-of-the-art neural network and non-parametric approaches, the proposed fundamental frequency tracking algorithm reduces the mean absolute errors and gross errors by 15\% and 20\% on the Keele pitch database and 36\% and 26\% on sustained /a/ sounds from a database of Parkinson's disease voices under 0 dB white Gaussian noise. A MATLAB version of the proposed algorithm is made freely available for reproduction of the results\footnote{An implementation of the proposed algorithm using MATLAB may be found in \url{https://tinyurl.com/yxn4a543}
A Variational EM Method for Pole-Zero Modeling of Speech with Mixed Block Sparse and Gaussian Excitation
Jun 24, 2017



Abstract:The modeling of speech can be used for speech synthesis and speech recognition. We present a speech analysis method based on pole-zero modeling of speech with mixed block sparse and Gaussian excitation. By using a pole-zero model, instead of the all-pole model, a better spectral fitting can be expected. Moreover, motivated by the block sparse glottal flow excitation during voiced speech and the white noise excitation for unvoiced speech, we model the excitation sequence as a combination of block sparse signals and white noise. A variational EM (VEM) method is proposed for estimating the posterior PDFs of the block sparse residuals and point estimates of mod- elling parameters within a sparse Bayesian learning framework. Compared to conventional pole-zero and all-pole based methods, experimental results show that the proposed method has lower spectral distortion and good performance in reconstructing of the block sparse excitation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge