Jesper Kjær Nielsen
Speech Decomposition Based on a Hybrid Speech Model and Optimal Segmentation
May 04, 2021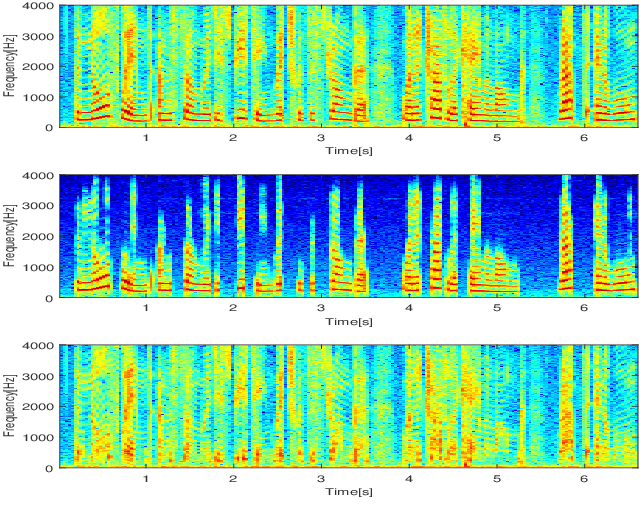
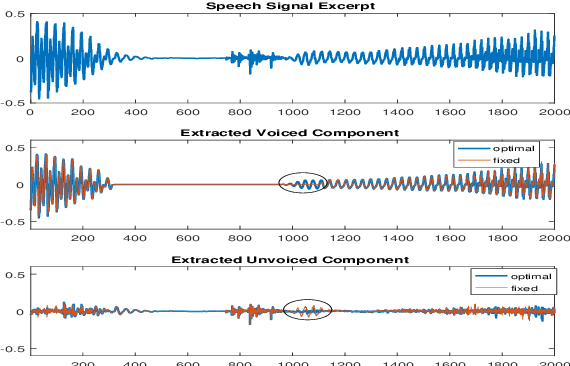

Abstract:In a hybrid speech model, both voiced and unvoiced components can coexist in a segment. Often, the voiced speech is regarded as the deterministic component, and the unvoiced speech and additive noise are the stochastic components. Typically, the speech signal is considered stationary within fixed segments of 20-40 ms, but the degree of stationarity varies over time. For decomposing noisy speech into its voiced and unvoiced components, a fixed segmentation may be too crude, and we here propose to adapt the segment length according to the signal local characteristics. The segmentation relies on parameter estimates of a hybrid speech model and the maximum a posteriori (MAP) and log-likelihood criteria as rules for model selection among the possible segment lengths, for voiced and unvoiced speech, respectively. Given the optimal segmentation markers and the estimated statistics, both components are estimated using linear filtering. A codebook-based approach differentiates between unvoiced speech and noise. A better extraction of the components is possible by taking into account the adaptive segmentation, compared to a fixed one. Also, a lower distortion for voiced speech and higher segSNR for both components is possible, as compared to other decomposition methods.
A Variational EM Method for Pole-Zero Modeling of Speech with Mixed Block Sparse and Gaussian Excitation
Jun 24, 2017



Abstract:The modeling of speech can be used for speech synthesis and speech recognition. We present a speech analysis method based on pole-zero modeling of speech with mixed block sparse and Gaussian excitation. By using a pole-zero model, instead of the all-pole model, a better spectral fitting can be expected. Moreover, motivated by the block sparse glottal flow excitation during voiced speech and the white noise excitation for unvoiced speech, we model the excitation sequence as a combination of block sparse signals and white noise. A variational EM (VEM) method is proposed for estimating the posterior PDFs of the block sparse residuals and point estimates of mod- elling parameters within a sparse Bayesian learning framework. Compared to conventional pole-zero and all-pole based methods, experimental results show that the proposed method has lower spectral distortion and good performance in reconstructing of the block sparse excitation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge