Liman Liu
DRMOT: A Dataset and Framework for RGBD Referring Multi-Object Tracking
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Referring Multi-Object Tracking (RMOT) aims to track specific targets based on language descriptions and is vital for interactive AI systems such as robotics and autonomous driving. However, existing RMOT models rely solely on 2D RGB data, making it challenging to accurately detect and associate targets characterized by complex spatial semantics (e.g., ``the person closest to the camera'') and to maintain reliable identities under severe occlusion, due to the absence of explicit 3D spatial information. In this work, we propose a novel task, RGBD Referring Multi-Object Tracking (DRMOT), which explicitly requires models to fuse RGB, Depth (D), and Language (L) modalities to achieve 3D-aware tracking. To advance research on the DRMOT task, we construct a tailored RGBD referring multi-object tracking dataset, named DRSet, designed to evaluate models' spatial-semantic grounding and tracking capabilities. Specifically, DRSet contains RGB images and depth maps from 187 scenes, along with 240 language descriptions, among which 56 descriptions incorporate depth-related information. Furthermore, we propose DRTrack, a MLLM-guided depth-referring tracking framework. DRTrack performs depth-aware target grounding from joint RGB-D-L inputs and enforces robust trajectory association by incorporating depth cues. Extensive experiments on the DRSet dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework.
IoU-uniform R-CNN: Breaking Through the Limitations of RPN
Dec 11, 2019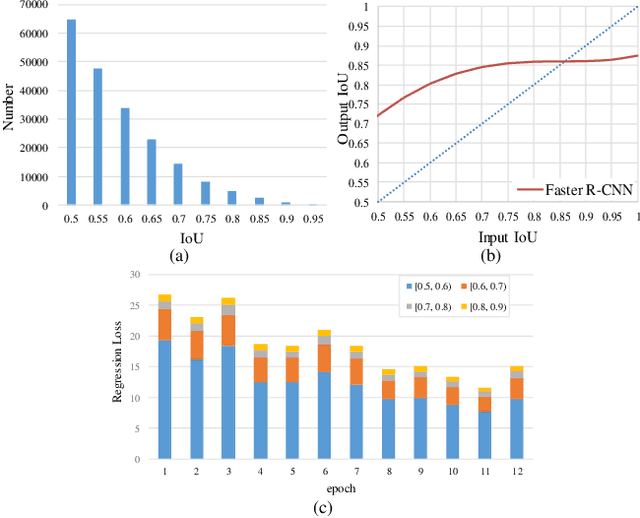
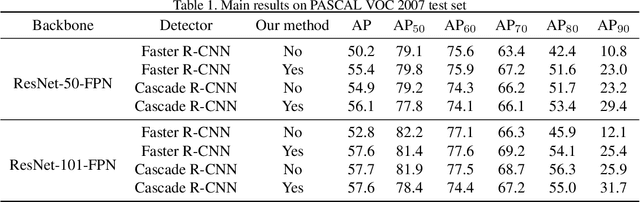
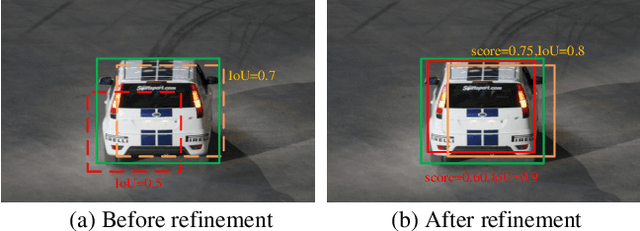
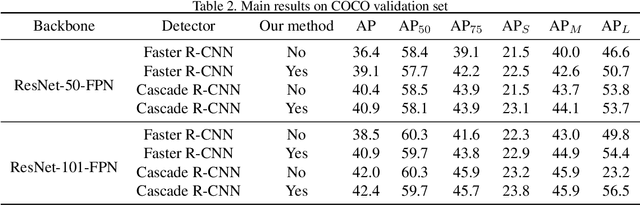
Abstract:Region Proposal Network (RPN) is the cornerstone of two-stage object detectors, it generates a sparse set of object proposals and alleviates the extrem foregroundbackground class imbalance problem during training. However, we find that the potential of the detector has not been fully exploited due to the IoU distribution imbalance and inadequate quantity of the training samples generated by RPN. With the increasing intersection over union (IoU), the exponentially smaller numbers of positive samples would lead to the distribution skewed towards lower IoUs, which hinders the optimization of detector at high IoU levels. In this paper, to break through the limitations of RPN, we propose IoU-Uniform R-CNN, a simple but effective method that directly generates training samples with uniform IoU distribution for the regression branch as well as the IoU prediction branch. Besides, we improve the performance of IoU prediction branch by eliminating the feature offsets of RoIs at inference, which helps the NMS procedure by preserving accurately localized bounding box. Extensive experiments on the PASCAL VOC and MS COCO dataset show the effectiveness of our method, as well as its compatibility and adaptivity to many object detection architectures. The code is made publicly available at https://github.com/zl1994/IoU-Uniform-R-CNN,
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge