Leonid Pugachev
Explain My Surprise: Learning Efficient Long-Term Memory by Predicting Uncertain Outcomes
Jul 27, 2022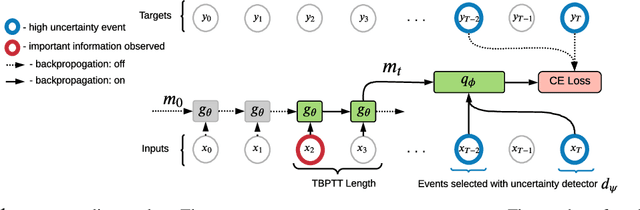
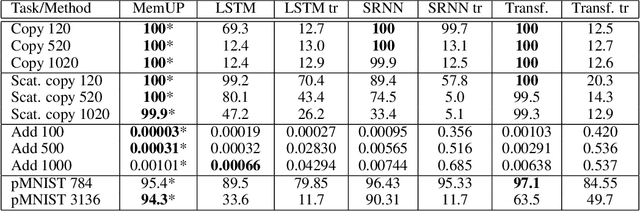
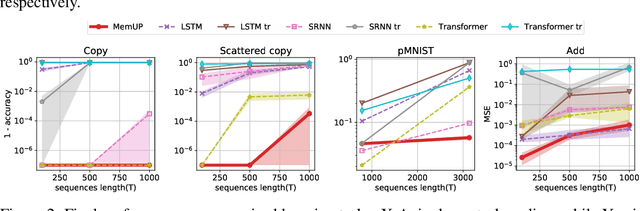
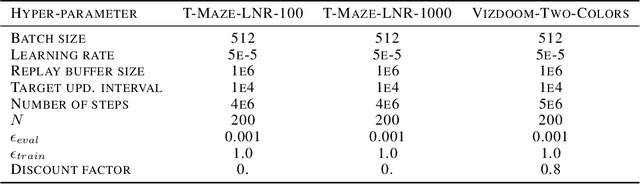
Abstract:In many sequential tasks, a model needs to remember relevant events from the distant past to make correct predictions. Unfortunately, a straightforward application of gradient based training requires intermediate computations to be stored for every element of a sequence. This requires prohibitively large computing memory if a sequence consists of thousands or even millions elements, and as a result, makes learning of very long-term dependencies infeasible. However, the majority of sequence elements can usually be predicted by taking into account only temporally local information. On the other hand, predictions affected by long-term dependencies are sparse and characterized by high uncertainty given only local information. We propose MemUP, a new training method that allows to learn long-term dependencies without backpropagating gradients through the whole sequence at a time. This method can be potentially applied to any gradient based sequence learning. MemUP implementation for recurrent architectures shows performances better or comparable to baselines while requiring significantly less computing memory.
Short Text Clustering with Transformers
Jan 31, 2021
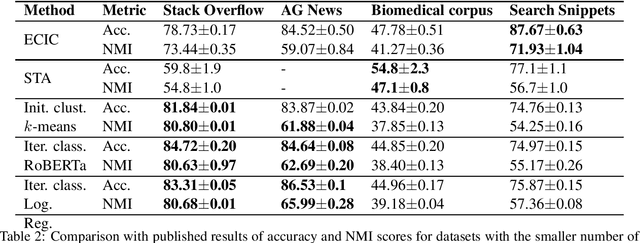
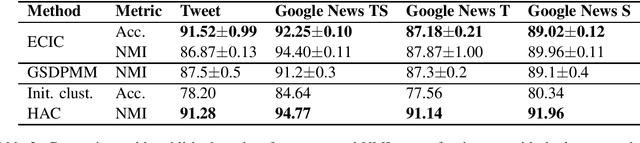
Abstract:Recent techniques for the task of short text clustering often rely on word embeddings as a transfer learning component. This paper shows that sentence vector representations from Transformers in conjunction with different clustering methods can be successfully applied to address the task. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the algorithm of enhancement of clustering via iterative classification can further improve initial clustering performance with different classifiers, including those based on pre-trained Transformer language models.
Goal-Oriented Multi-Task BERT-Based Dialogue State Tracker
Feb 05, 2020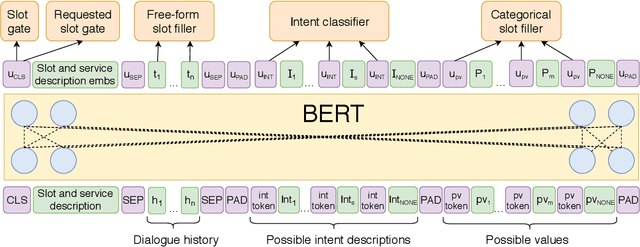
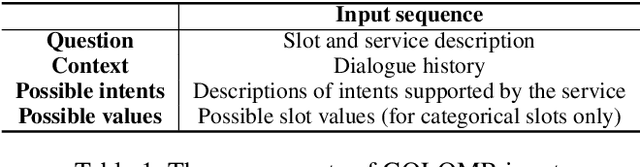
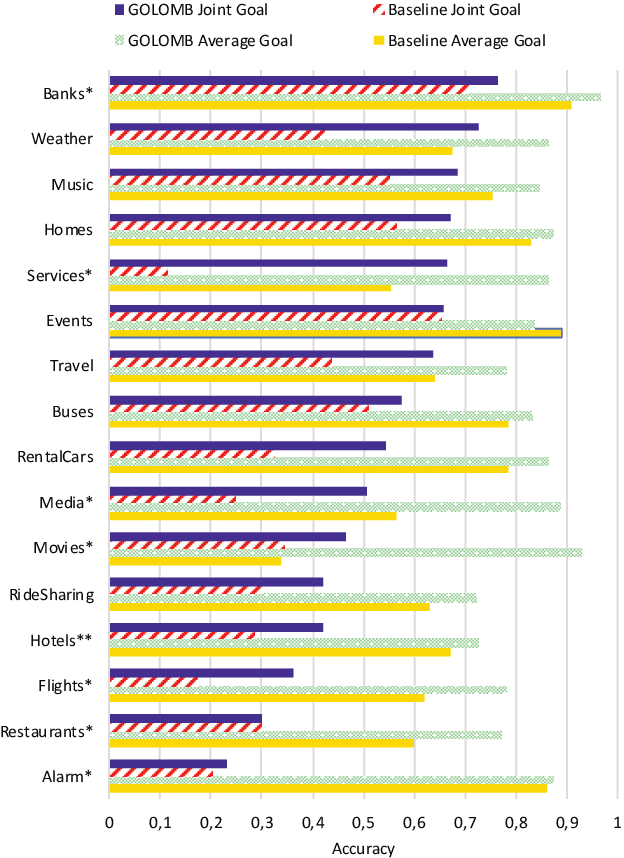
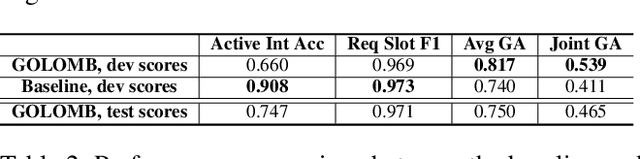
Abstract:Dialogue State Tracking (DST) is a core component of virtual assistants such as Alexa or Siri. To accomplish various tasks, these assistants need to support an increasing number of services and APIs. The Schema-Guided State Tracking track of the 8th Dialogue System Technology Challenge highlighted the DST problem for unseen services. The organizers introduced the Schema-Guided Dialogue (SGD) dataset with multi-domain conversations and released a zero-shot dialogue state tracking model. In this work, we propose a GOaL-Oriented Multi-task BERT-based dialogue state tracker (GOLOMB) inspired by architectures for reading comprehension question answering systems. The model "queries" dialogue history with descriptions of slots and services as well as possible values of slots. This allows to transfer slot values in multi-domain dialogues and have a capability to scale to unseen slot types. Our model achieves a joint goal accuracy of 53.97% on the SGD dataset, outperforming the baseline model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge