Leonardo Crespi
ARTInp: CBCT-to-CT Image Inpainting and Image Translation in Radiotherapy
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:A key step in Adaptive Radiation Therapy (ART) workflows is the evaluation of the patient's anatomy at treatment time to ensure the accuracy of the delivery. To this end, Cone Beam Computerized Tomography (CBCT) is widely used being cost-effective and easy to integrate into the treatment process. Nonetheless, CBCT images have lower resolution and more artifacts than CT scans, making them less reliable for precise treatment validation. Moreover, in complex treatments such as Total Marrow and Lymph Node Irradiation (TMLI), where full-body visualization of the patient is critical for accurate dose delivery, the CBCT images are often discontinuous, leaving gaps that could contain relevant anatomical information. To address these limitations, we propose ARTInp (Adaptive Radiation Therapy Inpainting), a novel deep-learning framework combining image inpainting and CBCT-to-CT translation. ARTInp employs a dual-network approach: a completion network that fills anatomical gaps in CBCT volumes and a custom Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to generate high-quality synthetic CT (sCT) images. We trained ARTInp on a dataset of paired CBCT and CT images from the SynthRad 2023 challenge, and the performance achieved on a test set of 18 patients demonstrates its potential for enhancing CBCT-based workflows in radiotherapy.
Leveraging Multimodal CycleGAN for the Generation of Anatomically Accurate Synthetic CT Scans from MRIs
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:In many clinical settings, the use of both Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance (MRI) is necessary to pursue a thorough understanding of the patient's anatomy and to plan a suitable therapeutical strategy; this is often the case in MRI-based radiotherapy, where CT is always necessary to prepare the dose delivery, as it provides the essential information about the radiation absorption properties of the tissues. Sometimes, MRI is preferred to contour the target volumes. However, this approach is often not the most efficient, as it is more expensive, time-consuming and, most importantly, stressful for the patients. To overcome this issue, in this work, we analyse the capabilities of different configurations of Deep Learning models to generate synthetic CT scans from MRI, leveraging the power of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and, in particular, the CycleGAN architecture, capable of working in an unsupervised manner and without paired images, which were not available. Several CycleGAN models were trained unsupervised to generate CT scans from different MRI modalities with and without contrast agents. To overcome the problem of not having a ground truth, distribution-based metrics were used to assess the model's performance quantitatively, together with a qualitative evaluation where physicians were asked to differentiate between real and synthetic images to understand how realistic the generated images were. The results show how, depending on the input modalities, the models can have very different performances; however, models with the best quantitative results, according to the distribution-based metrics used, can generate very difficult images to distinguish from the real ones, even for physicians, demonstrating the approach's potential.
Comparing Adversarial and Supervised Learning for Organs at Risk Segmentation in CT images
Mar 31, 2023



Abstract:Organ at Risk (OAR) segmentation from CT scans is a key component of the radiotherapy treatment workflow. In recent years, deep learning techniques have shown remarkable potential in automating this process. In this paper, we investigate the performance of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) compared to supervised learning approaches for segmenting OARs from CT images. We propose three GAN-based models with identical generator architectures but different discriminator networks. These models are compared with well-established CNN models, such as SE-ResUnet and DeepLabV3, using the StructSeg dataset, which consists of 50 annotated CT scans containing contours of six OARs. Our work aims to provide insight into the advantages and disadvantages of adversarial training in the context of OAR segmentation. The results are very promising and show that the proposed GAN-based approaches are similar or superior to their CNN-based counterparts, particularly when segmenting more challenging target organs.
Ensemble Methods for Multi-Organ Segmentation in CT Series
Mar 31, 2023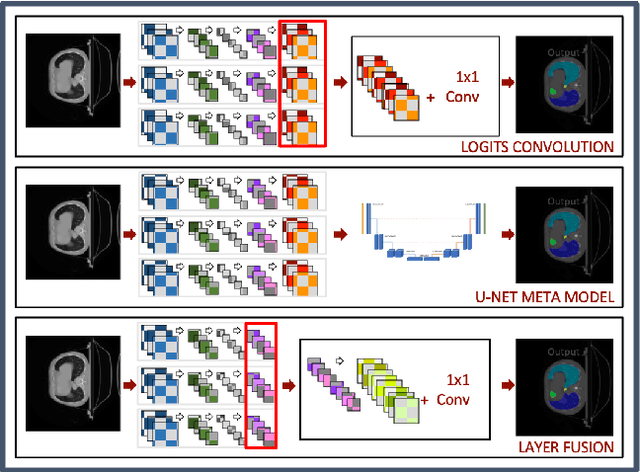
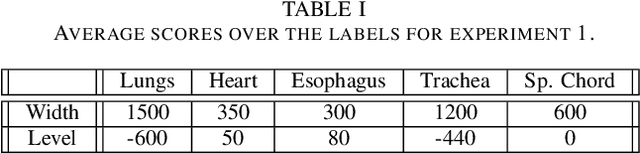
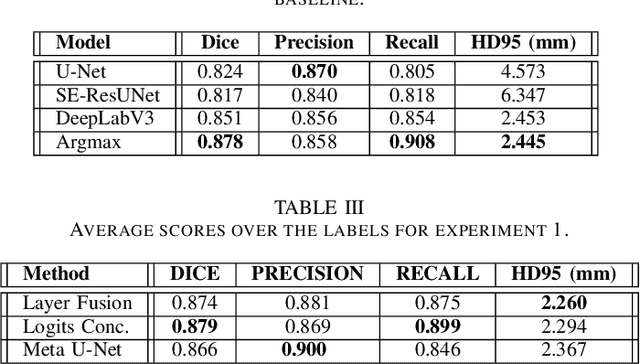
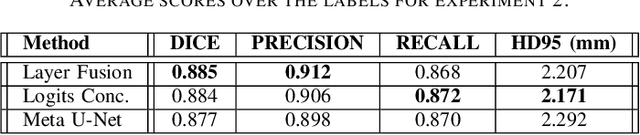
Abstract:In the medical images field, semantic segmentation is one of the most important, yet difficult and time-consuming tasks to be performed by physicians. Thanks to the recent advancement in the Deep Learning models regarding Computer Vision, the promise to automate this kind of task is getting more and more realistic. However, many problems are still to be solved, like the scarce availability of data and the difficulty to extend the efficiency of highly specialised models to general scenarios. Organs at risk segmentation for radiotherapy treatment planning falls in this category, as the limited data available negatively affects the possibility to develop general-purpose models; in this work, we focus on the possibility to solve this problem by presenting three types of ensembles of single-organ models able to produce multi-organ masks exploiting the different specialisations of their components. The results obtained are promising and prove that this is a possible solution to finding efficient multi-organ segmentation methods.
Chest X-Rays Image Classification from beta-Variational Autoencoders Latent Features
Sep 29, 2021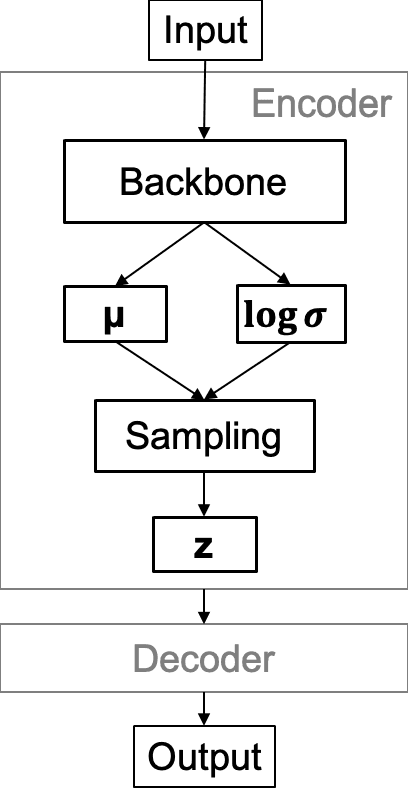
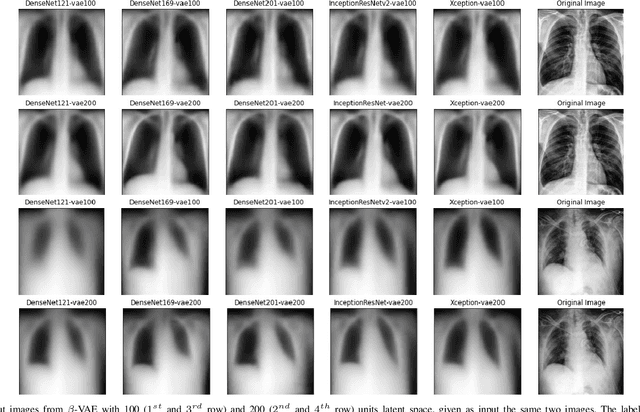
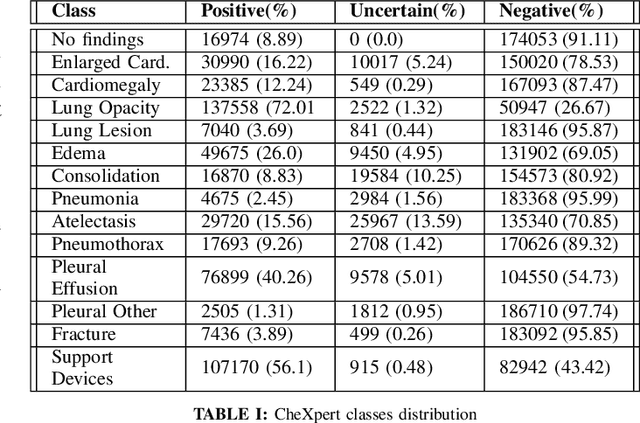
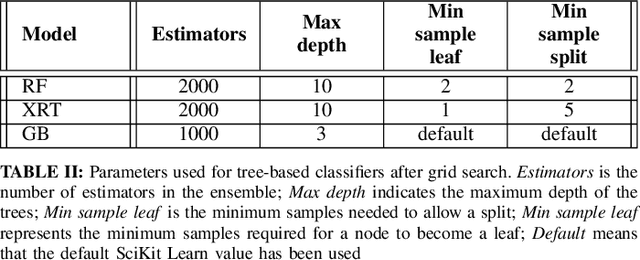
Abstract:Chest X-Ray (CXR) is one of the most common diagnostic techniques used in everyday clinical practice all around the world. We hereby present a work which intends to investigate and analyse the use of Deep Learning (DL) techniques to extract information from such images and allow to classify them, trying to keep our methodology as general as possible and possibly also usable in a real world scenario without much effort, in the future. To move in this direction, we trained several beta-Variational Autoencoder (beta-VAE) models on the CheXpert dataset, one of the largest publicly available collection of labeled CXR images; from these models, latent features have been extracted and used to train other Machine Learning models, able to classify the original images from the features extracted by the beta-VAE. Lastly, tree-based models have been combined together in ensemblings to improve the results without the necessity of further training or models engineering. Expecting some drop in pure performance with the respect to state of the art classification specific models, we obtained encouraging results, which show the viability of our approach and the usability of the high level features extracted by the autoencoders for classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge