Lena S. Bolliger
Language models emulate certain cognitive profiles: An investigation of how predictability measures interact with individual differences
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:To date, most investigations on surprisal and entropy effects in reading have been conducted on the group level, disregarding individual differences. In this work, we revisit the predictive power of surprisal and entropy measures estimated from a range of language models (LMs) on data of human reading times as a measure of processing effort by incorporating information of language users' cognitive capacities. To do so, we assess the predictive power of surprisal and entropy estimated from generative LMs on reading data obtained from individuals who also completed a wide range of psychometric tests. Specifically, we investigate if modulating surprisal and entropy relative to cognitive scores increases prediction accuracy of reading times, and we examine whether LMs exhibit systematic biases in the prediction of reading times for cognitively high- or low-performing groups, revealing what type of psycholinguistic subject a given LM emulates. Our study finds that in most cases, incorporating cognitive capacities increases predictive power of surprisal and entropy on reading times, and that generally, high performance in the psychometric tests is associated with lower sensitivity to predictability effects. Finally, our results suggest that the analyzed LMs emulate readers with lower verbal intelligence, suggesting that for a given target group (i.e., individuals with high verbal intelligence), these LMs provide less accurate predictability estimates.
ScanDL: A Diffusion Model for Generating Synthetic Scanpaths on Texts
Oct 24, 2023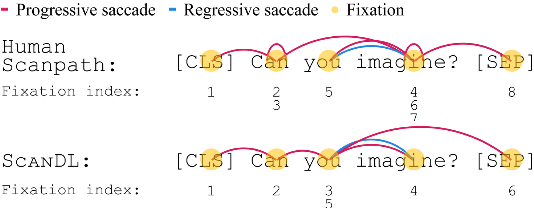
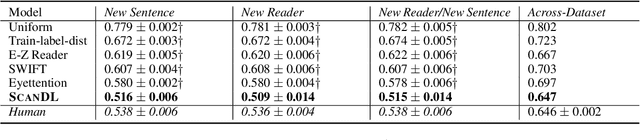
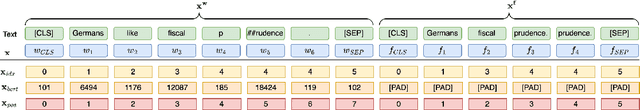
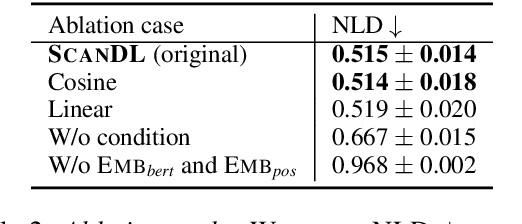
Abstract:Eye movements in reading play a crucial role in psycholinguistic research studying the cognitive mechanisms underlying human language processing. More recently, the tight coupling between eye movements and cognition has also been leveraged for language-related machine learning tasks such as the interpretability, enhancement, and pre-training of language models, as well as the inference of reader- and text-specific properties. However, scarcity of eye movement data and its unavailability at application time poses a major challenge for this line of research. Initially, this problem was tackled by resorting to cognitive models for synthesizing eye movement data. However, for the sole purpose of generating human-like scanpaths, purely data-driven machine-learning-based methods have proven to be more suitable. Following recent advances in adapting diffusion processes to discrete data, we propose ScanDL, a novel discrete sequence-to-sequence diffusion model that generates synthetic scanpaths on texts. By leveraging pre-trained word representations and jointly embedding both the stimulus text and the fixation sequence, our model captures multi-modal interactions between the two inputs. We evaluate ScanDL within- and across-dataset and demonstrate that it significantly outperforms state-of-the-art scanpath generation methods. Finally, we provide an extensive psycholinguistic analysis that underlines the model's ability to exhibit human-like reading behavior. Our implementation is made available at https://github.com/DiLi-Lab/ScanDL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge