Leen Stougie
Solving the Tree Containment Problem Using Graph Neural Networks
Apr 15, 2024Abstract:Tree Containment is a fundamental problem in phylogenetics useful for verifying a proposed phylogenetic network, representing the evolutionary history of certain species. Tree Containment asks whether the given phylogenetic tree (for instance, constructed from a DNA fragment showing tree-like evolution) is contained in the given phylogenetic network. In the general case, this is an NP-complete problem. We propose to solve it approximately using Graph Neural Networks. In particular, we propose to combine the given network and the tree and apply a Graph Neural Network to this network-tree graph. This way, we achieve the capability of solving the tree containment instances representing a larger number of species than the instances contained in the training dataset (i.e., our algorithm has the inductive learning ability). Our algorithm demonstrates an accuracy of over $95\%$ in solving the tree containment problem on instances with up to 100 leaves.
Constructing Phylogenetic Networks via Cherry Picking and Machine Learning
Mar 31, 2023Abstract:Combining a set of phylogenetic trees into a single phylogenetic network that explains all of them is a fundamental challenge in evolutionary studies. Existing methods are computationally expensive and can either handle only small numbers of phylogenetic trees or are limited to severely restricted classes of networks. In this paper, we apply the recently-introduced theoretical framework of cherry picking to design a class of efficient heuristics that are guaranteed to produce a network containing each of the input trees, for datasets consisting of binary trees. Some of the heuristics in this framework are based on the design and training of a machine learning model that captures essential information on the structure of the input trees and guides the algorithms towards better solutions. We also propose simple and fast randomised heuristics that prove to be very effective when run multiple times. Unlike the existing exact methods, our heuristics are applicable to datasets of practical size, and the experimental study we conducted on both simulated and real data shows that these solutions are qualitatively good, always within some small constant factor from the optimum. Moreover, our machine-learned heuristics are one of the first applications of machine learning to phylogenetics and show its promise.
A Universal Error Measure for Input Predictions Applied to Online Graph Problems
May 25, 2022
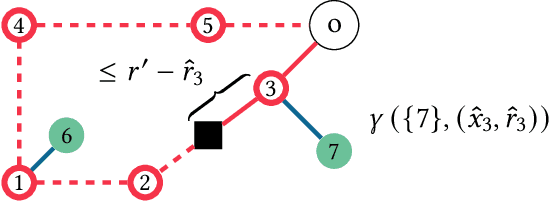


Abstract:We introduce a novel measure for quantifying the error in input predictions. The error is based on a minimum-cost hyperedge cover in a suitably defined hypergraph and provides a general template which we apply to online graph problems. The measure captures errors due to absent predicted requests as well as unpredicted actual requests; hence, predicted and actual inputs can be of arbitrary size. We achieve refined performance guarantees for previously studied network design problems in the online-list model, such as Steiner tree and facility location. Further, we initiate the study of learning-augmented algorithms for online routing problems, such as the traveling salesperson problem and dial-a-ride problem, where (transportation) requests arrive over time (online-time model). We provide a general algorithmic framework and we give error-dependent performance bounds that improve upon known worst-case barriers, when given accurate predictions, at the cost of slightly increased worst-case bounds when given predictions of arbitrary quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge