Laura Battaglia
Marginal Causal Flows for Validation and Inference
Nov 02, 2024Abstract:Investigating the marginal causal effect of an intervention on an outcome from complex data remains challenging due to the inflexibility of employed models and the lack of complexity in causal benchmark datasets, which often fail to reproduce intricate real-world data patterns. In this paper we introduce Frugal Flows, a novel likelihood-based machine learning model that uses normalising flows to flexibly learn the data-generating process, while also directly inferring the marginal causal quantities from observational data. We propose that these models are exceptionally well suited for generating synthetic data to validate causal methods. They can create synthetic datasets that closely resemble the empirical dataset, while automatically and exactly satisfying a user-defined average treatment effect. To our knowledge, Frugal Flows are the first generative model to both learn flexible data representations and also exactly parameterise quantities such as the average treatment effect and the degree of unobserved confounding. We demonstrate the above with experiments on both simulated and real-world datasets.
Inference for Regression with Variables Generated from Unstructured Data
Feb 23, 2024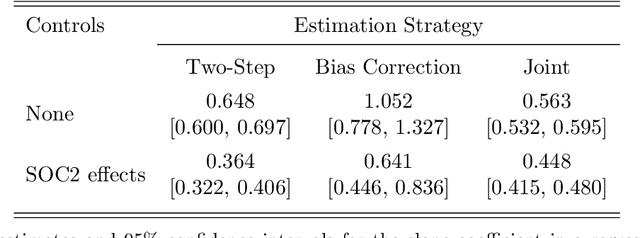
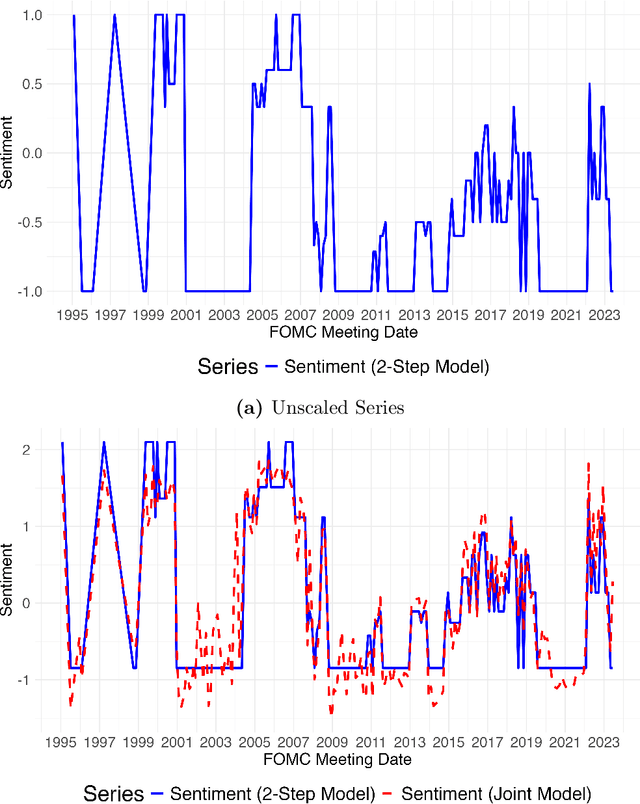
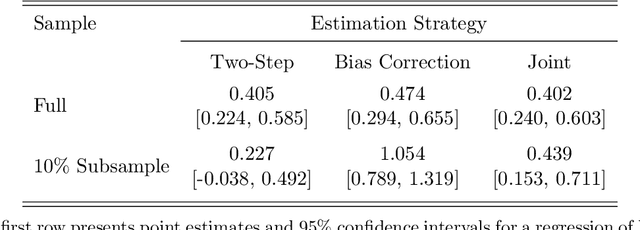
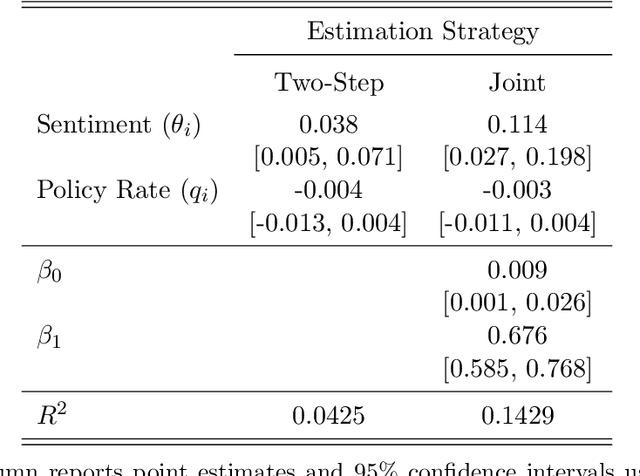
Abstract:The leading strategy for analyzing unstructured data uses two steps. First, latent variables of economic interest are estimated with an upstream information retrieval model. Second, the estimates are treated as "data" in a downstream econometric model. We establish theoretical arguments for why this two-step strategy leads to biased inference in empirically plausible settings. More constructively, we propose a one-step strategy for valid inference that uses the upstream and downstream models jointly. The one-step strategy (i) substantially reduces bias in simulations; (ii) has quantitatively important effects in a leading application using CEO time-use data; and (iii) can be readily adapted by applied researchers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge