L. Biferale
Reconstruction of turbulent data with deep generative models for semantic inpainting from TURB-Rot database
Jun 16, 2020


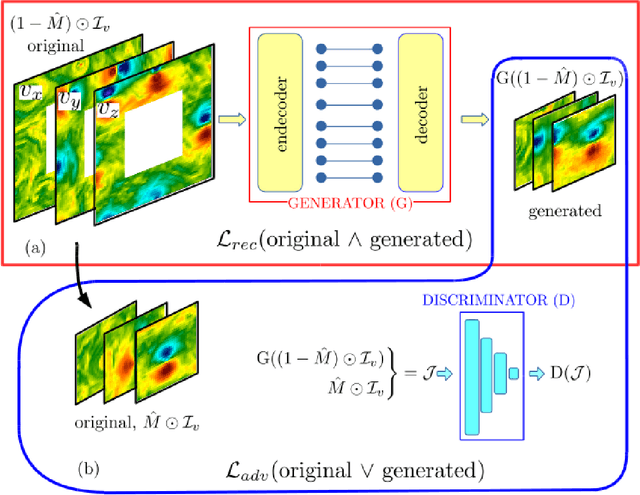
Abstract:We study the applicability of tools developed by the computer vision community for features learning and semantic image inpainting to perform data reconstruction of fluid turbulence configurations. The aim is twofold. First, we explore on a quantitative basis, the capability of Convolutional Neural Networks embedded in a Deep Generative Adversarial Model (Deep-GAN) to generate missing data in turbulence, a paradigmatic high dimensional chaotic system. In particular, we investigate their use in reconstructing two-dimensional damaged snapshots extracted from a large database of numerical configurations of 3d turbulence in the presence of rotation, a case with multi-scale random features where both large-scale organised structures and small-scale highly intermittent and non-Gaussian fluctuations are present. Second, following a reverse engineering approach, we aim to rank the input flow properties (features) in terms of their qualitative and quantitative importance to obtain a better set of reconstructed fields. We present two approaches both based on Context Encoders. The first one infers the missing data via a minimization of the L2 pixel-wise reconstruction loss, plus a small adversarial penalisation. The second searches for the closest encoding of the corrupted flow configuration from a previously trained generator. Finally, we present a comparison with a different data assimilation tool, based on Nudging, an equation-informed unbiased protocol, well known in the numerical weather prediction community. The TURB-Rot database, \url{http://smart-turb.roma2.infn.it}, of roughly 300K 2d turbulent images is released and details on how to download it are given.
TURB-Rot. A large database of 3d and 2d snapshots from turbulent rotating flows
Jun 14, 2020



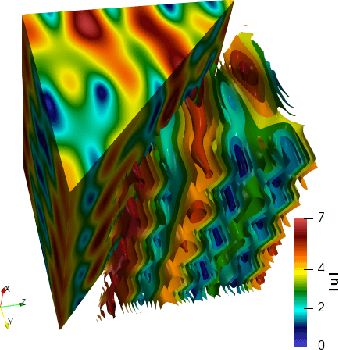
Abstract:We present TURB-Rot, a new open database of 3d and 2d snapshots of turbulent velocity fields, obtained by Direct Numerical Simulations (DNS) of the original Navier-Stokes equations in the presence of rotation. The aim is to provide the community interested in data-assimilation and/or computer vision with a new testing-ground made of roughly 300K complex images and fields. TURB-Rot data are characterized by multi-scales strongly non-Gaussian features and rough, non-differentiable, fields over almost two decades of scales. In addition, coming from fully resolved numerical simulations of the original partial differential equations, they offer the possibility to apply a wide range of approaches, from equation-free to physics-based models. TURB-Rot data are reachable at http://smart-turb.roma2.infn.it
Finding Efficient Swimming Strategies in a Three Dimensional Chaotic Flow by Reinforcement Learning
Dec 31, 2017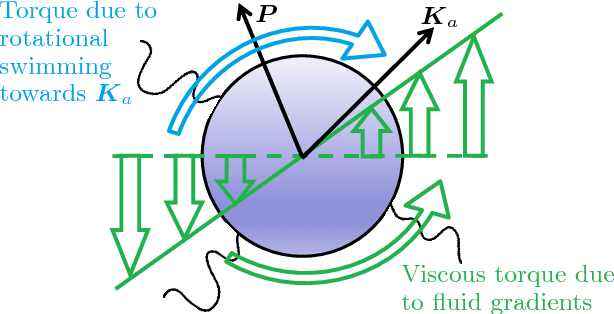
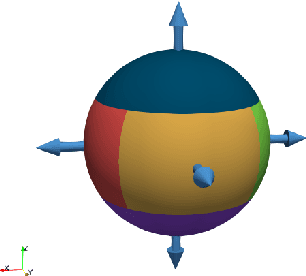
Abstract:We apply a reinforcement learning algorithm to show how smart particles can learn approximately optimal strategies to navigate in complex flows. In this paper we consider microswimmers in a paradigmatic three-dimensional case given by a stationary superposition of two Arnold-Beltrami-Childress flows with chaotic advection along streamlines. In such a flow, we study the evolution of point-like particles which can decide in which direction to swim, while keeping the velocity amplitude constant. We show that it is sufficient to endow the swimmers with a very restricted set of actions (six fixed swimming directions in our case) to have enough freedom to find efficient strategies to move upward and escape local fluid traps. The key ingredient is the learning-from-experience structure of the algorithm, which assigns positive or negative rewards depending on whether the taken action is, or is not, profitable for the predetermined goal in the long term horizon. This is another example supporting the efficiency of the reinforcement learning approach to learn how to accomplish difficult tasks in complex fluid environments.
* Published on Eur. Phys. J. E (December 14, 2017)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge