László Dobos
Generalization from Low- to Moderate-Resolution Spectra with Neural Networks for Stellar Parameter Estimation: A Case Study with DESI
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Cross-survey generalization is a critical challenge in stellar spectral analysis, particularly in cases such as transferring from low- to moderate-resolution surveys. We investigate this problem using pre-trained models, focusing on simple neural networks such as multilayer perceptrons (MLPs), with a case study transferring from LAMOST low-resolution spectra (LRS) to DESI medium-resolution spectra (MRS). Specifically, we pre-train MLPs on either LRS or their embeddings and fine-tune them for application to DESI stellar spectra. We compare MLPs trained directly on spectra with those trained on embeddings derived from transformer-based models (self-supervised foundation models pre-trained for multiple downstream tasks). We also evaluate different fine-tuning strategies, including residual-head adapters, LoRA, and full fine-tuning. We find that MLPs pre-trained on LAMOST LRS achieve strong performance, even without fine-tuning, and that modest fine-tuning with DESI spectra further improves the results. For iron abundance, embeddings from a transformer-based model yield advantages in the metal-rich ([Fe/H] > -1.0) regime, but underperform in the metal-poor regime compared to MLPs trained directly on LRS. We also show that the optimal fine-tuning strategy depends on the specific stellar parameter under consideration. These results highlight that simple pre-trained MLPs can provide competitive cross-survey generalization, while the role of spectral foundation models for cross-survey stellar parameter estimation requires further exploration.
Using Robust PCA to estimate regional characteristics of language use from geo-tagged Twitter messages
Nov 05, 2013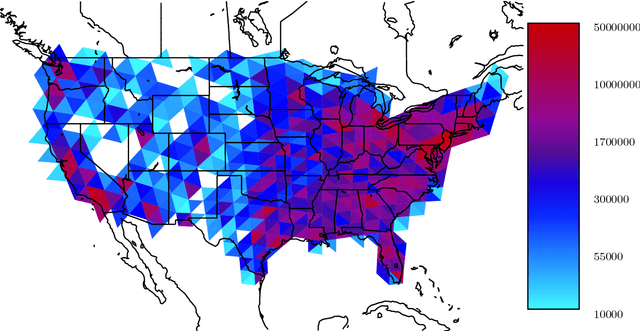
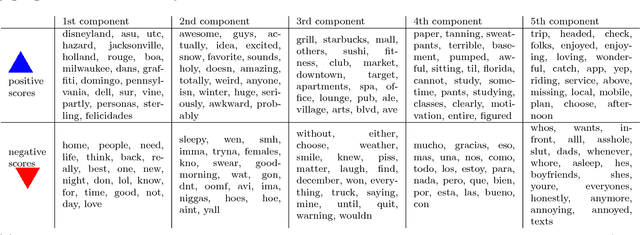
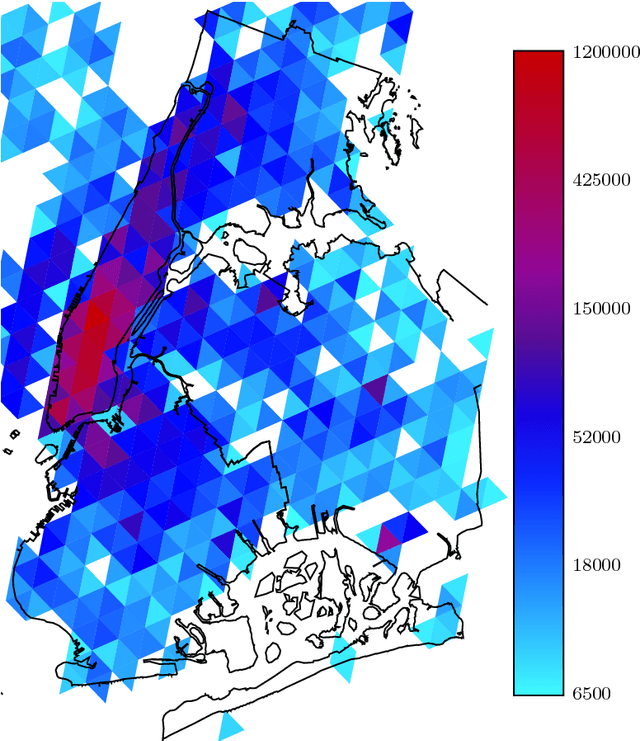
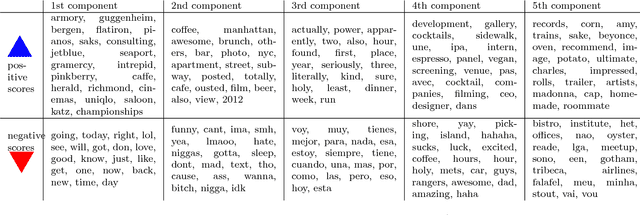
Abstract:Principal component analysis (PCA) and related techniques have been successfully employed in natural language processing. Text mining applications in the age of the online social media (OSM) face new challenges due to properties specific to these use cases (e.g. spelling issues specific to texts posted by users, the presence of spammers and bots, service announcements, etc.). In this paper, we employ a Robust PCA technique to separate typical outliers and highly localized topics from the low-dimensional structure present in language use in online social networks. Our focus is on identifying geospatial features among the messages posted by the users of the Twitter microblogging service. Using a dataset which consists of over 200 million geolocated tweets collected over the course of a year, we investigate whether the information present in word usage frequencies can be used to identify regional features of language use and topics of interest. Using the PCA pursuit method, we are able to identify important low-dimensional features, which constitute smoothly varying functions of the geographic location.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge