Kwong-Sak Leung
Field Evaluation of Four Low-cost PM Sensors and Design, Development and Field Evaluation of A Wearable PM Exposure Monitoring System
Jul 11, 2022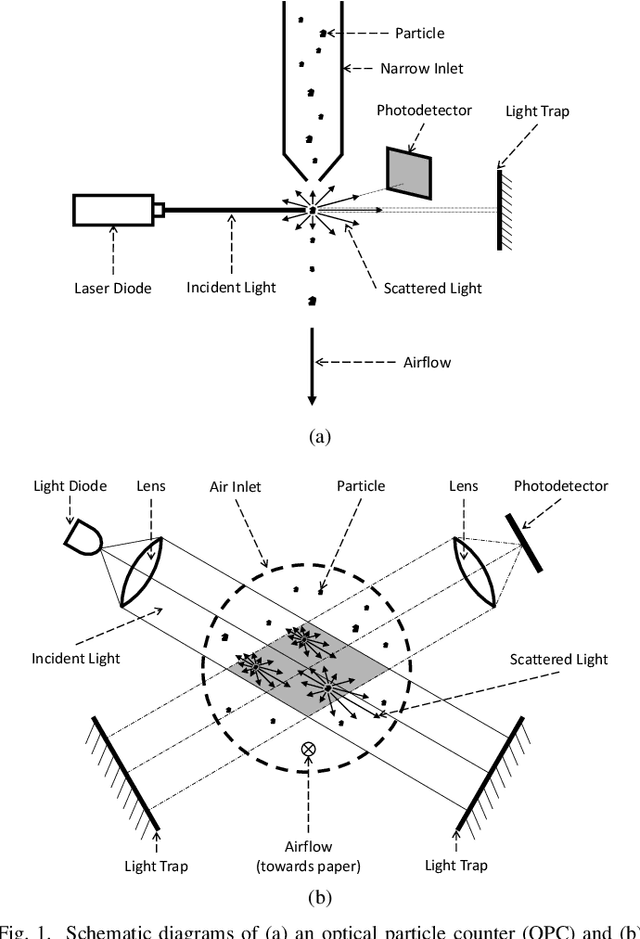
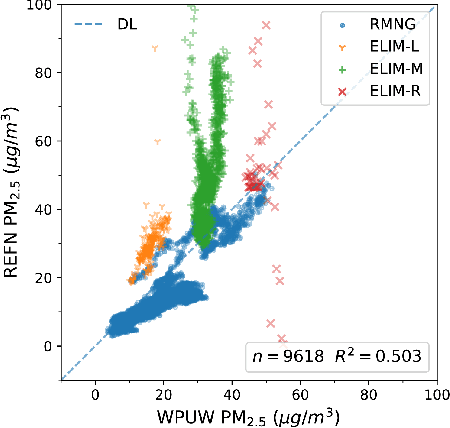
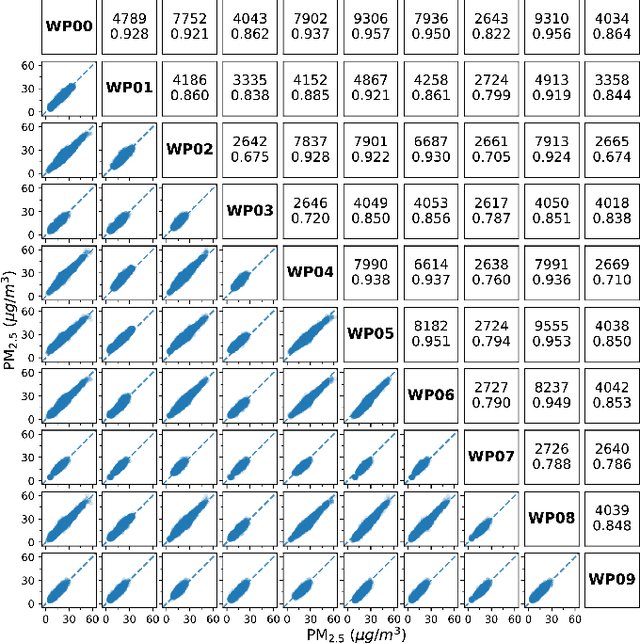
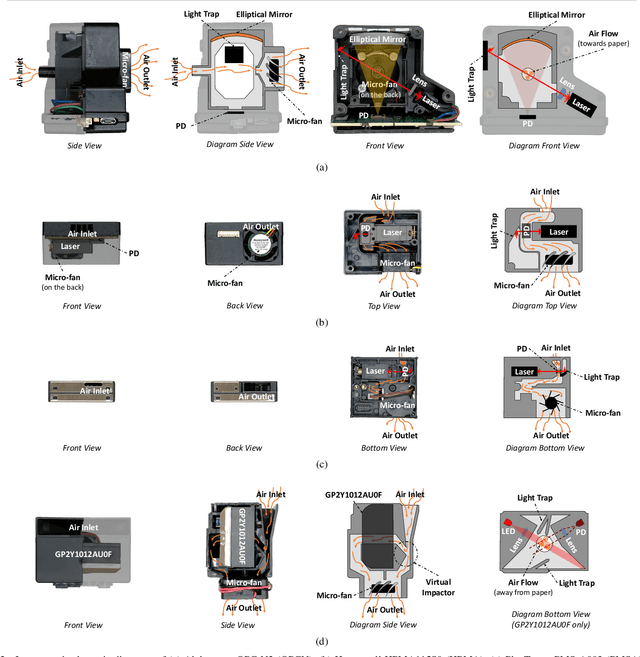
Abstract:To mitigate the significant biases/errors in research studying the associations between PM and health, which are introduced by the coarse/inadequate assessments of PM exposure from conventional PM monitoring paradigm, a personalized monitoring system consisting of a low-cost wearable PM device is proposed. However, due to the absence of a unifying evaluation protocol for low-cost PM sensors, the evaluation results/performance specifications from existing studies/datasheets are of limited reference values when attempting to determine the best candidate for the proposed system. In this regard, the authors appeal to the research community to develop a standardized evaluation protocol for low-cost PM sensors/devices, and a unifying attempt is established in this manuscript by adopting the definitive terminology from international documents and the evaluation metrics regarded as best practices. Collocated on the rooftop of the HKUST Supersite, four empirically selected PM sensors were compared against each other and calibrated against two reference monitors. They were then evaluated against the reference following the protocol. The PlanTower PMS-A003 sensor was selected for the wearable device as it outperformed the others in terms of affordability, portability, detection capability, data quality, as well as humidity and condensation insusceptibility. An automated approach was proposed to identify and remove the condensation associated abnormal measurements. The proposed device has better affordability and portability as well as similar usability and data accessibility compared to those existing devices recognized. The first 10 devices were also evaluated and calibrated at the Supersite. Additional 120 units were manufactured and delivered to the subjects to acquire their daily PM2.5 exposures for investigating the association with subclinical atherosclerosis.
Towards Personalized Healthcare in Cardiac Population: The Development of a Wearable ECG Monitoring System, an ECG Lossy Compression Schema, and a ResNet-Based AF Detector
Jul 11, 2022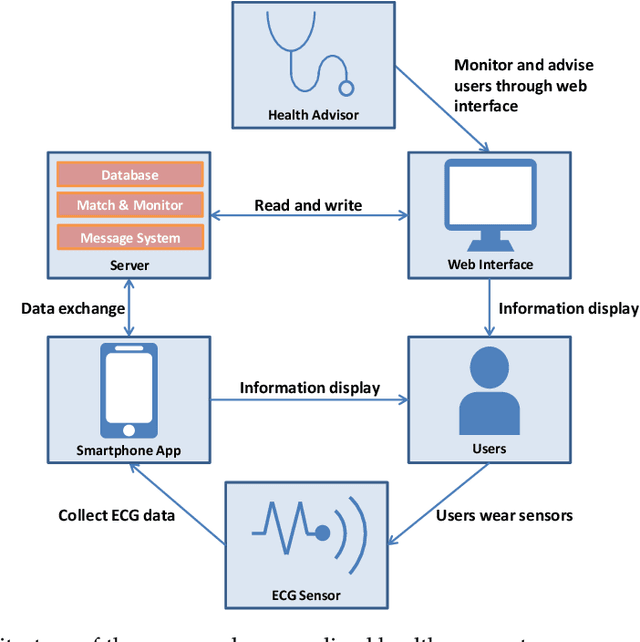
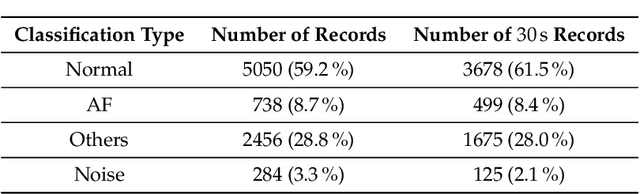
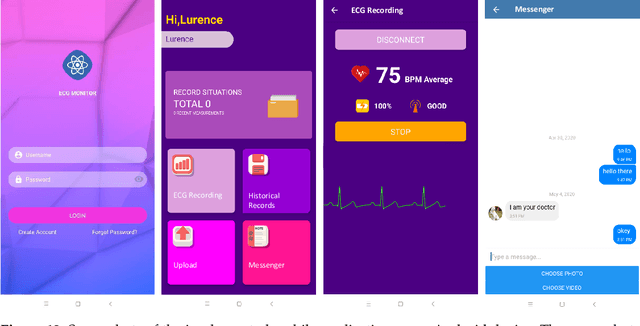
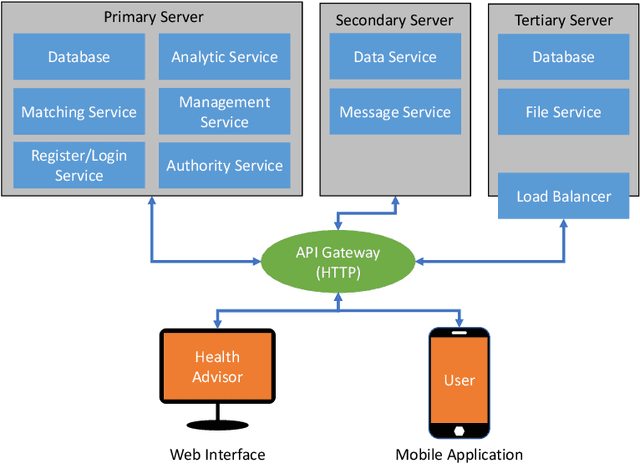
Abstract:Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death worldwide. While there is growing evidence that the atrial fibrillation (AF) has strong associations with various CVDs, this heart arrhythmia is usually diagnosed using electrocardiography (ECG) which is a risk-free, non-intrusive, and cost-efficient tool. Continuously and remotely monitoring the subjects' ECG information unlocks the potentials of prompt pre-diagnosis and timely pre-treatment of AF before the development of any life-threatening conditions/diseases. Ultimately, the CVDs associated mortality could be reduced. In this manuscript, the design and implementation of a personalized healthcare system embodying a wearable ECG device, a mobile application, and a back-end server are presented. This system continuously monitors the users' ECG information to provide personalized health warnings/feedbacks. The users are able to communicate with their paired health advisors through this system for remote diagnoses, interventions, etc. The implemented wearable ECG devices have been evaluated and showed excellent intra-consistency (CVRMS=5.5%), acceptable inter-consistency (CVRMS=12.1%), and negligible RR-interval errors (ARE<1.4%). To boost the battery life of the wearable devices, a lossy compression schema utilizing the quasi-periodic feature of ECG signals to achieve compression was proposed. Compared to the recognized schemata, it outperformed the others in terms of compression efficiency and distortion, and achieved at least 2x of CR at a certain PRD or RMSE for ECG signals from the MIT-BIH database. To enable automated AF diagnosis/screening in the proposed system, a ResNet-based AF detector was developed. For the ECG records from the 2017 PhysioNet CinC challenge, this AF detector obtained an average testing F1=85.10% and a best testing F1=87.31%, outperforming the state-of-the-art.
Stochastic Online Learning with Probabilistic Graph Feedback
Mar 04, 2019Abstract:We consider a problem of stochastic online learning with general probabilistic graph feedback. Two cases are covered. (a) The one-step case where for each edge $(i,j)$ with probability $p_{ij}$ in the probabilistic feedback graph. After playing arm $i$ the learner observes a sample reward feedback of arm $j$ with independent probability $p_{ij}$. (b) The cascade case where after playing arm $i$ the learner observes feedback of all arms $j$ in a probabilistic cascade starting from $i$ -- for each $(i,j)$ with probability $p_{ij}$, if arm $i$ is played or observed, then a reward sample of arm $j$ would be observed with independent probability $p_{ij}$. Previous works mainly focus on deterministic graphs which corresponds to one-step case with $p_{ij} \in \{0,1\}$, an adversarial sequence of graphs with certain topology guarantees or a specific type of random graphs. We analyze the asymptotic lower bounds and design algorithms in both cases. The regret upper bounds of the algorithms match the lower bounds with high probability.
Improved Algorithm on Online Clustering of Bandits
Feb 25, 2019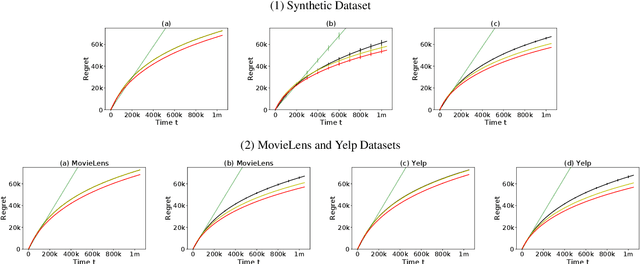
Abstract:We generalize the setting of online clustering of bandits by allowing non-uniform distribution over user frequencies. A more efficient algorithm is proposed with simple set structures to represent clusters. We prove a regret bound for the new algorithm which is free of the minimal frequency over users. The experiments on both synthetic and real datasets consistently show the advantage of the new algorithm over existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge