Kuntal Ghosh
The Impact of AI on Perceived Job Decency and Meaningfulness: A Case Study
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:The proliferation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in workplaces stands to change the way humans work, with job satisfaction intrinsically linked to work life. Existing research on human-AI collaboration tends to prioritize performance over the experiential aspects of work. In contrast, this paper explores the impact of AI on job decency and meaningfulness in workplaces. Through interviews in the Information Technology (IT) domain, we not only examined the current work environment, but also explored the perceived evolution of the workplace ecosystem with the introduction of an AI. Findings from the preliminary exploratory study reveal that respondents tend to visualize a workplace where humans continue to play a dominant role, even with the introduction of advanced AIs. In this prospective scenario, AI is seen as serving as a complement rather than replacing the human workforce. Furthermore, respondents believe that the introduction of AI will maintain or potentially increase overall job satisfaction.
BRI3L: A Brightness Illusion Image Dataset for Identification and Localization of Regions of Illusory Perception
Feb 07, 2024Abstract:Visual illusions play a significant role in understanding visual perception. Current methods in understanding and evaluating visual illusions are mostly deterministic filtering based approach and they evaluate on a handful of visual illusions, and the conclusions therefore, are not generic. To this end, we generate a large-scale dataset of 22,366 images (BRI3L: BRightness Illusion Image dataset for Identification and Localization of illusory perception) of the five types of brightness illusions and benchmark the dataset using data-driven neural network based approaches. The dataset contains label information - (1) whether a particular image is illusory/nonillusory, (2) the segmentation mask of the illusory region of the image. Hence, both the classification and segmentation task can be evaluated using this dataset. We follow the standard psychophysical experiments involving human subjects to validate the dataset. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to develop a dataset of visual illusions and benchmark using data-driven approach for illusion classification and localization. We consider five well-studied types of brightness illusions: 1) Hermann grid, 2) Simultaneous Brightness Contrast, 3) White illusion, 4) Grid illusion, and 5) Induced Grating illusion. Benchmarking on the dataset achieves 99.56% accuracy in illusion identification and 84.37% pixel accuracy in illusion localization. The application of deep learning model, it is shown, also generalizes over unseen brightness illusions like brightness assimilation to contrast transitions. We also test the ability of state-of-theart diffusion models to generate brightness illusions. We have provided all the code, dataset, instructions etc in the github repo: https://github.com/aniket004/BRI3L
Deep Neural Networks for Automatic Grain-matrix Segmentation in Plane and Cross-polarized Sandstone Photomicrographs
Nov 13, 2021
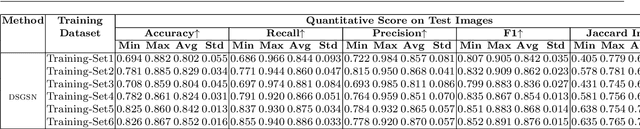

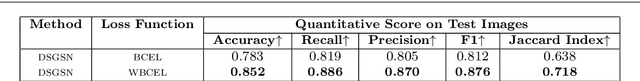
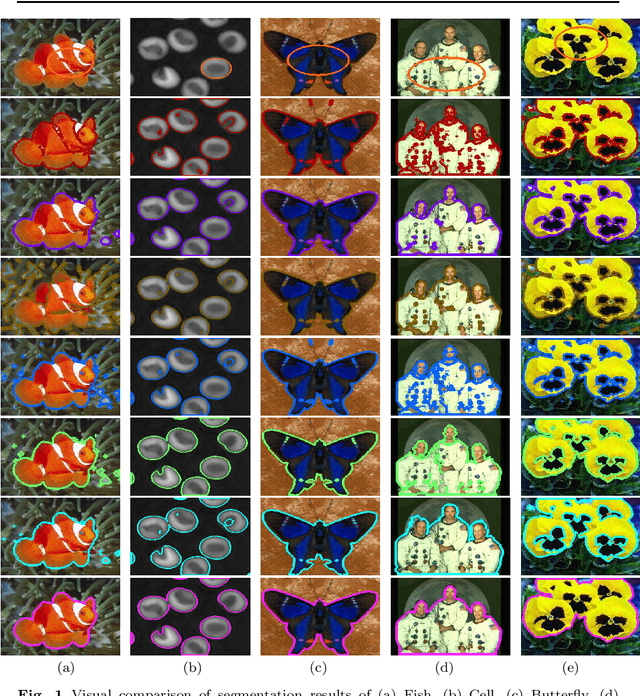
Abstract:Grain segmentation of sandstone that is partitioning the grain from its surrounding matrix/cement in the thin section is the primary step for computer-aided mineral identification and sandstone classification. The microscopic images of sandstone contain many mineral grains and their surrounding matrix/cement. The distinction between adjacent grains and the matrix is often ambiguous, making grain segmentation difficult. Various solutions exist in literature to handle these problems; however, they are not robust against sandstone petrography's varied pattern. In this paper, we formulate grain segmentation as a pixel-wise two-class (i.e., grain and background) semantic segmentation task. We develop a deep learning-based end-to-end trainable framework named Deep Semantic Grain Segmentation network (DSGSN), a data-driven method, and provide a generic solution. As per the authors' knowledge, this is the first work where the deep neural network is explored to solve the grain segmentation problem. Extensive experiments on microscopic images highlight that our method obtains better segmentation accuracy than various segmentation architectures with more parameters.
State-of-The-Art Fuzzy Active Contour Models for Image Segmentation
Aug 01, 2020


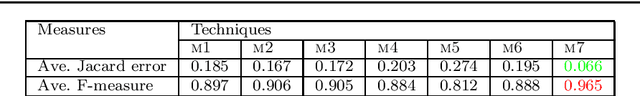
Abstract:Image segmentation is the initial step for every image analysis task. A large variety of segmentation algorithm has been proposed in the literature during several decades with some mixed success. Among them, the fuzzy energy based active contour models get attention to the researchers during last decade which results in development of various methods. A good segmentation algorithm should perform well in a large number of images containing noise, blur, low contrast, region in-homogeneity, etc. However, the performances of the most of the existing fuzzy energy based active contour models have been evaluated typically on the limited number of images. In this article, our aim is to review the existing fuzzy active contour models from the theoretical point of view and also evaluate them experimentally on a large set of images under the various conditions. The analysis under a large variety of images provides objective insight into the strengths and weaknesses of various fuzzy active contour models. Finally, we discuss several issues and future research direction on this particular topic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge