Kritish Pahi
Enhanced Deep Q-Learning for 2D Self-Driving Cars: Implementation and Evaluation on a Custom Track Environment
Feb 13, 2024



Abstract:This research project presents the implementation of a Deep Q-Learning Network (DQN) for a self-driving car on a 2-dimensional (2D) custom track, with the objective of enhancing the DQN network's performance. It encompasses the development of a custom driving environment using Pygame on a track surrounding the University of Memphis map, as well as the design and implementation of the DQN model. The algorithm utilizes data from 7 sensors installed in the car, which measure the distance between the car and the track. These sensors are positioned in front of the vehicle, spaced 20 degrees apart, enabling them to sense a wide area ahead. We successfully implemented the DQN and also a modified version of the DQN with a priority-based action selection mechanism, which we refer to as modified DQN. The model was trained over 1000 episodes, and the average reward received by the agent was found to be around 40, which is approximately 60% higher than the original DQN and around 50% higher than the vanilla neural network.
A Comparison of Semantic Similarity Methods for Maximum Human Interpretability
Oct 31, 2019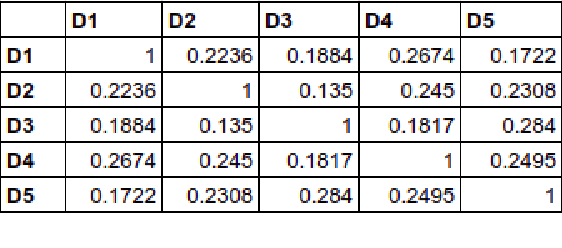
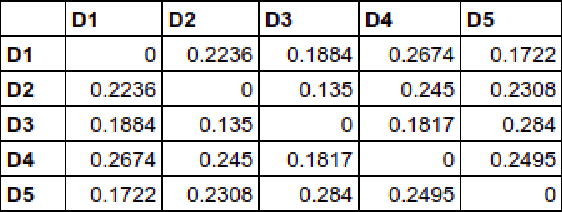


Abstract:The inclusion of semantic information in any similarity measures improves the efficiency of the similarity measure and provides human interpretable results for further analysis. The similarity calculation method that focuses on features related to the text's words only, will give less accurate results. This paper presents three different methods that not only focus on the text's words but also incorporates semantic information of texts in their feature vector and computes semantic similarities. These methods are based on corpus-based and knowledge-based methods, which are: cosine similarity using tf-idf vectors, cosine similarity using word embedding and soft cosine similarity using word embedding. Among these three, cosine similarity using tf-idf vectors performed best in finding similarities between short news texts. The similar texts given by the method are easy to interpret and can be used directly in other information retrieval applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge